Rút gọn rồi tính giá trị các biểu thức sau:
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) \sqrt{-9a}-\sqrt{9+12 a+4 a^{2}}−9a−9+12a+4a2
=\sqrt{-9 a}-\sqrt{3^{2}+2.3 .2 a+(2 a)^{2}}=−9a−32+2.3.2a+(2a)2
=\sqrt{3^{2} \cdot(-a)}-\sqrt{(3+2 a)^{2}}=32⋅(−a)−(3+2a)2
=3 \sqrt{-a}-|3+2 a|=3−a−∣3+2a∣
Thay a=-9a=−9 ta được:
3 \sqrt{9}-|3+2 \cdot(-9)|=3.3-15=-639−∣3+2⋅(−9)∣=3.3−15=−6.
b) Điều kiện: m \neq 2m=2

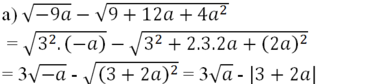
Tại a = -9 ta được:
= 3√-(-9) - |3 + 2(-9)|
= 3√32 - |3 - 18|
= 3.3 - |-15| = 9 - 15 = -6
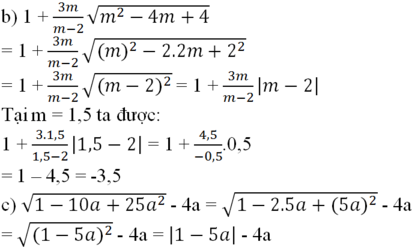
Tại a = √2 ta được:
= |1 - 5√2| - 4√2
= (5√2 - 1) - 4√2
= √2 - 1
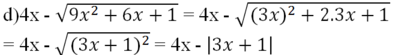
Tại x = -√3 ta được:
= 4(-√3) - |3(-√3) + 1|
= -4√3 - |-3√3 + 1|
= -4√3 - (3√3 - 1)
= -7√3 + 1

a: Thay x=49 vào A, ta được:
\(A=\dfrac{2\cdot7+1}{7-3}=\dfrac{14+1}{4}=\dfrac{15}{4}\)
b: \(B=\dfrac{2x+36}{x-9}-\dfrac{9}{\sqrt{x}-3}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+3}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x+36}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}-\dfrac{9}{\sqrt{x}-3}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+3}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x+36-9\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)-\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x+36-9\sqrt{x}-27-x+3\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-6\sqrt{x}+9}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)^2}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-3}{\sqrt{x}+3}\)
c: \(P=A\cdot B=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-3}{\sqrt{x}+3}\cdot\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-3}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+3}\)
P>1 khi P-1>0
=>\(\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+1-\sqrt{x}-3}{\sqrt{x}+3}>0\)
=>\(\sqrt{x}-2>0\)
=>\(\sqrt{x}>2\)
=>x>4
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>4\\x\ne9\end{matrix}\right.\)

a. = \(\dfrac{2}{x+5}\)+\(\dfrac{2x+30}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}\)
= 2.(x-5) + 2x+30
= 2x-10+2x+30
=4x+20
b. x=9
4x+20
=4.9+20
=36+20
=56

Câu 2:
a: Ta có: \(P=3x-\sqrt{x^2-10x+25}\)
\(=3x-\left|x-5\right|\)
\(=\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-x+5=2x+5\left(x\ge5\right)\\3x+x-5=4x-5\left(x< 5\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Vì x=2<5 nên \(P=4\cdot2-5=8-5=3\)

1.
\(A=\dfrac{2x-9}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{\left(2x+4\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x-9-\left(x^2-9\right)+\left(2x^2-8\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x-8}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+4\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+4}{x-3}\)
b.
\(A=2\Rightarrow\dfrac{x+4}{x-3}=2\Rightarrow x+4=2\left(x-3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x=10\) (thỏa mãn)
2.
\(x^4+2x^2y+y^2-9=\left(x^2+y\right)^2-3^2=\left(x^2+y-3\right)\left(x^2+y+3\right)\)

\(a,\dfrac{x^2+6x+9}{x+3}\\ đk:x\ne-3\\ =\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)^2}{x+3}=x+3\)
b, Thay \(x=-2\left(t/mđk\right)\) vào
\(-2+3=1\)
Vậy tại \(x=-2\) thì biểu thức = 1
\(A=\dfrac{x^2+6x+9}{x+3}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x^2+2.x.3+3^2}{x+3}\)
\(A=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)^2}{x+3}\)
\(A=x+3\)
b) Thay x = -2 vào A ta được A = -2 + 3 = 1
Vậy khi x = -2 thì A = 1

\(A=\dfrac{3-x}{x+3}.\dfrac{x^2+6x+9}{x^2-9}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne\pm3\right)\)
a, \(A=\dfrac{-\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)^2}{\left(x+3\right)^2\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\)
\(=-1+\dfrac{x}{x+3}=\dfrac{-x-3+x}{x+3}=\dfrac{-3}{x+3}\)
b, \(x^2-2x-3=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+x-3\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)+\left(x-3\right)\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
TH1 : Nếu x = 3 thì gt của biểu thức \(A=\dfrac{-3}{3+3}=-\dfrac{3}{6}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
TH2 : Nếu x = -2 thì gt của biểu thức \(A=\dfrac{-3}{-2+3}=-3\)
c, Để A nhận giá trị nguyên thì \(x+3\inƯ\left(3\right)\) ( Ư(-3 ) cũng được như nhau nhé ! )
Xét bảng :
| x + 3 | x |
| 1 | -2 |
| -1 | -4 |
| 3 | 0 |
| -3 | -6 |
Vậy để A nguyên thì \(x\in\left\{-6;-4;-2;0\right\}\)
Tại a = -9 ta được:
= 3√-(-9) - |3 + 2(-9)|
= 3√32 - |3 - 18|
= 3.3 - |-15| = 9 - 15 = -6