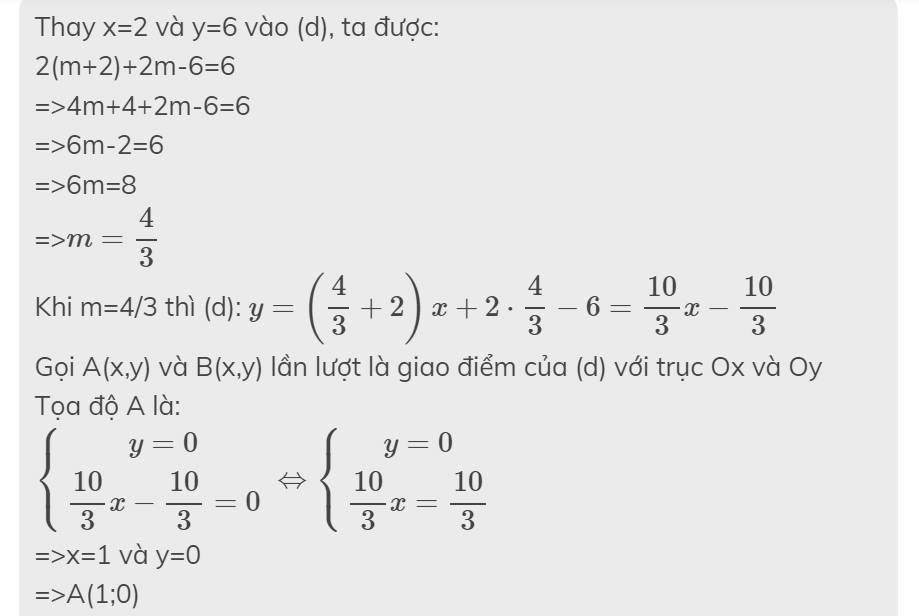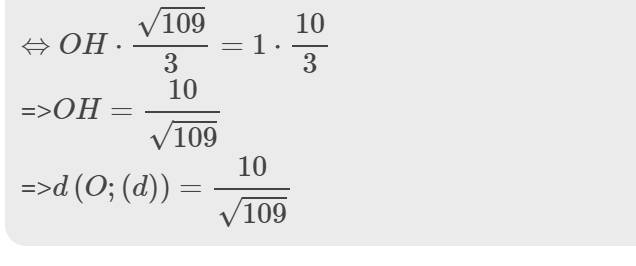Cho đường thẳng (d) : y=ax+3 ( a khác 0). Cho biết khoảng cách từ gốc tọa độ đến (d) là (3căn2)/2 . Xác định a.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(b,\) PT giao Ox và Oy:
\(y=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\Leftrightarrow A\left(2;0\right)\Leftrightarrow OA=2\\ x=0\Leftrightarrow y=-4\Leftrightarrow B\left(0;-4\right)\Leftrightarrow OB=4\)
Gọi H là chân đường cao từ O đến (d)
Áp dụng HTL: \(\dfrac{1}{OH^2}=\dfrac{1}{OA^2}+\dfrac{1}{OB^2}=\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{16}=\dfrac{5}{16}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow OH^2=\dfrac{16}{5}\Leftrightarrow OH=\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{5}}\left(cm\right)\)
Vậy k/c là \(\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{5}}\left(cm\right)\)
\(c,\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2;b\ne-4\\0a+b=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\b=3\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(ax-y+3=0\)
\(\frac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}=\frac{\left|3\right|}{\sqrt{a^2+1}}\Rightarrow\sqrt{a^2+1}=\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow a^2=1\Rightarrow a=\pm1\)

\(a,\) Gọi điểm cố định (d) luôn đi qua là \(A\left(x_0;y_0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y_0=\left(m-2\right)x_0+2\Leftrightarrow mx_0-2x_0+2-y_0=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_0=0\\2-2x_0-y_0=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_0=0\\y_0=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow A\left(0;2\right)\)
Vậy \(A\left(0;2\right)\) là điểm cố định mà (d) lun đi qua
\(b,\) PT giao Ox,Oy: \(y=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{2-m}\Leftrightarrow B\left(\dfrac{2}{2-m};0\right)\Leftrightarrow OB=\dfrac{2}{\left|m-2\right|}\\ x=0\Leftrightarrow y=2\Leftrightarrow C\left(0;2\right)\Leftrightarrow OC=2\)
Gọi H là chân đường cao từ O đến (d) \(\Leftrightarrow OH=1\)
Áp dụng HTL: \(\dfrac{1}{OH^2}=1=\dfrac{1}{OB^2}+\dfrac{1}{OC^2}=\dfrac{\left(m-2\right)^2}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-4m+4+1=4\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2-4m+1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=2+\sqrt{3}\\m=2-\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,\) Áp dụng HTL: \(\dfrac{1}{OH^2}=\dfrac{1}{OC^2}+\dfrac{1}{OB^2}=\dfrac{\left(m-2\right)^2}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Đặt \(OH^2=t\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{t}=\dfrac{m^2-4m+5}{4}\Leftrightarrow t=\dfrac{4}{\left(m-2\right)^2+1}\le\dfrac{4}{0+1}=4\\ \Leftrightarrow OH\le2\\ OH_{max}=2\Leftrightarrow m=2\)

\(a,\) Pt hoành độ giao điểm
\(x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow y=-2\cdot0+3=3\\ \Leftrightarrow A\left(0;3\right)\)
Pt tung độ giao điểm
\(y=0\\ \Leftrightarrow0=-2x+3\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\ \Leftrightarrow B\left(\dfrac{3}{2};0\right)\)

Thay x=2 và y=6 vào (d), ta được:
2(m+2)+2m-6=6
=>4m+4+2m-6=6
=>6m-2=6
=>6m=8
=>\(m=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
Khi m=4/3 thì (d): \(y=\left(\dfrac{4}{3}+2\right)x+2\cdot\dfrac{4}{3}-6=\dfrac{10}{3}x-\dfrac{10}{3}\)
Gọi A(x,y) và B(x,y) lần lượt là giao điểm của (d) với trục Ox và Oy
Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\dfrac{10}{3}x-\dfrac{10}{3}=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\dfrac{10}{3}x=\dfrac{10}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x=1 và y=0
=>A(1;0)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=\dfrac{10}{3}\cdot0-\dfrac{10}{3}=-\dfrac{10}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(B\left(0;-\dfrac{10}{3}\right)\)
O(0;0); A(1;0); B(0;-10/3)
=>\(OA=\sqrt{\left(1-0\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=1\)
\(OB=\sqrt{\left(0-0\right)^2+\left(-\dfrac{10}{3}-0\right)^2}=\dfrac{10}{3}\)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(0-1\right)^2+\left(-\dfrac{10}{3}-0\right)^2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{109}}{3}\)
Vì \(OA^2+OB^2=AB^2\)
nên ΔOAB vuông tại O
Kẻ OH vuông góc AB tại H
=>OH là khoảng cách từ O đến (d)
Xét ΔOAB vuông tại O có OH là đường cao
nên \(OH\cdot AB=OA\cdot OB\)
\(\Leftrightarrow OH\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{109}}{3}=1\cdot\dfrac{10}{3}\)
=>\(OH=\dfrac{10}{\sqrt{109}}\)
=>\(d\left(O;\left(d\right)\right)=\dfrac{10}{\sqrt{109}}\)