3x = 9
x4 = 16
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) 9 x 4 − 10 x 2 + 1 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 = t , điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 9 t 2 − 10 t + 1 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2):
Có a = 9 ; b = -10 ; c = 1
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ Phương trình (2) có nghiệm t 1 = 1 ; t 2 = c / a = 1 / 9
Cả hai nghiệm đều thỏa mãn điều kiện.
+ Với t = 1 ⇒ x 2 = 1 ⇒ x = 1 hoặc x = -1.
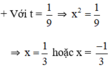
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm 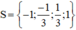
b)
5 x 4 + 2 x 2 - 16 = 10 - x 2 ⇔ 5 x 4 + 2 x 2 - 16 - 10 + x 2 = 0 ⇔ 5 x 4 + 3 x 2 - 26 = 0
Đặt x 2 = t , điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 5 t 2 + 3 t − 26 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) :
Có a = 5 ; b = 3 ; c = -26
⇒ Δ = 3 2 − 4.5 ⋅ ( − 26 ) = 529 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt
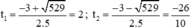
Đối chiếu điều kiện chỉ có t 1 = 2 thỏa mãn
+ Với t = 2 ⇒ ⇒ x 2 = 2 ⇒ x = √2 hoặc x = -√2.
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm S = {-√2; √2}
c) 0 , 3 x 4 + 1 , 8 x 2 + 1 , 5 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 = t , điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó, (1) trở thành : 0 , 3 t 2 + 1 , 8 t + 1 , 5 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) :
có a = 0,3 ; b = 1,8 ; c = 1,5
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm t 1 = − 1 và t 2 = − c / a = − 5
Cả hai nghiệm đều không thỏa mãn điều kiện.
Vậy phương trình (1) vô nghiệm.
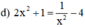
Điều kiện xác định: x ≠ 0.
Quy đồng, khử mẫu ta được :
2 x 4 + x 2 = 1 − 4 x 2 ⇔ 2 x 4 + x 2 + 4 x 2 − 1 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 4 + 5 x 2 − 1 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt t = x 2 , điều kiện t > 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 2 t 2 + 5 t - 1 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) :
Có a = 2 ; b = 5 ; c = -1
⇒ Δ = 5 2 − 4.2 ⋅ ( − 1 ) = 33 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt:
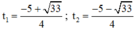
Đối chiếu với điều kiện thấy có nghiệm t 1 thỏa mãn.
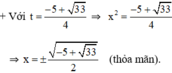
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 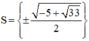
a) (15x2-1+9x4-6x3+2x) :( 5 + 3x2-2x)
b) ( -19x+ 10+ 3x4- 5x2+11x3) : ( 3x+ x2-2)
c) (x4-14-x) : (x-2)

c: \(\dfrac{x^4-x-14}{x-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^4-2x^3+2x^3-4x^2+4x^2-8x+7x-14}{x-2}\)
\(=x^3+2x^2+4x+7\)

a) (a - 2b)x(a + 2b)
b) x2-(y-3)2
=> (x-y+3)(x+y-3)
c) (2a + b - a)(2a + b + a)
=> (a+b)(3a+b)
d) (4(x - 1))2 - (5(x + y))2
⇔ (4x - 4 - 5x - 5y)(4x - 4 + 5x + 5y)
⇔ -(x + 5y + 4)(9x + 5y + -4)
e) (x + 5)2
f) (5x - 2y)2
h) (x - 5)(x2 + 5x + 25)
k) (x + 5)3

a, \(\dfrac{38}{7}\) + ( \(\dfrac{16}{7}\) - \(\dfrac{5}{3}\))
= \(\dfrac{38}{7}\) + \(\dfrac{16}{7}\) - \(\dfrac{5}{3}\)
= \(\dfrac{54}{7}\) - \(\dfrac{5}{3}\)
= \(\dfrac{162}{21}\) - \(\dfrac{35}{21}\)
= \(\dfrac{127}{21}\)
b, \(\dfrac{29}{9}\) - ( \(\dfrac{14}{9}\) + \(\dfrac{11}{9}\) )
= \(\dfrac{29-14-11}{9}\)
= \(\dfrac{4}{9}\)
c, ( \(\dfrac{2}{7}\) + \(\dfrac{3}{8}\) + \(\dfrac{12}{7}\) + \(\dfrac{5}{8}\) ) - \(\dfrac{19}{63}\)
= ( \(\dfrac{2+12}{7}\) + \(\dfrac{3+5}{8}\)) - \(\dfrac{19}{63}\)
= \(\left(1+2\right)\) - \(\dfrac{19}{63}\)
= \(3-\dfrac{19}{63}\)
= \(\dfrac{189}{63}\) - \(\dfrac{19}{63}\)
= \(\dfrac{170}{63}\)
d, \(\dfrac{3}{7}\) . \(\dfrac{4}{9}\) + \(\dfrac{4}{9}\) . \(\dfrac{4}{7}\) - \(\dfrac{4}{9}\)
= \(\dfrac{4}{9}\) . ( \(\dfrac{3}{7}\) + \(\dfrac{3}{7}\) ) - \(\dfrac{4}{9}\)
= \(\dfrac{4}{9}\) . \(1-\dfrac{4}{9}\)
= \(\dfrac{4}{9}\) - \(\dfrac{4}{9}\)
= 0



\(9x^4-10x^2+1=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(9x^4-9x^2\right)-\left(x^2-1\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow9x^2\left(x^2-1\right)-\left(x^2-1\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(9x^2-1\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-1\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đặt x^2 = t ( t>= 0 )
9t^2 - 10t + 1 = 0
ta có : a + b + c = 9 - 10 + 1 = 0
=> t = 1 ; t = 1/9
theo cách đặt x = 1 ; x = 1/3


a: \(50x^5-8x^3\)
\(=2x^3\left(25x^2-4\right)\)
\(=2x^3\left(5x-2\right)\left(5x+2\right)\)
b: \(x^4-5x^2-4y^2+10y\)
\(=\left(x^2-2y\right)\left(x^2+2y\right)-5\left(x^2-2y\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-2y\right)\left(x^2+2y-5\right)\)
c: \(36a^2+12a+1-b^2\)
\(=\left(6a+1\right)^2-b^2\)
\(=\left(6a+1-b\right)\left(6a+1+b\right)\)
d: \(x^3+y^3-xy^2-x^2y\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2-xy+y^2\right)-xy\left(x+y\right)\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2-2xy+y^2\right)\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)\cdot\left(x-y\right)^2\)
e: Ta có: \(4x^2+4x-3\)
\(=4x^2+6x-2x-3\)
\(=2x\left(2x+3\right)-\left(2x+3\right)\)
\(=\left(2x+3\right)\left(2x-1\right)\)
f: Ta có: \(9x^4+16x^2-4\)
\(=9x^4+18x^2-2x^2-4\)
\(=9x^2\left(x^2+2\right)-2\left(x^2+2\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+2\right)\left(9x^2-2\right)\)
g: Ta có: \(-6x^2+5xy+4y^2\)
\(=-6x^2+8xy-3xy+4y^2\)
\(=-2x\left(3x-4y\right)-y\left(3x-4y\right)\)
\(=\left(3x-4y\right)\left(-2x-y\right)\)
h: Ta có: \(\left(x^2+4x\right)^2+8\left(x^2+4x\right)+15\)
\(=\left(x^2+4x\right)^2+3\left(x^2+4x\right)+5\left(x^2+4x\right)+15\)
\(=\left(x^2+4x+3\right)\cdot\left(x^2+4x+5\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+4x+5\right)\)
1,x=2
2,x=2
hk tốt
32 = 9
24 = 16