Tìm Min, Max: y= cosx + cos(x+\(\frac{\pi}{3}\))
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a/ \(y=2\left(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx-\frac{1}{2}cosx\right)+5=2sin\left(x-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)+5\)
Do \(-1\le sin\left(x-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\le1\Rightarrow3\le y\le7\)
b/ \(y=2cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)cos\left(-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=\sqrt{3}cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
Do \(-1\le cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\le1\Rightarrow-\sqrt{3}\le y\le\sqrt{3}\)
c/ \(y=2\left(\frac{1}{2}sinx+\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}cosx\right)+12=2sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)+12\)
Do \(-1\le sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)\le1\Rightarrow10\le y\le14\)

ĐK: Biểu thức xác định với mọi `x`.
`y_(min) <=> (\sqrt(2-cos(x-π/6))+3)_(max) <=> (cos(x-π/6))_(max)`
`<=> cos(x-π/6)=1 <=> x-π/6=k2π <=> x = π/6+k2π ( k \in ZZ)`.
`=> y_(min) = 1`
`y_(max) <=> (\sqrt(2-cos(x-π/6))+3)_(min) <=> (cos(x-π/6))_(min)`
`<=> cos(x-π/6)=-1 <=> x -π/6= π+k2π <=> x = (7π)/6+k2π (k \in ZZ)`
`=> y_(max) = (6-2\sqrt3)/3`.

1, \(y=2-sin\left(\dfrac{3x}{2}+x\right).cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\)
\(y=2-\left(-cosx\right).\left(-sinx\right)\)
y = 2 - sinx.cosx
y = \(2-\dfrac{1}{2}sin2x\)
Max = 2 + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = 2,5
Min = \(2-\dfrac{1}{2}\) = 1,5
2, y = \(\sqrt{5-\dfrac{1}{2}sin^22x}\)
Min = \(\sqrt{5-\dfrac{1}{2}}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
Max = \(\sqrt{5}\)

\(y=sinx.cosx\left(sin^2x-cos^2x\right)=\frac{1}{2}sin2x.\left(-cos2x\right)=-\frac{1}{4}sin4x\)
Do \(-1\le sin4x\le1\Rightarrow-\frac{1}{4}\le y\le\frac{1}{4}\)
\(y_{min}=-\frac{1}{4}\) khi \(sin4x=1\)
\(y_{max}=\frac{1}{4}\) khi \(sin4x=-1\)

a) Với mọi \(x \in \mathbb{R}\) ta có \( - 1 \le cosx \le 1\)
Vậy phương trình \(cosx = - 3\;\) vô nghiệm.
\(\begin{array}{l}b)\,\;cosx = cos{15^o}\;\\ \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x = {15^o} + k{360^o},k \in \mathbb{Z}\\x = - {15^o} + k{360^o},k \in \mathbb{Z}\end{array} \right.\end{array}\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm \(x = {15^o} + k{360^o}\) hoặc \(x = - {15^o} + k{360^o},k \in \mathbb{Z}\).
\(\begin{array}{l}c)\;\,cos(x + \frac{\pi }{{12}}) = cos\frac{{3\pi }}{{12}}\\ \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x + \frac{\pi }{{12}} = \frac{{3\pi }}{{12}} + k2\pi ,k \in \mathbb{Z}\\x + \frac{\pi }{{12}} = - \frac{{3\pi }}{{12}} + k2\pi ,k \in \mathbb{Z}\end{array} \right.\\ \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x = \frac{\pi }{6} + k2\pi ,k \in \mathbb{Z}\\x = - \frac{\pi }{3} + k2\pi ,k \in \mathbb{Z}\end{array} \right.\end{array}\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm \(x = \frac{\pi }{6} + k2\pi ,\) hoặc \(x = - \frac{\pi }{3} + k2\pi ,k \in \mathbb{Z}\).

\(0\le cos^2\left(x-\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\le1\Rightarrow1\le y\le2\)
\(y_{min}=1\) khi \(cos\left(x-\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=0\)
\(y_{max}=2\) khi \(cos^2\left(x-\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=1\)

1. Hàm số xác định `<=> 1-cosx \ne 0<=>cosx \ne 1<=>x \ne k2π`
Vì: `1+cosx >=0 forallx ; 1-cosx >=0 forall x`
2. Hàm số xác định `<=> sin^2x \ne cos^2x <=> (1-cos2x)/2 \ne (1+cos2x)/2`
`<=>cos2x \ne 0<=> 2x \ne π/2+kπ <=> x \ne π/4+kπ/2`
3. Hàm số xác định `<=> cos2x \ne 0<=> x \ne π/4+kπ/2 (k \in ZZ)`.
Bạn cho mình hỏi tại sao x khác k2\(\pi\) là lý thuyết ở đoạn nào thế ạ?

a) Vẽ đồ thị:
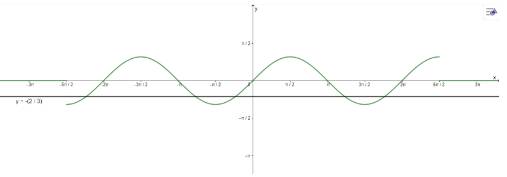
\(3\sin x + 2 = 0\) trên đoạn \(\left( { - \frac{{5\pi }}{2};\frac{{5\pi }}{2}} \right)\) có 5 nghiệm
b) Vẽ đồ thị:

\(\cos x = 0\) trên đoạn \(\left[ { - \frac{{5\pi }}{2};\frac{{5\pi }}{2}} \right]\) có 6 nghiệm
\(y=2cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)cos\left(\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=\sqrt{3}cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
Do \(-1\le cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\le1\) nên \(-\sqrt{3}\le y\le\sqrt{3}\)
\(y_{min}=-\sqrt{3}\) khi \(cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=-1\)
\(y_{max}=\sqrt{3}\) khi \(cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=1\)