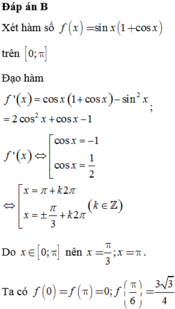giá trị dương nhỏ nhất của biến x (theo raddian) không thuộc tập xác định của hàm số f(x)=1/(sinx+cosx) là
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1.TXĐ: D = R.
![]()
3. Bảng biến thiên:
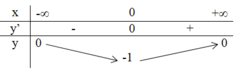
Vậy giá trị nhỏ nhất của hàm số đã cho là – 1 tại x = 0.

y = \(\dfrac{sin^2x}{cosx\left(sinx-cosx\right)}+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
y = \(\dfrac{sin^2x}{sinx.cosx-cos^2x}+\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{\dfrac{sin^2x}{cos^2x}}{\dfrac{sinx.cosx}{cos^2x}-1}+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
y = \(\dfrac{tan^2x}{tanx-1}+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
y = \(\dfrac{4tan^2x+tanx-1}{4tanx-4}\). Đặt t = tanx. Do x ∈ \(\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4};\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\) nên t ∈ (1 ; +\(\infty\))\
Ta đươc hàm số f(t) = \(\dfrac{4t^2+t-1}{4t-4}\)
⇒ ymin = \(\dfrac{17}{4}\) khi t = 2. hay x = arctan(2) + kπ

\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m-1\right)sinx-\left(m+2\right)cosx+4m-3\ge0\) ;\(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ge\dfrac{sinx+2cosx+3}{2sinx-cosx+4}=P\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ge P_{max}\)
Ta có: \(P=\dfrac{sinx+2cosx+3}{2sinx-cosx+4}\Leftrightarrow\left(2P-1\right)sinx-\left(P+2\right)cosx=3-4P\)
Theo điều kiện có nghiệm của pt lượng giác bậc nhất:
\(\left(2P-1\right)^2+\left(P+2\right)^2\ge\left(3-4P\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow11P^2-24P+4\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{2}{11}\le P\le2\)
\(\Rightarrow m\ge2\)

f(x) = sinx – bx + c nghịch biến trên R nếu ta có:
f′(x) = cosx – b ≤ 0, ∀ x ∈ R.
Vì |cosx| ≤ 1| nên f′(x) ≤ 0, ∀ x ∈ R ⇔ b ≥ 1.

f(x) = sinx – bx + c nghịch biến trên R nếu ta có:
f′(x) = cosx – b ≤ 0, ∀ x ∈ R.
Vì |cosx| ≤ 1| nên f′(x) ≤ 0, ∀ x ∈ R ⇔ b ≥ 1.

1.
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}cosx\ne0\\tanx-sinx\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}cosx\ne0\\\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}-sinx\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}cosx\ne0\\sinx\ne0\\cosx\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow sin2x\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
2.
ĐKXĐ: \(sin2x\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
3.
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sin\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\ne0\\cos\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\ne0\Leftrightarrow cos2x\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)