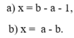Cho a,b thuộc Z. Tìm số nguyên x, biết: a) a + x = b + 2; b) a - x = b - 1
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

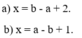

1 a
a+x=5
x=5-a
b
a-x=2
x=a-2
2a
a+x=b
x=b-a
b
a-x=b
x=a-b
tick nha nhanh nhat ne
x phu thuoc vao a va b nen ko xac dinh dc

1;Theo bài ra:3+(-2)+x=5
=>(-2)+x=5-3=2
=>x=2-(-2)
=>x=4
2,a+x=5
=>x=5-a
a-x=2
=>x=a-2
3;a+x=b
=>x=b-a
a-x=b
=>x=a-b

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\pm3\)
a
Khi x = 1:
\(A=\dfrac{3.1+2}{1-3}=\dfrac{5}{-2}=-2,5\)
Khi x = 2:
\(A=\dfrac{3.2+2}{2-3}=-8\)
Khi x = \(\dfrac{5}{2}:\)
\(A=\dfrac{3.2,5+2}{2,5-3}=\dfrac{9,5}{-0,5}=-19\)
b
Để A nguyên => \(\dfrac{3x+2}{x-3}\) nguyên
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+2⋮\left(x-3\right)\\3\left(x-3\right)+11⋮\left(x-3\right) \)
Vì \(3\left(x-3\right)⋮\left(x-3\right)\) nên \(11⋮\left(x-3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-3\right)\inƯ\left(11\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm11\right\}\\ \Rightarrow x\left\{4;2;-8;14\right\}\)
c
Để B nguyên => \(\dfrac{x^2+3x-7}{x+3}\) nguyên
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x+3\right)-7⋮\left(x+3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow-7⋮\left(x+3\right)\\ \Rightarrow x+3\inƯ\left\{\pm1;\pm7\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\left\{-4;-11;-2;4\right\}\)
d
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}A.nguyên.\Leftrightarrow x=\left\{-8;2;4;14\right\}\\B.nguyên\Leftrightarrow x=\left\{-11;-4;-2;4\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=> Để A, B cùng là số nguyên thì x = 4.

Câu này trong sách Bài tập Toán 6
a) a+x=5=>x=5-a
b) a-x=2=>x=a-2
Cái này chỉ là dạng tổng quát thôi. Ko có số nhất định đâu!