Biết y = f(x) = a\(x^2\) + bx +c là hàm số thoả mãn: f(x) + 2f(1-x) = 3\(x^2\) + 2x +5, mọi x thuộc R. Tính f(6)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Đặt ![]()
![]()
Khi đó
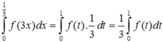
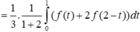
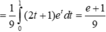
Chọn đáp án C. *Chú ý tính chất tích phân:
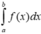
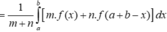
Chọn đáp án C.

Thế \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(0;-1\right)\) vào ta được \(f\left(0\right)=0\)
Thế \(y=0\Rightarrow f\left(f\left(x\right)\right)=x\)
Do vế phải của biểu thức trên là hàm bậc nhất \(\Rightarrow\) có tập giá trị là \(Z\Rightarrow f\) là toàn ánh
Giả sử tồn tại \(x_1;x_2\) sao cho \(f\left(x_1\right)=f\left(x_2\right)=a\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(f\left(x_1\right)\right)=x_1\Rightarrow f\left(a\right)=x_1\\f\left(f\left(x_2\right)\right)=x_2\Rightarrow f\left(a\right)=x_2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x_1=x_2\Rightarrow f\) là đơn ánh \(\Rightarrow f\) là song ánh
Thế \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1;-1\right)\Rightarrow f\left(0\right)=1+f\left(-1\right)\Rightarrow f\left(-1\right)=-1\)
Thế \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(-1;f\left(1\right)\right)\Rightarrow f\left(f\left(-1\right)+f^2\left(1\right)\right)=-1+f\left(f\left(1\right)\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(f^2\left(1\right)-1\right)=-1+1=0\Rightarrow f^2\left(1\right)-1=0\) (do \(f\) song ánh)
\(\Rightarrow f^2\left(1\right)=1\Rightarrow f\left(1\right)=1\) (cũng vẫn do \(f\) song ánh nên \(f\left(1\right)\ne-1\) do \(f\left(-1\right)=-1\))
Thế \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1;x\right)\Rightarrow f\left(1+x\right)=1+f\left(x\right)\) (1)
Từ đẳng thức trên, do \(x\in Z\) nên ta có thể quy nạp để tìm hàm \(f\):
- Với \(x=0\Rightarrow f\left(1\right)=1\)
- Với \(x=1\Rightarrow f\left(2\right)=f\left(1+1\right)=1+f\left(1\right)=2\)
- Giả sử \(f\left(k\right)=k\), ta cần chứng minh \(f\left(1+k\right)=1+k\), nhưng điều này hiển nhiên đúng theo (1)
Vậy \(f\left(x\right)=x\) là hàm cần tìm

Bài 1:
Cho $y=0$ thì: $f(x^3)=xf(x^2)$
Tương tự khi cho $x=0$
$\Rightarrow f(x^3-y^3)=xf(x^2)-yf(y^2)=f(x^3)-f(y^3)$
$\Rightarrow f(x-y)=f(x)-f(y)$ với mọi $x,y\in\mathbb{R}$
Cho $x=0$ thì $f(-y)=0-f(y)=-f(y)$
Cho $y\to -y$ thì: $f(x+y)=f(x)-f(-y)=f(x)--f(y)=f(x)+f(y)$ với mọi $x,y\in\mathbb{R}$
Đến đây ta có:
$f[(x+1)^3+(x-1)^3]=f(2x^3+6x)=f(2x^3)+f(6x)$
$=2f(x^3)+6f(x)=2xf(x^2)+6f(x)$
$f[(x+1)^3+(x-1)^3]=f[(x+1)^3-(1-x)^3]$
$=(x+1)f((x+1)^2)-(1-x)f((1-x)^2)$
$=(x+1)f(x^2+2x+1)+(x-1)f(x^2-2x+1)$
$=(x+1)[f(x^2)+2f(x)+f(1)]+(x-1)[f(x^2)-2f(x)+f(1)]$
$=2xf(x^2)+4f(x)+2xf(1)$
Do đó:
$2xf(x^2)+6f(x)=2xf(x^2)+4f(x)+2xf(1)$
$2f(x)=2xf(1)$
$f(x)=xf(1)=ax$ với $a=f(1)$

\(f\left(x^5+y^5+y\right)=x^3f\left(x^2\right)+y^3f\left(y^2\right)+f\left(y\right)\)
Sửa lại đề câu 2 !!
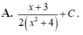
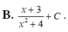
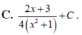
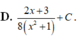

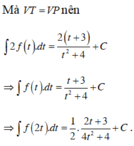
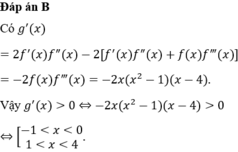
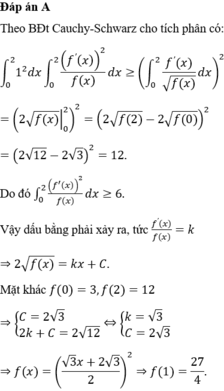
\(f\left(1-x\right)=a\left(1-x\right)^2+b\left(1-x\right)+c=ax^2-\left(2a+b\right)x+a+b+c\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)+2f\left(1-x\right)=3ax^2-\left(4a+b\right)x+2a+2b+3c\)
\(f\left(x\right)+2f\left(1-x\right)=3x^2+2x+5\) \(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3a=3\\4a+b=-2\\2a+2b+3c=5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\b=-6\\c=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=x^2-6x+5\Rightarrow f\left(6\right)=6^2-6.6+5=5\)