Vẽ đồ thị của hàm số :
\(y=\left|\dfrac{2}{3}x^2-\dfrac{8}{3}x+2\right|\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: Bảng giá trị:
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| \(y=3^x\) | 3 | 9 | 27 |
Vẽ đồ thị:
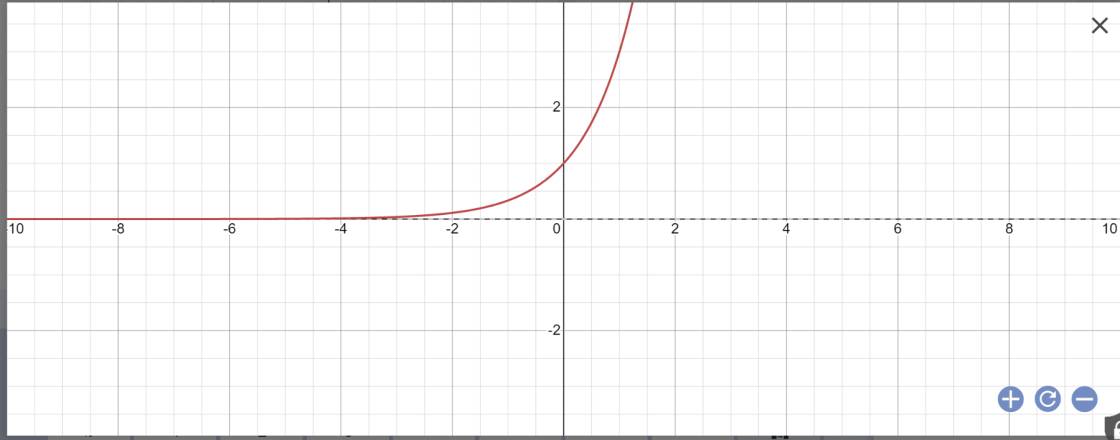
b: Bảng giá trị:
| x | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| \(y=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^x\) | 1/4 | 1/8 | 1/16 |
vẽ đồ thị:
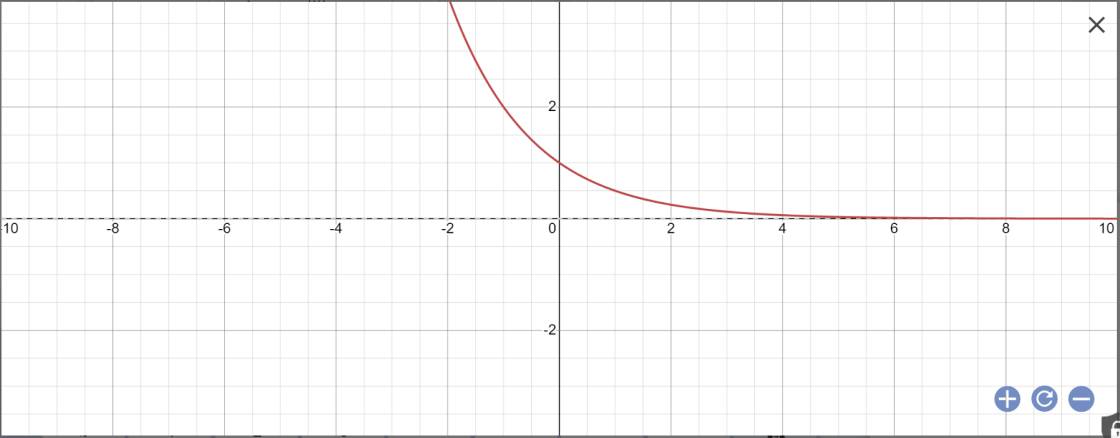

Bài 1:
a: Thay x=-2 và y=2 vào hàm số, ta được:
4a=2
hay a=1/2
Bài 2:
a: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+5y=3\\4x-12y=20\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}17y=-17\\x-3y=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\3y=x-5=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x}=1\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{5}=\dfrac{3}{10}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left(x,y\right)=\left(2;\dfrac{10}{3}\right)\)

a: Thay x=1 vào \(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}x\), ta được:
\(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot1=-\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Vậy: \(A\left(1;-\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\) thuộc đồ thị hàm số y=-5/2x
b: Thay x=2 vào \(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}x\), ta được:
\(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot2=-5\)
=>B(2;-5) thuộc đồ thị hàm số y=-5/2x
Thay x=3 vào y=-5/2x, ta được:
\(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot3=-\dfrac{15}{2}\)<>7
=>\(C\left(3;7\right)\) không thuộc đồ thị hàm số y=-5/2x
Thay x=1 vào y=-5/2x, ta được:
\(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot1=-\dfrac{5}{2}\)<>5/2
=>\(D\left(1;\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\) không thuộc đồ thị hàm số \(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}x\)
Thay x=0 vào \(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}x\), ta được:
\(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot0=0\)<>4
=>E(0;4) không thuộc đồ thị hàm số \(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}x\)



nên từ đồ thị (C) ta suy ra ngay đồ thị của hàm số :
\(y=\left|\dfrac{x^3}{6}+\dfrac{3x^2}{2}+\dfrac{5x}{2}\right|\) là hình 18


Hàm số \(y=\sqrt{3-m}\left(x+5\right)\) là hàm số bậc nhất khi \(\sqrt{3-m}\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3-m\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ne3\)
Tọa độ giao điểm của hai đồ thị hàm số \(y=\dfrac{1}{2}x-2\) và \(y=\dfrac{3}{2}x-2\) là nghiệm của hệ phương trình:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2}x-2=\dfrac{3}{2}x-2\\y=\dfrac{1}{2}x-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2}x-2-\dfrac{3}{2}x+2=0\\y=\dfrac{1}{2}x-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x=0\\y=\dfrac{1}{2}x-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot0-2=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Hai đồ thị hàm số \(y=\dfrac{1}{2}x-2\) và \(y=\dfrac{3}{2}x-2\) có tọa độ giao điểm là (0;-2)
\(y=\sqrt{3-m}.\left(x+5\right)\) là hàm số bậc nhất \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{3-m}\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne3\)
Lập PT hoành độ ta có:
\(\dfrac{1}{2}x-2=\dfrac{3}{2}x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{2}.0-2=-2\)
=> Tọa độ (0;-2)
Xác định các điểm parapol
\(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}\left(x^2-4x+3\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}\left(x-2\right)^2-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(1< x< 3\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)< 0\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le1\\x\ge3\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\ge0\)
\(\left|f\left(x\right)\right|=\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(x\right)\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le1\\x\ge1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\\-f\left(x\right)khi\left\{1< x< 3\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\)
*. đỉnh GTNN.P(2,-2/3)
.Giao với trục hoành A(1,0); B(3,0)
Giao trục tung C(0,2)
Vẽ