Cho \(K=\left|x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right|+\dfrac{3}{4}-x.\) Tìm min (max) của K.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


|x-1/2| =x-1/2 khi x >= 1/2
=> Min K =1/4 khi x>=1/2
không có max

a) đk: x\(\ge0\);
P = \(\left[\dfrac{x+2}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(x-\sqrt{x}+1\right)}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+1}\right].\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}}{3}\)
= \(\dfrac{x+2-x+\sqrt{x}-1}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(x-\sqrt{x}+1\right)}.\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}}{3}\)
= \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(x-\sqrt{x}+1\right)}.\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}}{3}=\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}}{3\left(x-\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
b) Để P = \(\dfrac{8}{9}\)
<=> \(\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}}{3\left(x-\sqrt{x}+1\right)}=\dfrac{8}{9}\)
<=> \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{x-\sqrt{x}+1}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
<=> \(\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}-2x+2\sqrt{x}-2}{3\left(x-\sqrt{x}+1\right)}=0\)
<=> \(-2x+5\sqrt{x}-2=0\)
<=> \(\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(2\sqrt{x}-1\right)=0\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
c)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x}=a\) (\(a\ge0\))
P = \(\dfrac{4a}{3\left(a^2-a+1\right)}\)
Xét P + \(\dfrac{4}{9}\) = \(\dfrac{4a}{3a^2-3a+3}+\dfrac{4}{9}=\dfrac{12a+4a^2-4a+4}{9\left(a^2-a+1\right)}=\dfrac{4a^2+8a+4}{9\left(a^2-a+1\right)}=\dfrac{4\left(a+1\right)^2}{9\left(a^2-a+1\right)}\ge0\)
Dấu "=" <=> a = -1 (loại)
=> Không tìm được Min của P
Xét P - \(\dfrac{4}{3}\) = \(\dfrac{4a}{3\left(a^2-a+1\right)}-\dfrac{4}{3}=\dfrac{4a-4a^2+4a-4}{3\left(a^2-a+1\right)}=\dfrac{-4a^2+8a-4}{3\left(a^2-a+1\right)}=\dfrac{-4\left(a-1\right)^2}{3\left(a^2-a+1\right)}\le0\)
<=> \(P\le\dfrac{4}{3}\)
Dấu "=" <=> a = 1 <=> x = 1 (tm)

ĐK: Biểu thức xác định với mọi `x`.
`y_(min) <=> (\sqrt(2-cos(x-π/6))+3)_(max) <=> (cos(x-π/6))_(max)`
`<=> cos(x-π/6)=1 <=> x-π/6=k2π <=> x = π/6+k2π ( k \in ZZ)`.
`=> y_(min) = 1`
`y_(max) <=> (\sqrt(2-cos(x-π/6))+3)_(min) <=> (cos(x-π/6))_(min)`
`<=> cos(x-π/6)=-1 <=> x -π/6= π+k2π <=> x = (7π)/6+k2π (k \in ZZ)`
`=> y_(max) = (6-2\sqrt3)/3`.

a: ĐKXĐ: x<>1; x<>2; x<>3
\(K=\left(\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{x^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{x^4+2x^2+1-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3-x^2+x^3-3x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x^2+1+x\right)\left(x^2+1-x\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^3-4x^2}{\left(x-2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{1}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x^4+x^2+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2}{x^4+x^2+1}\)
b:
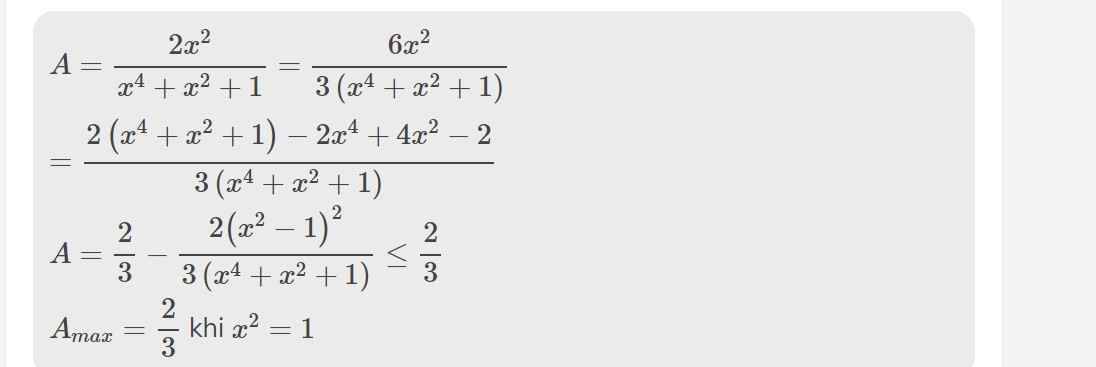

1, \(y=2-sin\left(\dfrac{3x}{2}+x\right).cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\)
\(y=2-\left(-cosx\right).\left(-sinx\right)\)
y = 2 - sinx.cosx
y = \(2-\dfrac{1}{2}sin2x\)
Max = 2 + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = 2,5
Min = \(2-\dfrac{1}{2}\) = 1,5
2, y = \(\sqrt{5-\dfrac{1}{2}sin^22x}\)
Min = \(\sqrt{5-\dfrac{1}{2}}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
Max = \(\sqrt{5}\)
Lời giải:
\(\bullet\)Nếu \(x\geq \frac{1}{2}\Rightarrow K=x-\frac{1}{2}+\frac{3}{4}-x=\frac{1}{4}\)
\(\bullet\) Nếu \(x<\frac{1}{2}\Rightarrow K=\frac{1}{2}-x+\frac{3}{4}-x=\frac{5}{4}-2x\)
Vì \(x<\frac{1}{2}\Rightarrow \frac{5}{4}-2x>\frac{5}{4}-1=\frac{1}{4}\)
Do đó \(K_{\min}=\frac{1}{4}\)
Hàm hiển nhiên không có max. Xét hàm \(\frac{5}{4}-2x\), với giá trị của \(x<\frac{1}{2}\), càng nhỏ thì $K$ càng lớn đến dương vô cùng.
TH1:Nếu x-\(\dfrac{1}{2}=0\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\)K=\(\left|\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}\right|+\dfrac{3}{4}-\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
TH2:Nếu x-\(\dfrac{1}{2}>0\Rightarrow x>\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow\left|x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right|=x-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow K=x-\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{3}{4}-x=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
TH3:Nếu \(x-\dfrac{1}{2}< 0\Rightarrow x< \dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow\left|x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right|=\dfrac{1}{2}-x\)
\(\Rightarrow K=\dfrac{1}{2}-x+\dfrac{3}{4}-x\)
\(\Rightarrow K=\dfrac{5}{4}-2x< \dfrac{1}{4}\)
Vậy Max K=\(\dfrac{1}{4}\Leftrightarrow x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\)