Giải giúp e vs ạ
E cần gấp
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1. Những cây sẵn trong tự nhiên, tự bản thân nó được dùng để trang trí: cây hoa (hoa hồng, hoa cẩm chướng..), cây tùng, cây sanh.
2. Phương pháp sinh sản vô tính: giâm cành bằng cát, ghép, chiết cành, nuôi cấy mô tế bào.
phương pháp sinh sản hữu tính: thụ phấn trong tự nhiên.
3. chọn chậu cây cảnh dựa trên các yếu tố: chất liệu, kích thước,
4. tránh hư hỏng do va đập cơ học
5. Sử dụng axit abxixic để ức chế sinh trưởng.
6. kỹ thuật sản xuất, an toàn thực phẩm, môi trường làm việc đảm bảo, nguồn gốc sản phẩm rõ ràng.

\(\dfrac{\sin\alpha}{\cos\alpha}=\dfrac{AC}{BC}:\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{AC}{AB}=\tan\alpha\)
\(\dfrac{\cos\alpha}{\sin\alpha}=\dfrac{AB}{BC}:\dfrac{AC}{BC}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}=\cot\alpha\)
\(\tan\alpha\cot\alpha=\dfrac{AC}{AB}\cdot\dfrac{AB}{AC}=1\)
\(\sin^2\alpha+\cos^2\alpha=\dfrac{AC^2}{BC^2}+\dfrac{AB^2}{BC^2}=\dfrac{AB^2+AC^2}{BC^2}=\dfrac{BC^2}{BC^2}=1\left(pytago\right)\)

Câu 4:
a) nC2H6O=0,3(mol)
PTHH: C2H6O + 3 O2 -to-> 2 CO2 + 3 H2O
0,3___________0,9_____0,6(mol)
=>V(CO2,đktc)=0,6 x 22,4= 13,44(l)
b) V(kk,dktc)=V(O2,dktc) . 100/20 = (0,9.22,4).5=100,8(l)
Câu 5:
C2H6O + 3 O2 -to-> 2 CO2 + 3 H2O
nH2O=0,9(mol)
=> nCO2= 2/3. 0,9=0,6(mol)
a) V(CO2,đktc)=0,6.22,4=13,44(l)
b) Vkk=5.V(O2,dktc)= 5.(0,9.22,4)= 100,8(l)

Bài 1:
1: \(\sqrt{3+2\sqrt{2}}=\sqrt{2}+1\)
2: \(\sqrt{5-2\sqrt{6}}=\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{2}\)
3: \(\sqrt{11-2\sqrt{30}}=\sqrt{6}-\sqrt{5}\)
4: \(\sqrt{7-2\sqrt{10}}=\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{2}\)

g: \(=\dfrac{x^2+2x-x^2-4x-2x+4}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{-4x+4}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
h: \(=\dfrac{2x^2+1-x^2+1-x^2+x-1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x^2-x+1}\)
\(e,=\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-2x+1}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{x^2+1}\\ f,=\dfrac{3x-1}{2\left(3x+1\right)}+\dfrac{3x+1}{2\left(3x-1\right)}-\dfrac{6x}{\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{9x^2-6x+1+9x^2+6x+1-12x}{2\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(3x-1\right)^2}{2\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)}=\dfrac{3x-1}{3x+1}\)
\(g,=\dfrac{x}{x\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{x^2+4x}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{2}{x\left(x+2\right)}\\ =\dfrac{x^2+2x-x^2-4x-2x+4}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{-4x+4}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\\ h,=\dfrac{2x^2+1-x^2+1-x^2+x-1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x^2-x+1}\)

1) \(\sqrt{2x-5}=7\)
\(\left(\sqrt{2x-5}\right)^2=7^2\)
\(2x-5=49\)
\(2x=54\)
\(x=27\)
2) \(3+\sqrt{x-2}=4\)
\(\sqrt{x-2}=1\)
\(\left(\sqrt{x-2}\right)^2=1^2\)
\(x-2=1\)
\(x=3\)
1) \(\sqrt{2x-5}=7\left(đk:x\ge\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-5=49\Leftrightarrow2x=54\Leftrightarrow x=27\left(tm\right)\)
2) \(3+\sqrt{x-2}=4\left(đk:x\ge2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-2}=1\Leftrightarrow x-2=1\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
3) \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)^2}=1\Leftrightarrow\left|x-1\right|=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=1\\x-1=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
4) \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2}=1\Leftrightarrow\left|x-2\right|=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=1\\x-2=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
5) \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(2x-1\right)^2}=\sqrt{\left(x+4\right)^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-1\right|=\left|x+4\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=x+4\\2x-1=-x-4\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
6) \(ĐK:x\ge-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\sqrt{x+2}-3\sqrt{x+2}-\sqrt{x+2}=\sqrt{x+7}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+2}=\sqrt{x+7}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2=x+7\Leftrightarrow2=7\left(VLý\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\varnothing\)
7) \(ĐK:x\ge-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\sqrt{2x+1}+3\sqrt{x+1}=4\sqrt{x+1}+4\sqrt{2x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x+1}=\sqrt{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+1=x+1\Leftrightarrow x=0\left(tm\right)\)

Xet tam giac BDC va tam giac CEB ta co
^BDC = ^CEB = 900
BC _ chung
^BCD = ^CBE ( gt )
=> tam giac BDC = tam giac CEB ( ch - gn )
=> ^DBC = ^ECB ( 2 goc tuong ung )
Ta co ^B - ^DBC = ^ABD
^C - ^ECB = ^ACE
=> ^ABD = ^ACE
Xet tam giac IBE va tam giac ICD
^ABD = ^ACE ( cmt )
^BIE = ^CID ( doi dinh )
^BEI = ^IDC = 900
Vay tam giac IBE = tam giac ICD (g.g.g)
c, Do BD vuong AC => BD la duong cao
CE vuong BA => CE la duong cao
ma BD giao CE = I => I la truc tam
=> AI la duong cao thu 3
=> AI vuong BC

 Giải giúp e vs ạ ,e đang cần gấp
Giải giúp e vs ạ ,e đang cần gấp
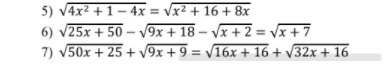
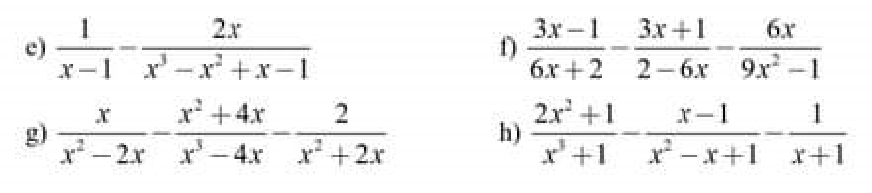


cos2x - (2m + 1)cosx + m + 1 = 0
⇔ 2cos2x - (2m + 1).cosx = 0
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx=0\left(1\right)\\2cosx=2m+1\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
(1) ⇔ \(x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\) với k thuộc Z. Mà \(x\in\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2};2\pi\right)\)
⇒ x = \(\dfrac{3\pi}{2}\)
Như vậy đã có 1 nghiệm trên \(\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2};2\pi\right)\) đó là x = \(\dfrac{3\pi}{2}\). Bây giờ cần tìm m để (2) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt trên \(\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2};2\pi\right)\) và trong 2 nghiệm đó không có nghiệm x = \(\dfrac{3\pi}{2}\). Tức là x = \(\dfrac{3\pi}{2}\) không thỏa mãn (2), tức là
2m + 1 ≠ 0 ⇔ \(m\ne-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
(2) ⇔ \(2.\left(2cos^2\dfrac{x}{2}-1\right)=2m+1\)
⇔ \(4cos^2\dfrac{x}{2}=2m+3\)
Do x \(\in\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2};2\pi\right)\) nên \(\dfrac{x}{2}\in\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4};\pi\right)\) nên cos\(\dfrac{x}{2}\) ∈ \(\left(-1;\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)\)
Đặt cos\(\dfrac{x}{2}\) = t ⇒ t ∈ \(\left(-1;\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)\). Ta được phương trình : 4t2 = 2m + 3
Cần tìm m để [phương trình được bôi đen] có 2 nghiệm t ∈ \(\left(-1;\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)\)
Dùng hàm số bậc 2 là ra. Nhớ kết hợp điều kiện \(m\ne-\dfrac{1}{2}\)