Với giá trụ nào của biến thì giá trị của biểu thức sau bằng 0:
\(\frac{x+1}{7}\);\(\frac{3x+3}{5}\);\(\frac{2x\left(x+1\right)}{3x+4}\);\(\frac{3x\left(x-5\right)}{x-7}\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

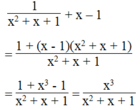
Biểu thức bằng 0 khi x 3 = 0 và x 2 + x + 1 ≠ 0
Ta có: x 3 = 0 ⇒ x = 0;
x 2 + x + 1 = x 2 + 2 . x . 1 / 2 + 1 / 4 + 3 / 4 = x + 1 / 2 2 + 3 / 4 ≠ 0 mọi x.
Vậy với x = 0 thì giá trị của biểu thức bằng 0.

\(\frac{3x-7}{21}-\frac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}\le\frac{x-2}{3}-\frac{x\left(x+1\right)}{7}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3x-7}{21}-\frac{3x\left(x-2\right)}{21}\le\frac{7x-14-3x\left(x+1\right)}{21}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-7-3x^2+6x\le7x-14-3x^2-3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x-7\le4x-14\Leftrightarrow5x\le-7\Leftrightarrow x\le-\frac{7}{5}\)
vậy tập nghiệm của bft là S = { x | x =< -7/5 }
\(\frac{3x-7}{21}-\frac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}\le\frac{x-2}{3}-\frac{x\left(x+1\right)}{7}\)
\(< =>\frac{3x-7}{21}-\frac{3x\left(x-2\right)}{21}\le\frac{7\left(x-2\right)}{21}-\frac{3x\left(x+1\right)}{21}\)
\(< =>3x-7-3x^2+6x\le7x-14-3x^2+3x\)
\(< =>-3x^2+3x+9x-7-10x+14\le0\)
\(< =>-x-7\le0\)
\(< =>x+7\ge0< =>x\ge-7\)
vậy với x >= -7 thì ....

Biểu thức xác định khi: x 2 - 4 = x + 2 x - 2 ≠ 0 và x + 2 2 ≠ 0 hay x ≠ ± 2
Ta có:
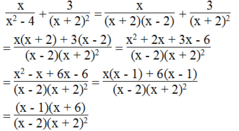
Biểu thức bằng 0 khi (x – 1)(x + 6) = 0 và x - 2 x + 2 2 ≠ 0
+) Ta có: (x - 1).(x + 6) = 0 khi x - 1= 0 hay x + 6 = 0
x - 1 = 0 khi x = 1 ( thỏa mãn điều kiện)
x + 6 = 0 khi x = -6 ( thỏa mãn điều kiện)
Vậy với x = 1 hoặc x = - 6 thì giá trị biểu thức bằng 0.

\(A=\frac{7-X}{X-10}\left(X\inℤ\right)\)
A) ĐỂ A CÓ NGHĨA => X - 10 ≠ 0 => X ≠ 10
B) ĐỂ A > 0
=> \(\frac{7-X}{X-10}>0\)
XÉT HAI TRƯỜNG HỢP :
1. \(\hept{\begin{cases}7-X>0\\X-10>0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}-X>-7\\X>10\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}X< 7\\X>10\end{cases}}\)( LOẠI )
2. \(\hept{\begin{cases}7-X< 0\\X-10< 0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}-X< -7\\X< 10\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}X>7\\X< 10\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow7< X< 10\)
VẬY VỚI 7 < X < 10 THÌ A > 0

ĐKXĐ \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne\pm1\end{cases}}\)
với ĐKXĐ ta có
=\(\left(\frac{x^2+2x+1-x^2+2x-1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\right):\frac{2x}{7\left(x-1\right)}\)
=\(\frac{4x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\times\frac{7\left(x-1\right)}{2x}\)
=\(\frac{14}{x+1}\)
b, x=6(t/m)
khi x=6 thì A=\(\frac{14}{6+1}=2\)
c,A=7<=>\(\frac{14}{x+1}=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x+7=14\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x=7\Leftrightarrow x=1\left(loại\right)\)
Vậy ko có giá trị x để A=7

a) Giá trị của \(\frac{x}{x^2-4}+\frac{3}{\left(x+2\right)^2}\) được xác định
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x-2\ne0\\x+2\ne0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ne\pm2\)
b) Giá trị của biểu thức bằng 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x}{x^2-4}+\frac{3}{\left(x+2\right)^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\frac{3}{\left(x+2\right)^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x\left(x+2\right)+3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+3x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+6x-x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+6\right)-\left(x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+6\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+6=0\\x-1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-6\\x=1\end{cases}}}\)( Thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định )
Vậy ......................
Ta có: \(\frac{x+1}{7}=0\Leftrightarrow x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Ta có: \(\frac{3x+3}{5}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Ta có: \(\frac{2x\left(x+1\right)}{3x+4}=0\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x \(\in\left\{-1;0\right\}\) thì \(\frac{2x\left(x+1\right)}{3x+4}=0\)
Ta có: \(\frac{2x\left(x-5\right)}{x-7}=0\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x-5=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=5\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{0;5\right\}\) thì \(\frac{2x\left(x-5\right)}{x-7}=0\)