(x-1)*(x-2)=0;
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a, (\(x-2\))2 - (2\(x\) + 3)2 = 0
(\(x\) - 2 - 2\(x\) - 3)(\(x\) - 2 + 2\(x\) + 3) = 0
(-\(x\) - 5)(3\(x\) +1) = 0
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}-x-5=0\\3x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\3x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\) { -5;- \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)}
b, 9.(2\(x\) + 1)2 - 4.(\(x\) + 1)2 = 0
{3.(2\(x\) + 1) - 2.(\(x\) +1)}{ 3.(2\(x\) +1) + 2.(\(x\) +1)} = 0
(6\(x\) + 3 - 2\(x\) - 2)(6\(x\) + 3 + 2\(x\) + 2) = 0
(4\(x\) + 1)(8\(x\) + 5) =0
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x+1=0\\8x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{4}\\x=-\dfrac{5}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
S = { - \(\dfrac{5}{8}\); \(\dfrac{-1}{4}\)}
d, \(x^2\)(\(x\) + 1) - \(x\) (\(x+1\)) + \(x\)(\(x\) -1) = 0
\(x\left(x+1\right)\).(\(x\) - 1) + \(x\)(\(x\) -1) = 0
\(x\)(\(x\) -1)(\(x\) + 1 + 1) = 0
\(x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\) = 0
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-1=0\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
S = { -2; 0; 1}

a) 4x(x+1)=8(x+1)
<=>4x(x+1)-8(x+1)=0
<=>(4x-8)(x+1)=0
<=>\(\left[\begin{array}{} 4x-8=0\\ x+1=0 \end{array} \right.\)
<=>\(\left[\begin{array}{} x=2\\ x=-1 \end{array} \right.\)
Vậy...
b)x(x-1)-2(1-x)=0
<=>(x+2)(x-1)=0
<=>\(\left[\begin{array}{} x+2=0\\ x-1=0 \end{array} \right.\)
<=>\(\left[\begin{array}{} x=-2\\ x=1 \end{array} \right.\)
Vậy...
c)5x(x-2)-(2-x)=0
<=>(5x+1)(x-2)=0
<=>\(\left[\begin{array}{} 5x+1=0\\ x-2 \end{array} \right.\)
<=>\(\left[\begin{array}{} x=-1/5\\ x=2 \end{array} \right.\)
d)5x(x-200)-x+200=0
<=>(5x-1)(x-200)=0
<=>\(\left[\begin{array}{} 5x-1=0\\ x-200=0 \end{array} \right.\)
<=>\(\left[\begin{array}{} x=1/5\\ x=200 \end{array} \right.\)
e)\(x^3+4x=0 \)
\(\Leftrightarrow x(x^2+4)=0 \)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{array}{} x=0\\ x^2+4=0 (loại vì x^2+4>=0 với mọi x) \end{array} \right.\)
Vậy x=0
f)\((x+1)=(x+1)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (x+1)-(x+1)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (x+1)(1-x-1)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (x+1)(-x)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{array}{} x=-1\\ x=0 \end{array} \right.\)
Vậy....

a) \(2{x^2} + 3x + 1 \ge 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = 2{x^2} + 3x + 1\) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x = - 1,x = \frac{{ - 1}}{2}\)
hệ số \(a = 2 > 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:
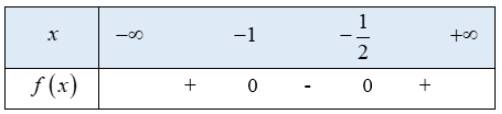
Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x \le - 1\\x \ge - \frac{1}{2}\end{array} \right.\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\left( { - \infty ; - 1} \right] \cup \left[ { - \frac{1}{2}; + \infty } \right)\)
b) \( - 3{x^2} + x + 1 > 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = - 3{x^2} + x + 1\) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x = \frac{{1 - \sqrt {13} }}{6},x = \frac{{1 + \sqrt {13} }}{6}\)
Hệ số \(a = - 3 < 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:

Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) > 0\)\( \Leftrightarrow \frac{{1 - \sqrt {13} }}{6} < x < \frac{{1 + \sqrt {13} }}{6}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\left( {\frac{{1 - \sqrt {13} }}{6};\frac{{1 + \sqrt {13} }}{6}} \right)\)
c) \(4{x^2} + 4x + 1 \ge 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = 4{x^2} + 4x + 1\) có nghiệm duy nhất \(x = \frac{{ - 1}}{2}\)
hệ số \(a = 4 > 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:

Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow x \in \mathbb{R}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\mathbb{R}\)
d) \( - 16{x^2} + 8x - 1 < 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = - 16{x^2} + 8x - 1\) có nghiệm duy nhất \(x = \frac{1}{4}\)
hệ số \(a = - 16 < 0\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu f(x) như sau:
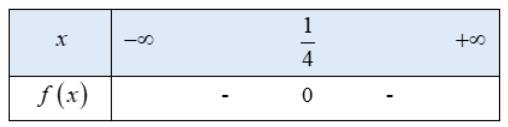
Từ bảng xét dấu ta thấy \(f\left( x \right) < 0 \Leftrightarrow x \ne \frac{1}{4}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(\mathbb{R}\backslash \left\{ {\frac{1}{4}} \right\}\)
e) \(2{x^2} + x + 3 < 0\)
Ta có \(\Delta = {1^2} - 4.2.3 = - 23 < 0\) và có \(a = 2 > 0\)
Sử dụng định lí về dấu của tam thức bậc hai, ta thấy tập hợp những giá trị của x sao cho \(2{x^2} + x + 3\) mang dấu “-” là \(\emptyset \)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \(2{x^2} + x + 3 < 0\) là \(\emptyset \)
g) \( - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5 < 0\)
Tam thức bậc hai \(f\left( x \right) = - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5\) có \(\Delta ' = {2^2} - \left( { - 3} \right).\left( { - 5} \right) = - 11 < 0\) và có \(a = - 3 < 0\)
Sử dụng định lí về dấu của tam thức bậc hai, ta thấy tập hợp những giá trị của x sao cho \( - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5\) mang dấu “-” là \(\mathbb{R}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \( - 3{x^2} + 4x - 5 < 0\) là \(\mathbb{R}\)

a) Ta có: \(x^2-2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\)hay x=1
Vậy: S={1}
c) Ta có: \(x+x^4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^3+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2-x+1>0\forall x\)
nên x(x+1)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={0;-1}

Giúp luôn Đức Hải Nguyễn câu e:
e, (x - 1)2 + 2(x - 1)(x + 2) + (x + 2)2 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) (x - 1 + x + 2)2 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) (2x + 1)2 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 2x + 1 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x = \(\frac{-1}{2}\)
Vậy S = {\(\frac{-1}{2}\)}
Chúc bn học tốt!!
a) (x - 3)(5 - 2x) = 0
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\5-2x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=\frac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) (x + 5)(x - 1) - 2x(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x - 1)(x + 5 - 2x) = 0
<=> (x - 1)(5 - x) = 0
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\5-x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) 5(x + 3)(x - 2) - 3(x + 5)(x - 2) = 0
<=> (x - 2)[5(x + 3) - 3(x + 5)] = 0
<=> (x - 2)(5x + 3 - 3x - 15) = 0
<=> (x - 2)(2x - 12) = 0
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\2x-12=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) (x - 6)(x + 1) - 2(x + 1) = 0
<=> (x + 1)(x - 6 - 2) = 0
<=> (x + 1)(x - 8) = 0
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\x-8=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
Câu e thì để mình nghĩ đã :)
#Học tốt!

a)\(\left(x-2\right)^2-\left(2x+3\right)^2=0\Rightarrow\left(x-2+2x+3\right)\left(x-2-2x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(-x-5\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+1=0\\-x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
b)\(9\left(2x+1\right)^2-4\left(x+1\right)^2=0\Rightarrow\left[3\left(2x+1\right)+2\left(x+1\right)\right]\left[3\left(2x+1\right)-2\left(x+1\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[8x+5\right]\left[4x+1\right]=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}8x+5=0\\4x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{5}{8}\\x=\dfrac{1}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c)\(x^3-6x^2+9x=0\Rightarrow x\left(x^2-6x+9\right)=0\Rightarrow x\left(x-3\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) \(x^2\left(x+1\right)-x\left(x+1\right)+x\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-1\right)+x\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+x\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x-1\right)\left[\left(x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)+1\right]=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x-1\right)\left[\left(x+1\right)^2+1\right]=0\)
Do \(\left(x+1\right)^2+1>0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x-1\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

1) Do x ∈ Z và 0 < x < 3
⇒ x ∈ {1; 2}
2) Do x ∈ Z và 0 < x ≤ 3
⇒ x ∈ {1; 2; 3}
3) Do x ∈ Z và -1 < x ≤ 4
⇒ x ∈ {0; 1; 2; 3; 4}

1)x^2-2x-1=0
<=> (x^2-2x+1)-2=0
<=>(x-1)2 =2
=>x-1 = \(\pm\sqrt{2}\)
=> x= \(\pm\sqrt{2}\) +1
2) x^2-x-1=0
<=> (x^2-x+1/4) -5/4=0
<=>(x+1/2)2= 5/4
=> x+1/2 = \(\pm\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{4}}\)
=>x=\(\pm\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{4}}\) - 1/2
3)x^2+x-3=0
<=> (x^2 + x + 1/4) -13/4=0
<=>(x+1/2)2 = 13/4
=> x+1/2 = \(\sqrt{\dfrac{13}{4}}\)
=> x= \(\sqrt{\dfrac{13}{4}}\) -1/2
4) 4x^2-4x-1=0
<=> (4x^2-4x+1)-2=0
<=>(2x-1)2 -2=0
<=> (2x-1)2 - \(\left(\sqrt{2}\right)^2\) =0
<=> (2x-1 - \(\sqrt{2}\) ) . (2x-1 +\(\sqrt{2}\) )=0
=> 2x-1-\(\sqrt{2}\) =0 hoặc 2x-1+\(\sqrt{2}\) =0
=> 2x= 1+\(\sqrt{2}\) hoặc 2x= 1 - \(\sqrt{2}\)
=> x=\(\dfrac{1+\sqrt{2}}{2}\) hoặc x=\(\dfrac{1-\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
\(\left(x-1\right).\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1=0\) hoặc \(x-2=0\)
+) \(x-1=0\Rightarrow x=1\)
+) \(x-2=0\Rightarrow x=2\)
Vậy \(x=1\) hoặc \(x=2\)
thanks nhé