Giải các phương trình sau: 11 – 2x = x – 1
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(2\left(3-4x\right)=10-\left(2x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-8x-10+2x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x+11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=-11\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{11}{6}\)
b) Ta có: \(3\left(2-4x\right)=11-\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-12x-11+3x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x=6\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)

a) Tìm được x = 2,2
b) Tìm được x = 2073
c) Tìm được x = 4 hoặc x = -2
d) Điều kiện x≠-1 . Tìm được x = 0 hoặc x = 3

\(a,\left(2x-3\right)\left(x^2-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,2x-\left(3-5x\right)=4\left(x+3\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow2x-3+5x=4x+12\\ \Leftrightarrow7x-3-4x-12=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3x-15=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=5\)
\(c,ĐKXĐ:\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne-1\\x\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x-2}-\dfrac{2}{x+1}=\dfrac{11-3x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{x-2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{11-3x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+1-x+2-11+3x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}=0\\ \Rightarrow3x-8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{8}{3}\left(tm\right)\)

`8(x-3)(x+1)=8x^2 +11`
`<=>8(x^2 +x-3x-3)-8x^2 -11=0`
`<=>8x^2 +8x-24x-24-8x^2 -11=0`
`<=>-16x-35=0`
`<=>-16x=35`
`<=>x=-35/16`
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-2}-\dfrac{2}{x^2-2x}=\dfrac{1}{x}\left(x\ne0;x\ne2\right)\\ < =>\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{2}{x\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{x-2}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
suy ra
`x^2 +2x-2=x-2`
`<=>x^2 +2x-x-2+2=0`
`<=>x^2 +x=0`
`<=>x(x+1)=0`
\(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(ktm\right)\\x=-1\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ < =>x=-1\)
\(a,8\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)=8x^2+11\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(8x-24\right)\left(x+1\right)=8x^2+11\\ \Leftrightarrow8x^2-24x+8x-24-8x^2-11=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-16x-35=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{-35}{16}\)
Vậy \(x=-\dfrac{35}{16}\)
\(b,đkxđ:x\ne2;x\ne0\)
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-2}-\dfrac{2}{x^2-2x}-\dfrac{1}{x}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{2}{x\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{x-2}{x\left(x-2\right)}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-2-x+2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(loại\right)\\x=-1\left(t/m\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x=-1\)
@ducminh

3:
a: u+v=14 và uv=40
=>u,v là nghiệm của pt là x^2-14x+40=0
=>x=4 hoặc x=10
=>(u,v)=(4;10) hoặc (u,v)=(10;4)
b: u+v=-7 và uv=12
=>u,v là các nghiệm của pt:
x^2+7x+12=0
=>x=-3 hoặc x=-4
=>(u,v)=(-3;-4) hoặc (u,v)=(-4;-3)
c; u+v=-5 và uv=-24
=>u,v là các nghiệm của phương trình:
x^2+5x-24=0
=>x=-8 hoặc x=3
=>(u,v)=(-8;3) hoặc (u,v)=(3;-8)

Ta có: x + 1 1 + x + 1 x - 2 = x + x - 2 2 x - 1 = 2 x 2 - 1 2 x - 1
ĐKXĐ của phương trình là x ≠ 2; x ≠ 1/2; x ≠ 1; x ≠ -1; x ≠ 13.
Ta biến đổi phương trình đã cho thành 2 x - 1 x 2 - 1 = 6 3 x - 1
Khử mẫu và rút gọn:
(2x − 1)(3x − 1) = 6( x 2 − 1)
⇔−5x + 1 = −6 ⇔ x = 7/5
Giá trị x = 7/5 thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ.
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là x = 7/5

\(\dfrac{2x-3}{2}>\dfrac{8x-11}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(2x-3\right)}{6}>\dfrac{8x-11}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(2x-3\right)>8x-11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-9>8x-11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x>-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 1\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{x|x< 1\right\}\)
\(2x-3\le8x-11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x\le-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge\dfrac{8}{6}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{x|x\ge\dfrac{8}{6}\right\}\)
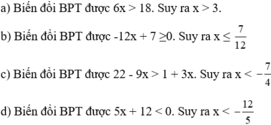
11 – 2x = x – 1 ⇔ 11 + 1 = x + 2x ⇔ 12 = 3x ⇔ x = 4