Câu5: giải phương trình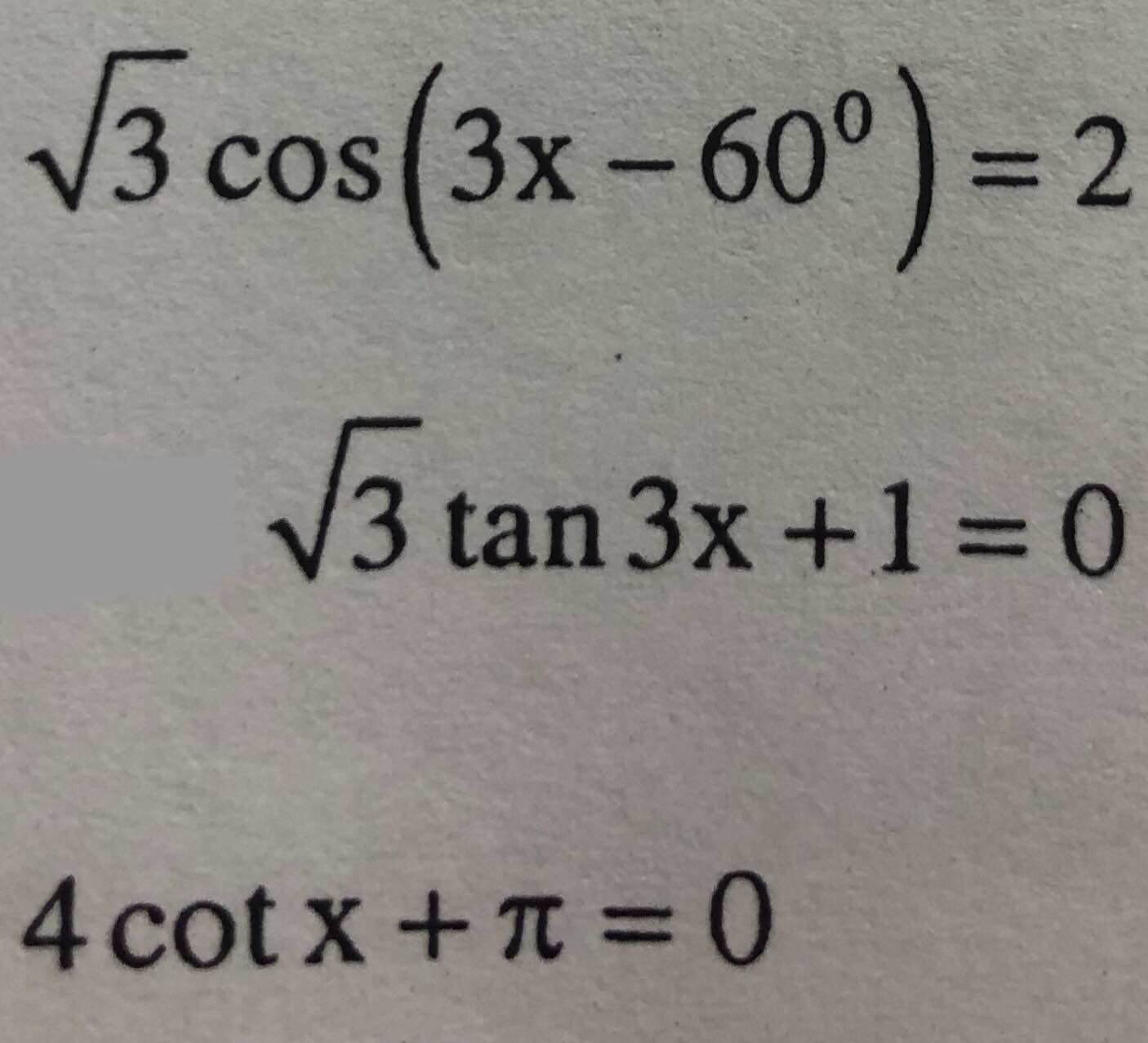
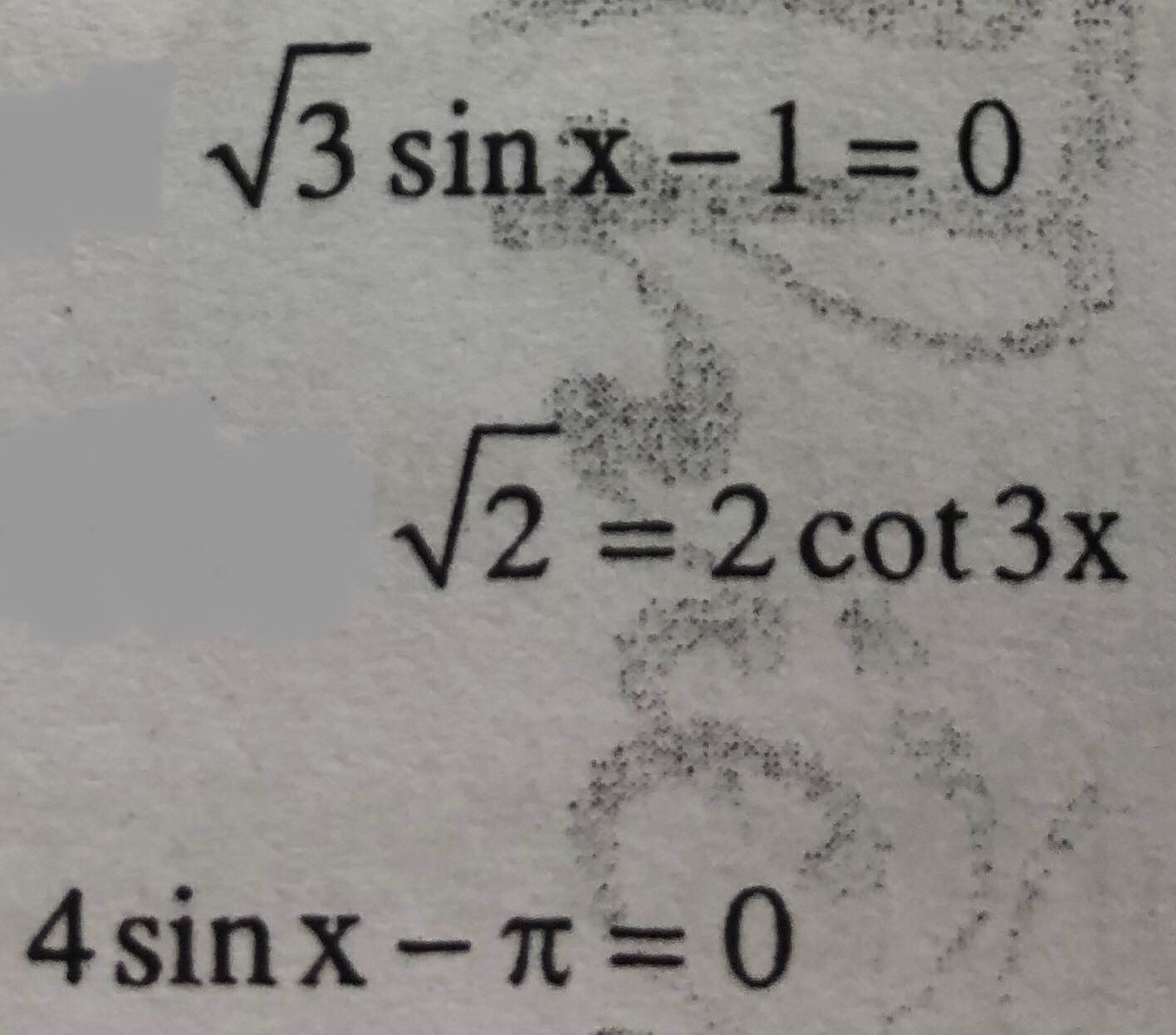
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Câu 1 : \(a,\hept{\begin{cases}4x+7y=16\left(1\right)\\4x-3y=-24\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
Lấy ( 1 ) trừ ( 2 ) ta được :
10y = 40
=> y = 4
Thay y = 4 vào ( 1 ) ta được :
4x + 7 x 4 = 16
=> 4x + 28 = 16
=> 4x = 16 - 28
=> 4x = - 12
=> x = - 3
Vậy x = - 3 ; y = 4
\(b,\hept{\begin{cases}3x+5y=1\\2x+y=-4\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}3x+5.\left(-4-2x\right)=1\\y=-4-2x\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}3x-20-10x=1\\y=-4-2x\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}-7x-20=1\\y=-4-2x\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}-7x=21\\y=-4-2x\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=-3\\y=-4-2.\left(-3\right)\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=-3\\y=2\end{cases}}\)

Câu 1 : \(a,\hept{\begin{cases}4x+7y=16\left(1\right)\\4x-3y=-24\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
Lấy ( 1 ) trừ ( 2 ) ta được :
10y = 40
=> y = 4
Thay y = 4 vào ( 1 ) ta được :
4x + 7 . 4 = 16
=> 4x + 28 = 16
=> 4x = 16 - 28
=> 4x = -12
=> x = - 3
Vậy x = - 3 ; y = 4
\(b,\hept{\begin{cases}3x+5y=1\\2x+y=-4\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}6x+10y=2\left(1\right)\\6x+3y=-12\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
Lấy ( 1 ) trừ ( 2 ) ta được :
7y = 14
=> y = 2
Thay y = 2 vào ( 1 )
Ta được : 6x + 10 . 2 = 2
=> 6x + 20 = 2
=> 6x = 2 - 20
=> 6x = - 18
=> x= - 3
Vậy x = - 3 ; y = 2

Theo đề bài ta có:
\(\dfrac{x-2}{2}+1=2156\Rightarrow\dfrac{x-2}{2}=2155\)
\(\Rightarrow x-2=2155\times2=4310\Rightarrow x=4310+2=4312\)

Câu 5:
a: 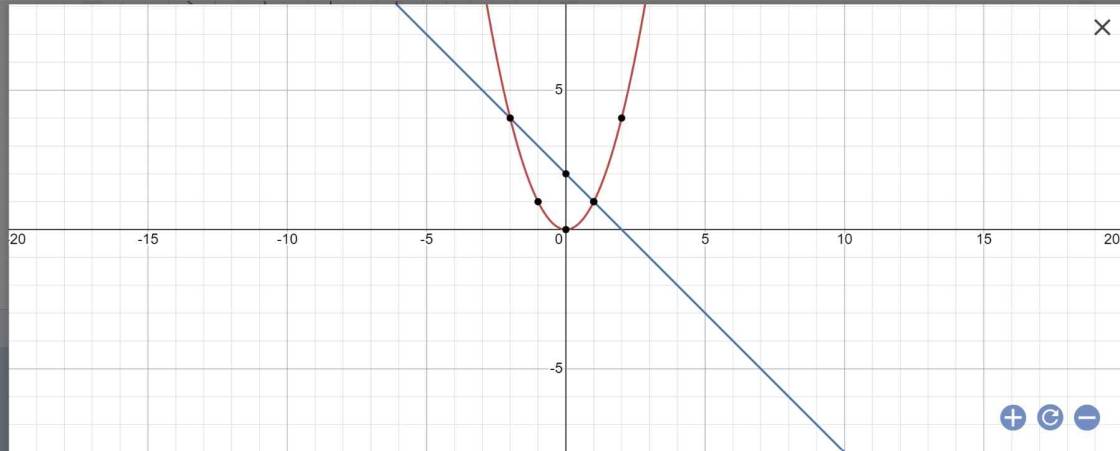
b: PTHĐGĐ là:
x^2+x-2=0
=>(x+2)(x-1)=0
=>x=-2 hoặc x=1
Khi x=-2 thì y=4
Khi x=1 thì y=1

ta có :
\(\left|x+1\right|+\left|x-1\right|=1+\left|\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-1\right|\left|x+1\right|-\left|x-1\right|-\left|x+1\right|+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\left|x-1\right|-1\right)\left(\left|x+1\right|-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left|x-1\right|=1\\\left|x+1\right|=1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-2,0,2\right\}\)

Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(2\left(3-4x\right)=10-\left(2x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-8x-10+2x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x+11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=-11\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{11}{6}\)
b) Ta có: \(3\left(2-4x\right)=11-\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-12x-11+3x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x=6\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
 câu5
câu5
a.
\(cos\left(3x-60^0\right)=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}>1\) (ktm)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm
b.
\(tan3x=-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{\pi}{18}+\dfrac{k\pi}{3}\)
c.
\(4cotx+\pi=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cotx=-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=arccot\left(-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)+k\pi\)
d.
\(\sqrt{3}sinx-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sinx=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=arcsin\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\right)+k2\pi\\x=\pi-arcsin\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\right)+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
e.
\(2cot3x=\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cot3x=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=arccos\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}arccot\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)+\dfrac{k\pi}{3}\)
f.
\(sinx=\dfrac{\pi}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=arcsin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)+k2\pi\\x=\pi-arcsin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)