Tìm nghiệm của đa thức x^2 - x - 6
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Cho `f(x)=0`
`=>(x^2-2)(3x^4+6)=0`
Mà `3x^4+6 > 0 AA x`
`=>x^2=2`
`=>x^2=2`
`=>x=+-\sqrt{2}`
Vậy nghiệm của đa thức `f(x)` là `x=\sqrt{2}` hoặc `x=-\sqrt{2}`

\(f\left(x\right)=x2-7x+6\)
ta có f(x)=0
hay\(x2-7x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x2-7x=-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(-5\right)=-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{6}{5}\)
vậy nghiệm của đa thức f(x) là 6/5
\(f\left(x\right)=x^2-7x+6\)
\(f\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-7x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-6x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left(x-1\right)-6.\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right).\left(x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x-6=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}z=1\\x=6\end{cases}}\)
Vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(x=\left\{1,6\right\}\)

a) x2-x-6 =0
x2-3x+2x-6=0
(x2-3x)+(2x-6)=0
x(x-3)+2(x-3)=0
(x+2)(x-3)=0
=>x+2=0 hoặc x-3= 0
x = -2 x= 3
vậy x = -2 ,x= 3 là nghiệm của đa thức
b) 3x2+11x+6=0
3x2+9x+2x +6=0
3x(x+3)+2(x +3)=0
(3x+2)(x+3)=0
=> 3x+2=0 hoặc x+3=0
x = -2/3 x = -3
vậy x = -2/3 ,x = -3 là nghiệm của đa thức

Phân tích đa thức thành nhân tử thôi bạn :
Ta có :
\(h\left(x\right)=x^2+5x+6\)
\(h\left(x\right)=x\left(x+2\right)+3\left(x+2\right)\)
\(h\left(x\right)=\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow N_oh\left(x\right)=-2;-3\)
\(g\left(x\right)=2x^2+7x-9\)
\(g\left(x\right)=2x^2+9x-2x-9\)
\(g\left(x\right)=2x\left(x-1\right)+9\left(x-1\right)\)
\(g\left(x\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+9\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow N_og\left(x\right)=1;-4,5\)

a. cậu thu gọn bằng cách dùng t/c kết hợp và giao hoán
b. cậu thay từng giá vào biểu thức vừa được rút gọn để tìm
c. thì.... tớ ko biết

a: f(x)=3x^4+2x^3+6x^2-x+2
g(x)=-3x^4-2x^3-5x^2+x-6
b: H(x)=f(x)+g(x)
=3x^4+2x^3+6x^2-x+2-3x^4-2x^3-5x^2+x-6
=x^2-4
f(x)-g(x)
=3x^4+2x^3+6x^2-x+2+3x^4+2x^3+5x^2-x+6
=6x^4+4x^3+11x^2-2x+8
c: H(x)=0
=>x^2-4=0
=>x=2 hoặc x=-2

\(n\left(x\right)=3x-6=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=2\)
\(n\left(x\right)=x^2-36=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2=\left(\pm6\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)

1. F(-1) = 2.(-1)2 – 3. (-1) – 2 = 2.1 + 3 – 2 = 3
F(0) = 2. 02 – 3 . 0 – 2 = -2
F(1) = 2.12 – 3.1 – 2 = 2 – 3 – 2 = -3
F(2) = 2.22 – 3.2 – 2 = 8 – 6 – 2 = 0
Vì F(2) = 0 nên 0 là 1 nghiệm của đa thức F(x)
2. Vì đa thức E(x) có hệ số tự do bằng 0 nên có một nghiệm là x = 0.

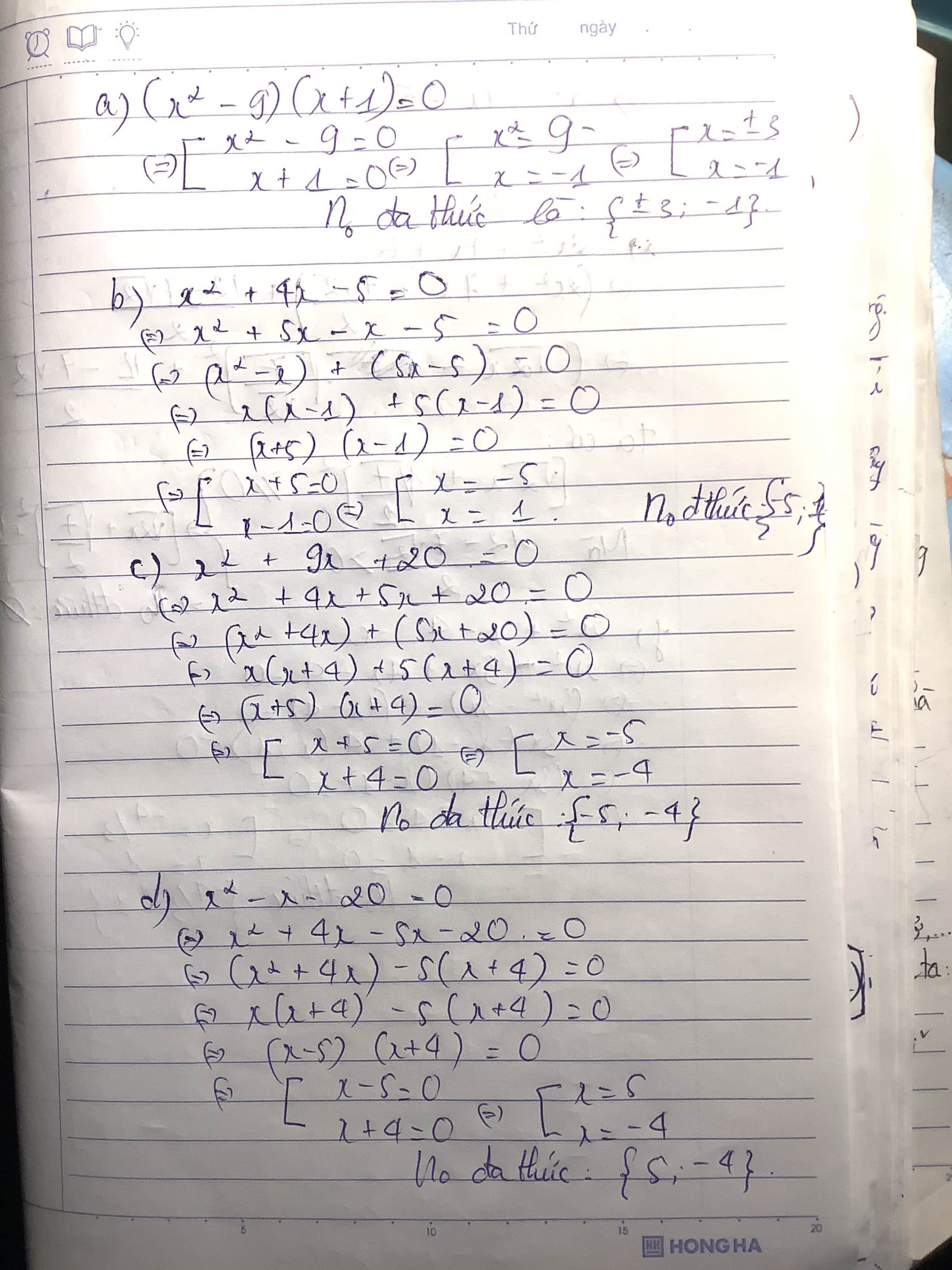

Ta có x2-x-6=0
\(\Rightarrow x^2-x=6\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x-1\right)=6=2\cdot3\)
\(\Rightarrow x=3\)
\(f\left(x\right)=x^2-x-6\)
Để f(x) có nghiệm
\(\Rightarrow x^2-x-6=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-\frac{1}{2}x-\frac{1}{2}x+\frac{1}{4}-\frac{1}{4}-6=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)-\frac{1}{2}\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)-\frac{25}{4}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)-\frac{25}{4}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2=\frac{25}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow x-\frac{1}{2}=\pm\frac{5}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-\frac{1}{2}=\frac{5}{2}\\x-\frac{1}{2}=\frac{-5}{2}\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{2}+\frac{1}{2}=\frac{6}{2}=3\\x=\frac{-5}{2}+\frac{1}{2}=\frac{-4}{2}=-2\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x=3; x=-2 là nghiệm của f(x)