a, Với giá trị nào của x thì biểu thức sau \(\frac{2x+1}{5}\) bằng 2; -2; 0; 4
b, Với giá trị nào của x thì các biểu thượng sau có giá trị bằng 0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\text{Giải}\)
\(A=\left(\frac{x+2}{2x-4}-\frac{2-x}{2x+4}+\frac{32}{4x^2-16}\right):\frac{x-1}{x-2}\)
\(A=\left(\frac{x+2}{2x-4}-\frac{2-x}{2x+4}+\frac{32}{\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4\right)}\right):\frac{x-1}{x-2}\)
\(A=\left(\frac{\left(x+2\right)\left(2x+4\right)}{\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4\right)}-\frac{\left(2-x\right)\left(2x-4\right)}{\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4\right)}+\frac{32}{\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4\right)}\right):\frac{x-1}{x-2}\)
\(A=\left(\frac{2x^2+8x+8}{\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4\right)}-\frac{4x^2-8+4x}{\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4\right)}+\frac{32}{\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4\right)}\right):\frac{x-1}{x-2}\)
\(A=\frac{2x^2+8x+8-4x^2+8-4x+32}{\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4\right)}:\frac{x-1}{x-2}\)
\(A=\frac{4x-2x^2+48}{\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4\right)}:\frac{x-1}{x-2}\)
\(A=\frac{2\left(2x-x^2+24\right)}{\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4\right)}:\frac{x-1}{x-2}=\frac{2\left(2x-x^2+24\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\frac{2\left(2x-x^2+24\right)\left(x-2\right)}{4\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\frac{2x-x^2+24}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
c, Bạn tự giải hệ pt nhé :)

Ta có: -2 2 x – 1 = 2 x 2 + 2x +3 ⇔ 2 x 2 +2x + 3 + 2 2 x + 1=0
⇔ 2 x 2 + 2(1 + 2 )x +4 =0
∆ ' = b ' 2 – ac= 1 + 2 2 - √2 .4= 1+2 2 +2 - 4 2
= 1-2 2 +2 = 2 - 1 2 > 0
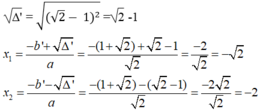
Vậy với x= - 2 hoặc x = -2 thì giá trị của hai biểu thức trên bằng nhau

Ta có: 3 x 2 + 2x -1 = 2 3 x + 3 ⇔ 3 x 2 + 2x - 2 3 x -3 -1 = 0
⇔ 3 x 2 + (2 - 2 3 )x -4 =0 ⇔ 3 x 2 + 2(1 - 3 )x -4 = 0
∆ ' = b ' 2 – ac= 1 - 3 2 - 3 (-4) =1 - 2 3 +3 +4 3
= 1 + 2 3 +3 = 1 - 3 2 > 0
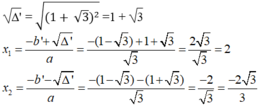
Vậy với x= 2 hoặc x = (-2 3 )/3 thì giá trị của hai biểu thức trên bằng nhau

\(\frac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x^2+2x}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\)
\(=\frac{x\left(x^2+2x\right)+2\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\)
\(=\frac{x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x\left(x^2-1+4\left(x-1\right)\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
a/ Để biểu thức xác đinh => 2x(x+5) khác 0 => x khác 0 và x khác -5
b/ Gọi biểu thức là A. Rút gọn A ta được:
\(A=\frac{x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x-1}{2}\left(x\ne0;x\ne-5\right)\)
A=1 => x-1=2 => x=3
c/ A=-1/2 <=> x-1=-1 => x=0
d/ A=-3 <=> x-1=-6 => x=-5

\(a,ĐK:x\ne\pm2\\ b,A=\dfrac{x^2+4x+4+x^2-4x+4+16}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\\ A=\dfrac{2x^2+32}{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+16}{x^2-4}\\ c,A=-3\Leftrightarrow-3x^2+12=x^2+16\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2=-4\Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)

\(A=\frac{x}{2x-2}+\frac{x^2+1}{2-2x^2}\)
a) Để A có nghĩa \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2x-2\ne0\\2-2x^2\ne0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow x\ne\pm1\)
b) Ta có \(A=\frac{x}{2x-2}+\frac{x^2+1}{2-2x^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow2A=\frac{x}{x-1}+\frac{x^2+1}{1-x^2}=\frac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\frac{x^2+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^2+x-x^2-1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\frac{x-1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\frac{1}{x+1}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\frac{1}{2x+2}\)
KL...
c) Để \(A=\frac{1}{2}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{2x+2}=\frac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+2=2\Leftrightarrow2x=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\)(t/m ĐKXĐ)
KL...

Ta có: \(\frac{x+1}{7}=0\Leftrightarrow x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Ta có: \(\frac{3x+3}{5}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Ta có: \(\frac{2x\left(x+1\right)}{3x+4}=0\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x \(\in\left\{-1;0\right\}\) thì \(\frac{2x\left(x+1\right)}{3x+4}=0\)
Ta có: \(\frac{2x\left(x-5\right)}{x-7}=0\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x-5=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=5\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{0;5\right\}\) thì \(\frac{2x\left(x-5\right)}{x-7}=0\)
Bạn chỉ cần đặt xong rồi tìm x như bình thường