2/3 x+1/3(x+2)=0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1) Do x ∈ Z và 0 < x < 3
⇒ x ∈ {1; 2}
2) Do x ∈ Z và 0 < x ≤ 3
⇒ x ∈ {1; 2; 3}
3) Do x ∈ Z và -1 < x ≤ 4
⇒ x ∈ {0; 1; 2; 3; 4}

\(\left(x-3\right)^3+\left(x+3\right)^3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-9x^2+27x-27+x^3+9x^2+27x+27=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3+54x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(2x+54\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2x+54=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-27\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,\left(x+1\right)^3-\left(x-1\right)^3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+3x^2+3x+1-x^3+3x^2-3x+1=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=-3\) ( vô lí)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm
\(c,x^2-4x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(d,4x^2+4x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-1\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(e,\left(x+2\right)^2-\left(x+3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2-x-3\right)\left(x+2+x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=5\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Học tốt nha you <3

\(\left(x-3\right)^3+\left(x+3\right)^3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-9x^2+27x-27+x^3+9x^2+27x+27=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3+54x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(2x+54\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2x+54=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-27\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,\left(x+1\right)^3-\left(x-1\right)^3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+3x^2+3x+1-x^3+3x^2-3x+1=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=-3\) ( vô lí)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm
\(c,x^2-4x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(d,4x^2+4x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-1\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(e,\left(x+2\right)^2-\left(x+3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2-x-3\right)\left(x+2+x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=5\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Học tốt nha you <3

\(\left(x-3\right)^3+\left(x+3\right)^3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-9x^2+27x-27+x^3+9x^2+27x+27=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3+54x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(2x+54\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2x+54=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-27\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,\left(x+1\right)^3-\left(x-1\right)^3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+3x^2+3x+1-x^3+3x^2-3x+1=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=-3\) ( vô lí)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm
\(c,x^2-4x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(d,4x^2+4x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-1\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(e,\left(x+2\right)^2-\left(x+3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2-x-3\right)\left(x+2+x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=5\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Học tốt nha you <3

\(2x^3-50x=0\)
<=> \(2x\left(x^2-25\right)=0\)
<=> \(2x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
đến đây
bạn tự giải nhé
hk tốt

a: \(\dfrac{x+5}{x-1}+\dfrac{8}{x^2-4x+3}=\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}\)
=>(x+5)(x-3)+8=x^2-1
=>x^2+2x-15+8=x^2-1
=>2x-7=-1
=>x=3(loại)
b: \(\dfrac{x-4}{x-1}-\dfrac{x^2+3}{1-x^2}+\dfrac{5}{x+1}=0\)
=>(x-4)(x+1)+x^2+3+5(x-1)=0
=>x^2-3x-4+x^2+3+5x-5=0
=>2x^2+2x-6=0
=>x^2+x-3=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{-1\pm\sqrt{13}}{2}\)
e: =>x^2-2x+1+2x+2=5x+5
=>x^2+3=5x+5
=>x^2-5x-2=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{33}}{2}\)
g: (x-3)(x+4)*x=0
=>x=0 hoặc x-3=0 hoặc x+4=0
=>x=0;x=3;x=-4

Bài 3:
1. \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)+5x-5=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)+5\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2+5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy.......................
2. \(\left(3x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)-6x-10=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(3x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)-2\left(3x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(3x+5\right)\left(x-3-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+5=0\\x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{5}{3}\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy........................
3. \(\left(x-2\right)\left(2x+3\right)-7x^2+14x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(2x+3\right)-7x\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(2x+3-7x\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\-5x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{3}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy............................
4, 5 tương tự nhé bn!
bài 3
1 (x-1)(x+2)+5x-5=0
=>(x-1)(x+2)+(5x-5)=o
=>(x-1)(x+2)+5(x-1)=0
=>(x-1)(x+2+5)=0
=>(x-1)(x+7)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\) =>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy x=1 hoặc x=-7
2. (3x+5)(x-3)-6x-10=0
=>(3x+5)(x-3)-(6x+10)=0
=>(3x+5)(x-3)-2(3x+5)=0
=>(3x+5)(x-3-2)=0
=>(3x+5)(x-5)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+5=0\\x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{5}{3}\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) \(2{x^2} + 3x + 1 \ge 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} + 3x + 1\) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x = - 1,x = \frac{{ - 1}}{2}\)
hệ số \(a = 2 > 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:
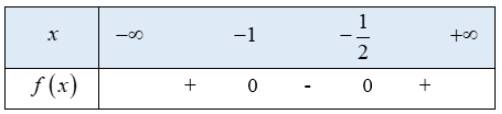
Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x \le - 1\\x \ge - \frac{1}{2}\end{array} \right.\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\left( { - \infty ; - 1} \right] \cup \left[ { - \frac{1}{2}; + \infty } \right)\)
b) \( - 3{x^2} + x + 1 > 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = - 3{x^2} + x + 1\) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x = \frac{{1 - \sqrt {13} }}{6},x = \frac{{1 + \sqrt {13} }}{6}\)
Hệ số \(a = - 3 < 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:

Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) > 0\)\( \Leftrightarrow \frac{{1 - \sqrt {13} }}{6} < x < \frac{{1 + \sqrt {13} }}{6}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\left( {\frac{{1 - \sqrt {13} }}{6};\frac{{1 + \sqrt {13} }}{6}} \right)\)
c) \(4{x^2} + 4x + 1 \ge 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = 4{x^2} + 4x + 1\) có nghiệm duy nhất \(x = \frac{{ - 1}}{2}\)
hệ số \(a = 4 > 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:

Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow x \in \mathbb{R}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\mathbb{R}\)
d) \( - 16{x^2} + 8x - 1 < 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = - 16{x^2} + 8x - 1\) có nghiệm duy nhất \(x = \frac{1}{4}\)
hệ số \(a = - 16 < 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:
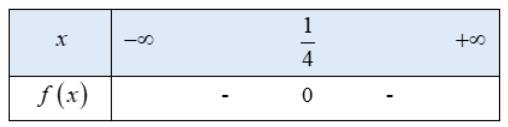
Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) < 0 \Leftrightarrow x \ne \frac{1}{4}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\mathbb{R}\backslash \left\{ {\frac{1}{4}} \right\}\)
e) \(2{x^2} + x + 3 < 0\)
Ta có \(\Delta = {1^2} - 4.2.3 = - 23 < 0\) và có \(a = 2 > 0\)
Sử dụng định lí về dấu của tam thức bậc hai, ta thấy tập hợp những giá trị của x sao cho \(2{x^2} + x + 3\) mang dấu “-” là \(\emptyset \)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \(2{x^2} + x + 3 < 0\) là \(\emptyset \)
g) \( - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5 < 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5\) có \(\Delta ' = {2^2} - \left( { - 3} \right).\left( { - 5} \right) = - 11 < 0\) và có \(a = - 3 < 0\)
Sử dụng định lí về dấu của tam thức bậc hai, ta thấy tập hợp những giá trị của x sao cho \( - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5\) mang dấu “-” là \(\mathbb{R}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \( - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5 < 0\) là \(\mathbb{R}\)
2/3 x + 1/3(x+2) = 0
2/3x + 1/3x +1/3 . 2 = 0
(2/3 + 1/3)x + 2/3 = 0
1x = -2/3
x = -2/3
. là dấu nhân
2/3 x X+1/3x (X+2)=0
2/3 x X + 1/3 x X +1/3 x 2=0
2/3 x X + 1/3 x X + 2/3=0
(2/3+1/3) x X + 2/3=0
1x X+ 2/3= 0
X+2/3=0
X=0-2/3
X= -2/3
x là nhân còn X là số cần tìm