Tìm só nguyên dương x,y,z thỏa mãn xy+yz+xz=xyz
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.




Đặt \(A=\sqrt{x+yz}+\sqrt{y+zx}+\sqrt{z+xy}\)
Ta có:
\(x^2+xy+yz+zx=x+xyz=x\left(x+yz\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{x\left(x+yz\right)}{x}=\frac{x^2+xy+yz+zx}{x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+yz=\frac{x^2+xy+yz+zx}{x}=\frac{\left(x^2+xy\right)+\left(yz+zx\right)}{x}=\frac{\left(x+z\right)\left(x+y\right)}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x+yz}=\sqrt{\frac{\left(x+y\right)\left(x+z\right)}{x}}\)
Vì x, y, z >0 nên áp dụng bất đẳng thức Bunhiacopxki cho 2 số dương, ta được:
\(\left(x+y\right)\left(x+z\right)\ge\left(\sqrt{x^2}.+\sqrt{yz}\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{\left(x+y\right)\left(x+z\right)}\ge x+\sqrt{yz}\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{\frac{\left(x+y\right)\left(x+z\right)}{x}}\ge\frac{x+\sqrt{yz}}{\sqrt{x}}\)
Do đó \(\sqrt{x+yz}\ge\frac{x+\sqrt{yz}}{\sqrt{x}}\left(1\right)\)
Chứng minh tương tự, ta được:
\(\sqrt{y+xz}\ge\frac{y+\sqrt{xz}}{\sqrt{y}}\left(2\right)\)
Chứng minh tương tự, ta được:
\(\sqrt{z+xy}\ge\frac{z+\sqrt{xy}}{\sqrt{z}}\left(3\right)\)
Từ (1), (2) và (3), ta được:
\(\sqrt{x+yz}+\sqrt{y+zx}+\sqrt{z+xy}\)\(\ge\frac{x+\sqrt{yz}}{\sqrt{x}}+\frac{y+\sqrt{zx}}{\sqrt{y}}+\frac{z+\sqrt{xy}}{\sqrt{z}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A\ge\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{\frac{yz}{x}}+\sqrt{y}+\sqrt{\frac{xz}{y}}+\sqrt{z}+\sqrt{\frac{xy}{z}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A\ge\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}+\sqrt{z}+\frac{yz+zx+xy}{\sqrt{xyz}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A\ge\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}+\sqrt{z}+\frac{xyz}{\sqrt{xyz}}\)(vì \(xy+yz+zx=xyz\))
\(\Leftrightarrow A\ge\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}+\sqrt{z}+\sqrt{xyz}\)(điều phải chứng minh).
Dấu bằng xảy ra.
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=y=z>0\\xy+yz+zx=xyz\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow x=y=z=3\)
Vậy với x, y, z là các số thực dương thỏa mãn xy + yz + zx =xyz thì:
\(\sqrt{x+yz}+\sqrt{y+zx}+\sqrt{z+xy}\ge\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}+\sqrt{z}+\sqrt{xyz}\).
\(\)


Ta có \(\frac{x+2xy+1}{x+xy+xz+1}=\frac{x+2xy+xyz}{x+xy+xz+xyz}=\frac{1+2y+yz}{\left(y+1\right)\left(z+1\right)}\)
Tương tự => \(M=\frac{1+2y+yz}{\left(y+1\right)\left(z+1\right)}+\frac{1+2z+zx}{\left(1+x\right)\left(z+1\right)}+\frac{1+2x+xy}{\left(1+x\right)\left(y+1\right)}\)
=> \(M=\frac{\left(1+2y+yz\right)\left(1+x\right)+\left(1+2z+zx\right)\left(1+y\right)+\left(1+2x+xy\right)\left(1+z\right)}{\left(1+x\right)\left(1+y\right)\left(1+z\right)}\)
=>\(M=\frac{6+3\left(x+y+z\right)+3\left(xy+yz+xz\right)}{2+\left(x+y+z\right)+\left(xy+yz+xz\right)}=3\)

\(gt\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{y}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{z}}=1\)
\(P=\dfrac{1}{xyz}\left(x\sqrt{2y^2+yz+2z^2}+y\sqrt{2x^2+xz+2z^2}+z\sqrt{2y^2+xy+2x^2}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{xyz}\left(x\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{4}\left(y+z\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\left(y-z\right)^2}+y\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{4}\left(x+z\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\left(x-z\right)^2}+z\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{4}\left(x+y\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\left(x-y\right)^2}\right)\)
\(\ge\dfrac{1}{xyz}\left[x.\dfrac{\sqrt{5}\left(z+y\right)}{2}+y.\dfrac{\sqrt{5}\left(x+z\right)}{2}+z.\dfrac{\sqrt{5}\left(x+y\right)}{2}\right]\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}\left(z+y\right)}{2yz}+\dfrac{\sqrt{5}\left(x+z\right)}{2xz}+\dfrac{\sqrt{5}\left(x+y\right)}{2xy}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\left(1+1+1\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}+\dfrac{1}{z}\right)\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{y}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{z}}\right)^2=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\) (bunhia)
Dấu = xảy ra khi \(x=y=z=9\)
Thấy : \(\sqrt{2y^2+yz+2z^2}=\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{4}\left(y+z\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\left(y-z\right)^2}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(y+z\right)>0\)
CMTT : \(\sqrt{2x^2+xz+2z^2}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(x+z\right)\) ; \(\sqrt{2y^2+xy+2x^2}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(x+y\right)\)
Suy ra : \(P\ge\dfrac{1}{xyz}.\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\left[x\left(y+z\right)+y\left(x+z\right)+z\left(x+y\right)\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow P\ge\sqrt{5}\left(\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}+\dfrac{1}{z}\right)\)
Ta có : \(\sqrt{xy}+\sqrt{yz}+\sqrt{xz}=\sqrt{xyz}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{y}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{z}}=1\)
Mặt khác : \(\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}+\dfrac{1}{z}\ge\dfrac{\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{y}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{z}}\right)^2}{3}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Suy ra : \(P\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\)
" = " \(\Leftrightarrow x=y=z=9\)

Không mất tính tổng quát giả sử: \(x\ge y\ge z>0\)
Ta có: \(xy\ge yz;xy\ge xz\)
Ta có: \(xy+yz+xz\le3xy\)
\(\Rightarrow xyz\le3xy\Leftrightarrow z\le3\)
Xét với \(z\in\left\{3;2;1\right\}\left(z\in Z^+\right)\)

Từ \(xy+yz+xz=xyz\Rightarrow\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}+\frac{1}{z}=1\)
Đặt \(\left(\frac{1}{x};\frac{1}{y};\frac{1}{z}\right)\rightarrow\left(a,b,c\right)\) thì có
\(\frac{c^3}{\left(a+1\right)\left(b+1\right)}+\frac{b^3}{\left(a+1\right)\left(c+1\right)}+\frac{a^3}{\left(b+1\right)\left(c+1\right)}\ge\frac{1}{16}\)\(\forall\hept{\begin{cases}a+b+c=1\\a,b,c>0\end{cases}}\)
Áp dụng BĐT AM-GM ta có:
\(\frac{a^3}{\left(b+1\right)\left(c+1\right)}+\frac{b+1}{64}+\frac{c+1}{64}\ge\frac{3a}{16}\)
Tương tự cho 2 BĐT còn lại rồi cộng theo vế
\(VT+\frac{2\left(a+b+c+3\right)}{64}\ge\frac{3\left(a+b+c\right)}{16}\Leftrightarrow VT\ge\frac{1}{16}\)
Khi \(a=b=c=\frac{1}{3}\Leftrightarrow x=y=z=1\)
a) x4+x3+2x2+x+1=(x4+x3+x2)+(x2+x+1)=x2(x2+x+1)+(x2+x+1)=(x2+x+1)(x2+1)
b)a3+b3+c3-3abc=a3+3ab(a+b)+b3+c3 -(3ab(a+b)+3abc)=(a+b)3+c3-3ab(a+b+c)
=(a+b+c)((a+b)2-(a+b)c+c2)-3ab(a+b+c)=(a+b+c)(a2+2ab+b2-ac-ab+c2-3ab)=(a+b+c)(a2+b2+c2-ab-ac-bc)
c)Đặt x-y=a;y-z=b;z-x=c
a+b+c=x-y-z+z-x=o
đưa về như bài b
d)nhóm 2 hạng tử đầu lại và 2hangj tử sau lại để 2 hạng tử sau ở trong ngoặc sau đó áp dụng hằng đẳng thức dề tính sau đó dặt nhân tử chung
e)x2(y-z)+y2(z-x)+z2(x-y)=x2(y-z)-y2((y-z)+(x-y))+z2(x-y)
=x2(y-z)-y2(y-z)-y2(x-y)+z2(x-y)=(y-z)(x2-y2)-(x-y)(y2-z2)=(y-z)(x2-2y2+xy+xz+yz)

Ta có: \(P=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{1+x+xy}+\frac{\sqrt{y}}{1+y+yz}+\frac{\sqrt{z}}{1+z+xz}\)
\(P=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{xy+x+1}+\frac{x\sqrt{y}}{x+xy+xyz}+\frac{xy\sqrt{z}}{xy+xyz+x^2yz}\)
\(P=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{xy+x+1}+\frac{x\sqrt{y}}{xy+x+1}+\frac{\sqrt{xy}.\sqrt{xyz}}{xy+x+1}\)
\(P=\frac{\sqrt{x}+x\sqrt{y}+\sqrt{xy}}{xy+x+1}\le\frac{\frac{x+1}{2}+\frac{x\left(y+1\right)}{2}+\frac{xy+1}{2}}{xy+x+1}\) (bđt cosi)
=> \(P\le\frac{x+1+xy+x+xy+1}{2\left(xy+x+1\right)}=\frac{2\left(xy+x+1\right)}{2\left(xy+x+1\right)}=1\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra<=> x = y = z = 1
Vậy MaxP = 1 <=> x = y = z = 1
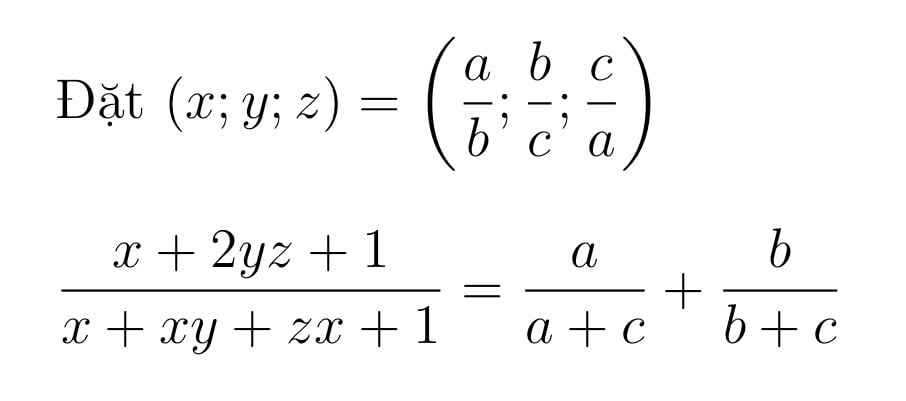
Vì vai trò của ba số x,y,z là như nhau
giả sử
\(x\ge y\ge z>0\)
\(\Rightarrow xy\ge yz;xy\ge xz\)
\(\Rightarrow xy+yz+xz\le3xy\)
\(\Leftrightarrow xyz\le3xy\)
\(\Rightarrow z\le3\)
\(\Rightarrow z\in\left\{1;2;3\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x;y;z\right)=\left(1;2;3\right)\) và hoán vị của chúng thỏa mãn phương trình