Tìm giá trị của x thuộc Z để biểu thức có giá trị nguyên
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Để biểu thức nguyên thì \(3⋮\sqrt{x}+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=1\)
hay x=1

\(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}+2}\in Z< =>\sqrt{x}+2\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\)
mà \(x>0=>\sqrt{x}+2>2\) nên \(\sqrt{x}+2=\left\{3\right\}=>x=1\left(tm\right)\)
Vaayy.....
Để biểu thức \(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}+2}\) nguyên thì \(3⋮\sqrt{x}+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=1\)
hay x=1

10 chia hết cho n-2 => n -2 E Ư(10) cò n lại tự tí nh ha

\(A=12-\dfrac{5}{x+1}\in Z\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{x+1}\in Z\Leftrightarrow5⋮x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow x+1\inƯ\left(5\right)=\left\{-5;-1;1;5\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-6;-2;0;4\right\}\)

a) Ta có: \(M=\dfrac{8x+1}{4x-5}=\dfrac{8x-10+11}{4x-5}=\dfrac{2\left(x-5\right)+11}{4x-5}=2+\dfrac{11}{4x-5}\)
Để M nhận giá trị nguyên thì \(2+\dfrac{11}{4x-5}\) nhận giá trị nguyên
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{11}{4x-5}\) nhận giá trị nguyên
\(\Rightarrow11⋮4x-5\)
Vì \(x\in Z\) nên \(4x-5\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow4x-5\inƯ\left(11\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm11\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{1;\pm1,5;4\right\}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{1;4\right\}\) thỏa mãn \(x\in Z\).
b) Ta có: \(A=\dfrac{5}{4-x}\). ĐK: \(x\ne4\)
Nếu 4 - x < 0 thì x > 4 \(\Rightarrow A>0\)
4 - x > 0 thì x < 4 \(\Rightarrow A< 0\)
Để A đạt GTLN thì 4 - x là số nguyên dương nhỏ nhất
\(\Rightarrow4-x=1\Rightarrow x=3\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{5}{4-3}=5\)
Vậy MaxA = 5 tại x = 3
c) \(B=\dfrac{8-x}{x-3}\). ĐK: \(x\ne3\).
Ta có: \(B=\dfrac{8-x}{x-3}=\dfrac{-\left(x-8\right)}{x-3}=\dfrac{-\left(x-3\right)+5}{x-3}=\dfrac{5}{x-3}-1\)
Để B đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất thì \(\dfrac{5}{x-3}-1\) nhỏ nhất
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{x-3}\) nhỏ nhất
Nếu x - 3 > 0 thì x > 3 \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{x-3}>0\)
x - 3 < 0 thì x < 3 \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{x-3}< 0\)
Để \(\dfrac{5}{x-3}\) nhỏ nhất thì x - 3 là số nguyên âm lớn nhất
\(\Rightarrow x-3=-1\Rightarrow x=2\)
\(\Rightarrow B=\dfrac{8-2}{2-3}=-6\)
Vậy MaxB = -6 tại x = 2.
Mình làm sai câu a...
Ta có: \(M=\dfrac{8x+1}{4x-1}=\dfrac{8x-2+3}{4x-1}=\dfrac{2\left(4x-1\right)+3}{4x-1}=2+\dfrac{3}{4x-1}\)
Để M nhận giá trị nguyên thì \(2+\dfrac{3}{4x-1}\) nhận giá trị nguyên
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{3}{4x-1}\) nhận giá trị nguyên
Vì \(4x-1\in Z\) nên \(4x-1\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{\pm0,5;0;1\right\}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{0;1\right\}\) thỏa mãn \(x\in Z\).

Để A nguyên thì \(2\sqrt{x}+3⋮3\sqrt{x}-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6\sqrt{x}+9⋮3\sqrt{x}-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x}-1\in\left\{-1;1;11\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x}\in\left\{0;12\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{0;16\right\}\)

ta có: \(M=\frac{x^2-5}{x^2-2}=\frac{x^2-2-3}{x^2-2}=1-\frac{3}{x^2-2}\)
Để M có giá trị nguyên
=> 3/x^2 - 2 thuộc Z
=> 3 chia hết cho x^2 - 2
=> x^2-2 thuộc Ư(3)={1;-1;3;-3}
nếu x^2-2 = 1 => x^2 = 3 \(\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{3};x=-\sqrt{3}\) (Loại)
x^2-2 = -1 => x^2 = 1 => x = 1 hoặc x = -1 (TM)
x^2-2 = 3 => x^2 = 5 \(\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{5};x=-\sqrt{5}\) (Loại)
x^2-2 = -3 => x^2 = -1 => không tìm được x
KL:...
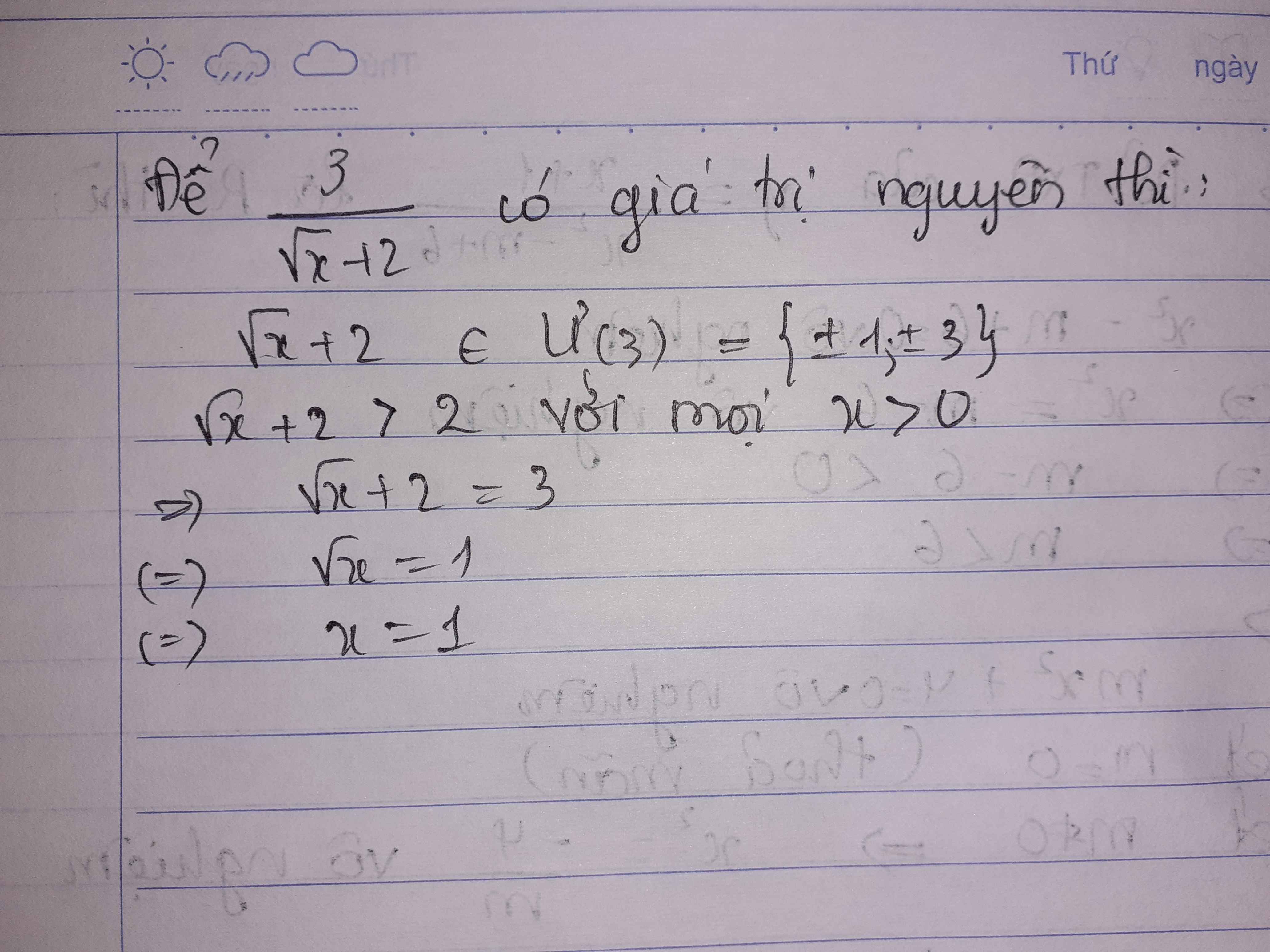
x=1
Đặt A = \(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)
Để A \(\in Z\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}+2}\in z\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\inƯ\left(3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\in\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\)
Ta có bẳng sau:
Vậy \(x=1\) thỏa mãn