tìm các số tự nhiên n để biểu thức n/n-4 nhận giá trị nguyên
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\frac{2n}{n-2}=\frac{2\left(n-2\right)+4}{n-2}=2+\frac{4}{n-2}\)(ĐK:n\(\ne2\))
để biểu thức nhận gái trị nguyên thì 4\(⋮\)(n-2)
=> (n-2) là ước của 4 mà Ư\(_{\left(4\right)}\)=\(\pm1;\pm2;\pm4\)
=>n-2=1 =>n=3 (tm)
n-2=-1 =>n=1 (tm)
n-2=2 =>n=4 (tm)
n-2=-2 =>n=0 (tm)
n-2=4=>n=6 (tm)
n-2=-4=>n=-2 (tm)


Câu 1:
a) \(A=\left[\dfrac{2}{3x}-\dfrac{2}{x+1}.\left(\dfrac{x+1}{3x}-x-1\right)\right]:\dfrac{x-1}{x}\)
\(=\left[\dfrac{2}{3x}-\dfrac{2}{3x}+\dfrac{2x}{x+1}+\dfrac{2}{x+1}\right]\dfrac{x}{x-1}\)
\(=\left[\dfrac{2x}{x+1}+\dfrac{2}{x+1}\right]\dfrac{x}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x+2}{x+1}.\dfrac{x}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{x+1}.\dfrac{x}{x-1}\)
\(=2.\dfrac{x}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x}{x-1}\)
Câu 1:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-1;1\right\}\)
a) Ta có: \(A=\left(\dfrac{2}{3x}-\dfrac{2}{x+1}\cdot\left(\dfrac{x+1}{3x}-x-1\right)\right):\dfrac{x-1}{x}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{2}{3x}-\dfrac{2}{x+1}\cdot\left(\dfrac{x+1}{3x}-\dfrac{3x\left(x+1\right)}{3x}\right)\right):\dfrac{x-1}{x}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{2}{3x}-\dfrac{2}{x+1}\cdot\dfrac{x+1-3x^2-3x}{3x}\right):\dfrac{x-1}{x}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{2}{3x}-\dfrac{2}{x+1}\cdot\dfrac{-3x^2-2x+1}{3x}\right):\dfrac{x-1}{x}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{3x\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{2\cdot\left(-3x^2-2x+1\right)}{3x\left(x+1\right)}\right):\dfrac{x-1}{x}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x+2+6x^2+4x-2}{3x\left(x+1\right)}:\dfrac{x-1}{x}\)
\(=\dfrac{6x^2+6x}{3x\left(x+1\right)}:\dfrac{x-1}{x}\)
\(=\dfrac{6x\left(x+1\right)}{3x\left(x+1\right)}:\dfrac{x-1}{x}\)
\(=2\cdot\dfrac{x}{x-1}=\dfrac{2x}{x-1}\)
b) Để A nguyên thì \(2x⋮x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-2+2⋮x-1\)
mà \(2x-2⋮x-1\)
nên \(2⋮x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{2;0;3;-1\right\}\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: \(x\in\left\{2;3\right\}\)
Vậy: Để A nguyên thì \(x\in\left\{2;3\right\}\)

Đáp án cần chọn là: C
Vì C∈N nên C∈Z. Do đó ta tìm n∈Z để C∈Z
Vì n∈Z nên để C∈Z thì 2n + 1∈U(11) = {±1;±11}
Ta có bảng
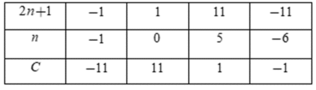
Vì C∈N nên ta chỉ nhận các giá trị n = 0;n = 5

Đáp án cần chọn là: B
Vì C∈N nên C∈Z. Do đó ta tìm n∈Z để C∈Z
Vì n∈Z nên để C∈Z thì 3n − 2∈U(12) = {±1;±2;±3;±4;±6;±12}
Ta có bảng:
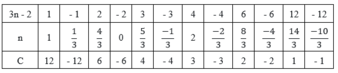
Vì C∈N và n∈Z nên ta chỉ nhận các giá trị n = 1;n = 2
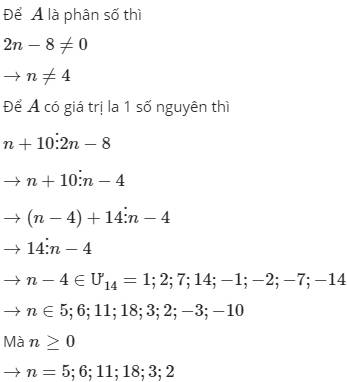
\(\frac{n}{n-4}\)nhận giá trị nguyên <=> n\(⋮\)n - 4
< => ( n - 4 ) + 4 \(⋮\) n - 4
<=> 4 \(⋮\) n - 4
<=> n - 4 \(\in\)Ư ( 4 )
<=> n - 4 \(\in\){ 1;2;4;-1;-2;-4 }
<=> n \(\in\){ 5;6;8;3;2;0 }
vậy ....
Để biểu thức đạt giá trị nguyên thì:
\(\frac{n}{n-4}\in Z\Rightarrow n⋮n-4\)
Xét từng th -> giải.