HELP
tìm các số nguyên x để x4 - x2 + 2x + 2 là số chính phương
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a. \(x=\left\{4;9;16\right\}\)
b. \(x=1\)
c. \(x=\left\{-2;-1\right\}\)


-Đặt \(x^2+8x=a^2\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+8x+16=a^2+16\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+4\right)^2-a^2=16\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+a+4\right)\left(x-a+4\right)=16\)
-Vì \(x,a\) là các số nguyên dương \(\Rightarrow x+a+4>x-a+4\) và \(16=16.1=8.2=4.4\)
\(\Rightarrow x+a+4=16;x-a+4=1\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{9}{2};a=\dfrac{15}{2}\left(loại\right)\)
\(x+a+4=8;x-a+4=2\Rightarrow x=1;a=3\left(nhận\right)\)
\(x+a+4=4;x-a+4=4\Rightarrow x=a=0\left(nhận\right)\)
-Vậy \(x\in\left\{0;1\right\}\)

đăt. x^2 + 2x +1 +1 = n^2 ( n dương) suy ra n^2 - (x + 1)^2 = 1 hay (n-x-1)(n+x+1) = 1.1
suy ra n - x -1 = 1 và n + x + 1 =1 suy ra n = 1; x = -1.liên hệ 0972315132

Để x^2 - 2x - 14 là số chính pương
<=> x^2 - 2x - 14 = y^2
<=> x^2 - 2x + 1 - 15 = y^2
<=> (x - 1)^2 - 15 = y^2
<=> (x - 1)^2 - y^2 = 15
<=> (x - y - 1)(x + y - 1) = 3*5 = 1*15 = -5*(-3) = -15*(-1)
Vì x - y - 1 < x + y - 1
=> TH1: x - y - 1 = 3 ; x + y - 1 = 5
<=> x - y = 4 ; x + y = 6
<=> x = 5
TH2: x - y - 1 = 1 ; x + y - 1 = 15
<=> x - y = 2 ; x + y = 16
<=> x = 9
TH3: x - y - 1 = -5 ; x + y - 1 = -3
<=> x - y = -4 ; x + y = -2
<=> x = -3
TH4: x - y - 1 = -15 ; x + y - 1 = -1
<=> x - y = -14 ; x + y = 0
<=> x = -7
Vậy x = 5; x = 9; x = -3; x = -7
NHỚ LIKE CHO MÌNH NHÉ! MÌNH CẢM ƠN!

Đáp án là B.
Đặt t = x - 2 x Đạo hàm t , = 1 + 2 x 2 > 0
Do đó t ( 1 ) ≤ t ≤ t ( 2 ) , ∀ x ∈ [ 1 ; 2 ] , suy ra - 1 ≤ t ≤ 1
Ta có x 2 + 4 x 2 = t 2 + 4 , x 4 + 16 x 4 = ( x 2 + 4 x 2 ) 2 - 8 = ( t 2 + 4 ) 2 - 8 = t 4 + 8 t 2 + 8
Phương trình đã cho trở thành
t 4 + 8 t 2 + 8 - 4 ( t 2 + 4 ) - 12 t = m ⇔ t 4 + 4 t 2 - 12 t = m + 8 ( * )
Phương trình đã cho có nghiệm trong đoạn [1;2] khi và chỉ khi phương trình (*) có nghiệm trong [-1;1] Xét hàm số y=f(t)= t 4 + 4 t 2 - 12 t trên [-1;1]
Đạo hàm y , = 4 t 8 + 8 t - 12 , t ∈ ( - 1 ; 1 ) . y , = 4 ( t - 1 ) ( t 2 + t + 3 ) < 0 , ∀ t ∈ ( - 1 ; 1 )
Bảng biến thiên:
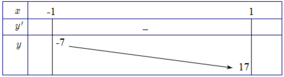
Do đó để phương trình đã cho có nghiệm trên [1;2] thì - 7 ≤ m + 8 ≤ 17 ⇔ - 15 ≤ m ≤ 9

Giải:
Dùng biến đổi tương đương chứng minh được:
\(\left(x^2+x+2\right)^2=x^4+5x^3+4x+4>x^4+2x^3+2x^2+x+3>\) \(x^4+2x^3+x^2=\left(x^2+x\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow x^4+2x^3+2x^2+x+3=\left(x^2+x+1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+2x^3+2x^2+x+3=x^4+2x^3+3x^2+2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-2=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(x=1\) hoặc \(x=-2\) thì phương trình trên là số chính phương
dùng phương pháp hệ số bất định ý bạn gọi đa thức đó là bình phương của đa thức (x^2+ax+b)^2 rồi khai triển là ok
P/s: nói trước là tớ ko chắc đúng đâu nhé ;)
Đặt \(A=x^4-x^2+2x+2\)
\(A=x^2\left(x^2-1\right)+2\left(x+1\right)\)
\(A=x^2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+2\left(x+1\right)\)
\(A=\left(x+1\right)\left[x^2\left(x-1\right)+2\right]\)
\(A=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^3-x^2+2\right)\)
\(A=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^3-2x^2+x^2+2\right)\)
\(A=\left(x+1\right)\left[x^2\left(x+1\right)-2\left(x^2-1\right)\right]\)
\(A=\left(x+1\right)\left[x^2\left(x+1\right)-2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\right]\)
\(A=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left[x^2-2\left(x-1\right)\right]\)
\(A=\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x^2-2x+2\right)\)
Dễ thấy \(\left(x+1\right)^2\)là số chính phương nên để A là số chính phương thì \(x^2-2x+2\)là số chính phương
Đặt \(x^2-2x+2=k^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1+1-k^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2-k^2=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-k-1\right)\left(x+k-1\right)=-1\)
TH1 :\(\hept{\begin{cases}x-k-1=1\\x+k-1=-1\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x-k=2\\x+k=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\k=-1\end{cases}}}}\)( thỏa mãn )
TH2 :\(\hept{\begin{cases}x-k-1=-1\\x+k-1=1\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x-k=0\\x+k=2\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x=k=1}}\)( thỏa mãn )
Vậy x = 1 thì A là số chính phương
bn lm sai bước cuối thì phải