Tìm các giá trị của biểu thức A= 3x-|2x-1|-2 có giá trị bằng 0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Biểu thức 2 x - 3 x - 1 x + 2 xác định khi x ≠ 1 và x ≠ - 2
Ta có: ![]() khi (2x – 3)(x + 2) = 0 và x – 1
≠
0
khi (2x – 3)(x + 2) = 0 và x – 1
≠
0
(2x – 3)(x + 2) = 0 ⇔ 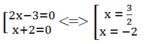
x – 1 ≠ 0 ⇔ x ≠ 1
x = - 2 không thỏa mãn điều kiện
Vậy x = 1,5 thì biểu thức 2 x - 3 x - 1 x + 2 có giá trị bằng 0.

Phân thức 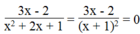 khi 3x – 2 = 0 và
x
+
1
2
≠
0
khi 3x – 2 = 0 và
x
+
1
2
≠
0
Ta có: x + 1 2 ≠ 0 ⇔ x + 1 ≠ 0 ⇔ x ≠ - 1
3x – 2 = 0 ⇔ 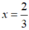
Ta có: 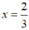 thỏa mãn điều kiện x
≠
- 1
thỏa mãn điều kiện x
≠
- 1
Vậy 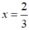 thì phân thức
thì phân thức 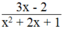 có giá trị bằng 0.
có giá trị bằng 0.

a, A xác định
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^3-19x^2+33x-9\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^3-x^2-18x^2+6x+27x-9\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(3x-1\right)-6x\left(3x-1\right)+9\left(3x-1\right)\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2\ne0\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne\frac{1}{3}\\x\ne3\end{cases}}\)
b, \(\frac{3x^3-14x^2+3x+36}{3x^2-19x^2+33x-9}=\frac{3x^2\left(x-3\right)-5x\left(x-3\right)-12\left(x-3\right)}{\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2}\)
\(=\frac{\left(3x^2-5x-12\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2}=\frac{\left(3x+4\right)\left(x-3\right)^2}{\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2}=\frac{3x+4}{3x-1}\)
\(A=0\Leftrightarrow\frac{3x+4}{3x-1}=0\Leftrightarrow3x+4=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{4}{3}\) (thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
c, \(A=\frac{3x+4}{3x-1}=1+\frac{5}{3x-1}\in Z\Rightarrow5⋮\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow3x-1\inƯ\left(5\right)=\left\{-5;-1;1;5\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{-\frac{4}{3};0;\frac{2}{3};2\right\}\)
Mà \(x\in Z,x\ne\left\{\frac{1}{3};3\right\}\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;2\right\}\)
Bài của Hùng rất thông minh
Đang định có cách khác mà dài hơn cách Hùng nên thui
^^ 2k5 kết bạn nhé


Bài 2:
(1 + x)3 + (1 - x)3 - 6x(x + 1) = 6
<=> x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 - x3 + 3x2 - 3x + 1 - 6x2 - 6x = 6
<=> -6x + 2 = 6
<=> -6x = 6 - 2
<=> -6x = 4
<=> x = -4/6 = -2/3
Bài 3:
a) (7x - 2x)(2x - 1)(x + 3) = 0
<=> 10x3 + 25x2 - 15x = 0
<=> 5x(2x - 1)(x + 3) = 0
<=> 5x = 0 hoặc 2x - 1 = 0 hoặc x + 3 = 0
<=> x = 0 hoặc x = 1/2 hoặc x = -3
b) (4x - 1)(x - 3) - (x - 3)(5x + 2) = 0
<=> 4x2 - 13x + 3 - 5x2 + 13x + 6 = 0
<=> -x2 + 9 = 0
<=> -x2 = -9
<=> x2 = 9
<=> x = +-3
c) (x + 4)(5x + 9) - x2 + 16 = 0
<=> 5x2 + 9x + 20x + 36 - x2 + 16 = 0
<=> 4x2 + 29x + 52 = 0
<=> 4x2 + 13x + 16x + 52 = 0
<=> 4x(x + 4) + 13(x + 4) = 0
<=> (4x + 13)(x + 4) = 0
<=> 4x + 13 = 0 hoặc x + 4 = 0
<=> x = -13/4 hoặc x = -4

\(\frac{x-2}{3x+2}=0\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\) (vì 3x+2=0 thì A vô nghĩa)
<=>x=2
vậy x=2 thì A=0

a: Để \(\dfrac{3x-2}{4}\) không nhỏ hơn \(\dfrac{3x+3}{6}\) thì \(\dfrac{3x-2}{4}>=\dfrac{3x+3}{6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{6\left(3x-2\right)}{24}>=\dfrac{4\left(3x+3\right)}{24}\)
=>18x-12>=12x+12
=>6x>=24
=>x>=4
b: Để \(\left(x+1\right)^2\) nhỏ hơn \(\left(x-1\right)^2\) thì \(\left(x+1\right)^2< \left(x-1\right)^2\)
=>\(x^2+2x+1< x^2-2x+1\)
=>4x<0
=>x<0
c: Để \(\dfrac{2x-3}{35}+\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}\) không lớn hơn \(\dfrac{x^2}{7}-\dfrac{2x-3}{5}\) thì
\(\dfrac{2x-3}{35}+\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}< =\dfrac{x^2}{7}-\dfrac{2x-3}{5}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x-3+5x\left(x-2\right)}{35}< =\dfrac{5x^2-7\cdot\left(2x-3\right)}{35}\)
=>\(2x-3+5x^2-10x< =5x^2-14x+21\)
=>-8x-3<=-14x+21
=>6x<=24
=>x<=4
bạn là army ak