Tìm x
x. 0,(2) + 0,(3) = 0,(77)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Lời giải:
PT $\Leftrightarrow (x^3-2x^2)+(x^2-4)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2(x-2)+(x-2)(x+2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x^2+x+2)=0$
$\Rightarrow x-2=0$ hoặc $x^2+x+2=0$
Nếu $x-2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2$ (tm)
Nếu $x^2+x+2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+\frac{1}{2})^2=-\frac{7}{4}<0$ (vô lý)
Vậy pt có nghiệm duy nhất $x=2$

\(x^3-2x^2+x-2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-2\right)+\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+1=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2=-1\left(vô.lí\right)\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\\ Vậy:x=2\\ ---\\ 2x\left(3x-5\right)=10-6x\\ \Leftrightarrow6x^2-10x-10+6x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow6x^2-4x-10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow6x^2+6x-10x-10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow6x\left(x+1\right)-10\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(6x-10\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}6x-10=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{3}\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(4-x=2\left(x-4\right)^2\\ \Leftrightarrow4-x=2\left(x^2-8x+16\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2-16x+32+x-4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2-15x+28=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2-8x-7x+28=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x\left(x-4\right)-7\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x-7\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-7=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\\ ---\\ 4-6x+x\left(3x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4-6x+3x^2-2x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3x^2-8x+4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3x^2-6x-2x+4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3x\left(x-2\right)-2\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-2=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\dfrac{-12}{25}.\left(\dfrac{3}{4}-x+\dfrac{6}{-11}-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)=0\)
\(\dfrac{3}{4}-x+\dfrac{-6}{11}-\dfrac{5}{6}=0\)
\(\dfrac{3}{4}-x+\dfrac{-91}{66}=0\)
\(\dfrac{3}{4}-x=0-\left(\dfrac{-91}{66}\right)\)
\(\dfrac{3}{4}-x=\dfrac{91}{66}\)
\(x=\dfrac{-83}{132}\)

a. (80x - 801) . 12 = 0
<=> 80x - 801 = 0
<=> 80x = 801
<=> x = \(\dfrac{801}{80}\)
(Mấy câu tiếp mik ko hiểu đề, bn viết lại để dễ hiểu hơn nhé)
c: Ta có: \(\overline{xxx}=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow100x+10x+1=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow101x=16\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{16}{101}\)

`x+1+2sqrtx<=0`
`<=>x+2sqrtx+1<=0`
`<=>(sqrtx+1)^2<=0`(vô lý)
Vì `sqrtx>=0=>sqrtx+1>=1`
`=>(sqrtx+1)^2>=1>0`
Mà đề bài cho `(sqrtx+1)^2<=0`
Vậy BPT vô nghiệm

a) \(x-452=77+48\)
\(=>x-452=125\)
\(=>x=125+452\)
\(=>x=577\)
____
b) \(x+58=64+58\)
\(=>x+58=122\)
\(=>x=122-58\)
\(=>x=64\)
_____
c) \(x-1-2-3-4=0\)
\(=>x-10=0\)
\(=>x=0+10\)
\(=>x=10\)

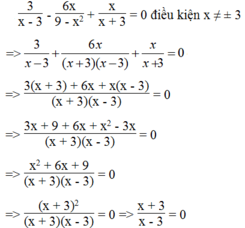
Biểu thức bằng 0 khi tử bằng 0 và mẫu khác 0
Ta có: x + 3 = 0 => x = -3 (không thỏa mãn điều kiện)
Vậy không có giá trị nào của x để biểu thức bằng 0.
\(x.0,\left(2\right)+0,\left(3\right)=0,\left(77\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x.\frac{2}{9}+\frac{3}{9}=\frac{7}{9}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{2x}{9}=\frac{7}{9}-\frac{3}{9}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{2x}{9}=\frac{4}{9}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=2\)
Vậy x = 2