Cho biểu thức A =(1/x-1 -2x/x3+x-x2-1):(1-2x/x2+1)
a/tìm điều kiện xác định và rút gọn A
b/tìm x để A<0
c/tìm các số nguyên x để A có giá trị nguyên
Giup1 mình bài này nhé bài này khó quá![]()
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) x ≠ 0 , x ≠ − 2
b) Ta có D = x 2 - 2x - 2.
c) Chú ý D = - x 2 - 2x - 2 = - ( x + 1 ) 2 - 1 ≤ -1. Từ đó tìm được giá trị lớn nhất của D = -1 khi x = -1.

\(a,A=\dfrac{x+1+2-2x+5-x}{\left(1-x\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(1-x\right)\left(x+1\right)}{2x-1}\left(x\ne1;x\ne-1;x\ne\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\\ A=\dfrac{8-2x}{2x-1}\\ b,A>0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{8-2x}{2x-1}>0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}8-2x>0\\2x-1>0\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}8-2x< 0\\2x-1< 0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 4\\x>\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>4\\x< \dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2}< x< 4\\x\in\varnothing\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}< x< 4\)

a) Ta có: x - 1 ≠ 0 ⇒ x ≠ 1
x2 - 1 = (x + 1)(x - 1) ≠ 0 ⇔ x ≠ -1 và x ≠ 1
x2 - 2x + 1 = (x - 1)2 ≠ 0 ⇔ x - 1 ≠ 0 ⇔ x ≠ 1
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ -1 và x ≠ 1

![]()
![]()
![]()
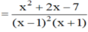

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
Ta có: \(A=\left(\dfrac{1}{2x-1}+\dfrac{3}{1-4x^2}-\dfrac{2}{2x+1}\right):\left(\dfrac{x^2}{2x^2+x}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}-\dfrac{3}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}-\dfrac{2\left(2x-1\right)}{\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)}\right):\left(\dfrac{x^2}{x\left(2x+1\right)}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{2x+1-3-4x+2}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}:\dfrac{x}{2x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2x}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{2x+1}{x}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2}{2x-1}\)
b) Ta có: \(\left|2x-1\right|=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=2\\2x-1=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=3\\2x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(nhận\right)\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\) vào biểu thức \(A=\dfrac{-2}{2x-1}\), ta được:
\(A=-2:\left(2\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}-1\right)=-2:\left(3-1\right)=-2:2=-1\)
Vậy: Khi \(\left|2x-1\right|=2\) thì A=-1
c) Để \(A=\dfrac{1}{3}\) thì \(\dfrac{-2}{2x-1}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1=-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-5\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\)(thỏa ĐK)
Vậy: Để \(A=\dfrac{1}{3}\) thì \(x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\)
a; \(A=\left(\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\right):\left(1-\dfrac{2x}{x^2+1}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-2x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}:\dfrac{x^2+1-2x}{x^2+1}=\dfrac{1}{x-1}\)
b: Để A<0 thì x-1<0
hay x<1
c: Để A nguyên thì \(x-1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{2;0\right\}\)