Cho △ABC nhọn có AB<AC. Gọi I là giao điểm tia phân giác của góc B và góc C. Từ I lần lượt kẻ các đường thẳng vuông góc với BC, AC, AB tại M, N, P. Chứng minh:
a) BM=BP
b) IM=IN
c) BP + CN = BC
d) AI là tia phân giác của góc BAC
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

LƯU Ý: NHỚ CHỌN ĐÚNG NHÉ !
Câu a: So sánh góc \(\angle B A D\) và \(\angle D A C\)
Vì \(A D\) là đường cao, nên \(\triangle A B D\) và \(\triangle A C D\) đều là tam giác vuông tại \(D\).
- Ta có \(A C > A B\), tức là \(\triangle A C D\) lớn hơn \(\triangle A B D\).
- Trong tam giác \(\triangle A B C\), cạnh đối diện với góc lớn hơn sẽ có góc lớn hơn.
- Vì \(A C > A B\), nên \(\angle D A C > \angle B A D\).
Kết luận:
\(\angle D A C > \angle B A D\)
Câu b: So sánh \(D B\) và \(D C\)
Xét tam giác vuông \(\triangle B D C\) tại \(D\), ta có:
- \(\angle D B C = \angle D A C\) và \(\angle D C B = \angle B A D\) do cùng phụ với góc \(\angle A D B\).
- Do \(\angle D A C > \angle B A D\) (theo câu a), suy ra \(\angle D B C > \angle D C B\).
- Trong một tam giác, cạnh đối diện với góc lớn hơn sẽ lớn hơn.
Suy ra:
\(D B > D C\)
Câu c: Chứng minh \(\angle D A E = \angle D C K\)
Chứng minh:
- \(H E \bot A C\) và \(A D \bot B C\).
- Gọi \(K\) là giao điểm của \(H E\) và \(A D\), ta có:
- \(\triangle A D K\) và \(\triangle E H K\) là các tam giác vuông.
- \(\angle D A E\) và \(\angle D C K\) là hai góc tương ứng tạo bởi các đường vuông góc với \(A C\) và \(B C\).
Do đó, ta suy ra:
\(\angle D A E = \angle D C K\)

a: Xét ΔABC có \(\widehat{ABC}+\widehat{ACB}+\widehat{BAC}=180^0\)
=>\(2\left(\widehat{IBC}+\widehat{ICB}\right)=180^0-\widehat{BAC}\)
=>\(\widehat{IBC}+\widehat{ICB}=90^0-\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\widehat{BAC}\)
Xét ΔIBC có \(\widehat{IBC}+\widehat{ICB}+\widehat{BIC}=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{BIC}+90^0-\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\widehat{BAC}=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{BIC}=180^0-90^0+\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\widehat{BAC}=90^0+\dfrac{\widehat{BAC}}{2}\)
b: Kẻ JH\(\perp\)AB tại H; JM\(\perp\)BC tại M; JN\(\perp\)AC tại N
Xét ΔBHJ vuông tại H và ΔBMJ vuông tại M có
BJ chung
\(\widehat{HBJ}=\widehat{MBJ}\)
Do đó: ΔBHJ=ΔBMJ
=>JH=JM(1)
Xét ΔCMJ vuông tại M và ΔCNJ vuông tại N có
CJ chung
\(\widehat{MCJ}=\widehat{NCJ}\)
Do đó: ΔCMJ=ΔCNJ
=>JM=JN(2)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra JH=JN
Xét ΔAHJ vuông tại H và ΔANJ vuông tại N có
AJ chung
JH=JN
Do đó: ΔAHJ=ΔANJ
=>\(\widehat{HAJ}=\widehat{NAJ}\)
=>AJ là phân giác của góc BAC
mà AI là phân giác của góc BAC
và AJ,AI có điểm chung là A
nên A,I,J thẳng hàng
a: Xét ΔABC có \(\hat{A B C} + \hat{A C B} + \hat{B A C} = 18 0^{0}\)
=>\(2 \left(\right. \hat{I B C} + \hat{I C B} \left.\right) = 18 0^{0} - \hat{B A C}\)
=>\(\hat{I B C} + \hat{I C B} = 9 0^{0} - \frac{1}{2} \cdot \hat{B A C}\)
Xét ΔIBC có \(\hat{I B C} + \hat{I C B} + \hat{B I C} = 18 0^{0}\)
=>\(\hat{B I C} + 9 0^{0} - \frac{1}{2} \cdot \hat{B A C} = 18 0^{0}\)
=>\(\hat{B I C} = 18 0^{0} - 9 0^{0} + \frac{1}{2} \cdot \hat{B A C} = 9 0^{0} + \frac{\hat{B A C}}{2}\)
b: Kẻ JH\(\bot\)AB tại H; JM\(\bot\)BC tại M; JN\(\bot\)AC tại N
Xét ΔBHJ vuông tại H và ΔBMJ vuông tại M có
BJ chung
\(\hat{H B J} = \hat{M B J}\)
Do đó: ΔBHJ=ΔBMJ
=>JH=JM(1)
Xét ΔCMJ vuông tại M và ΔCNJ vuông tại N có
CJ chung
\(\hat{M C J} = \hat{N C J}\)
Do đó: ΔCMJ=ΔCNJ
=>JM=JN(2)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra JH=JN
Xét ΔAHJ vuông tại H và ΔANJ vuông tại N có
AJ chung
JH=JN
Do đó: ΔAHJ=ΔANJ
=>\(\hat{H A J} = \hat{N A J}\)
=>AJ là phân giác của góc BAC
mà AI là phân giác của góc BAC
và AJ,AI có điểm chung là A
nên A,I,J thẳng hàng

Câu nói "Gia đình là nơi tình yêu bắt đầu cũng là nơi tình yêu không bao giờ kết thúc" gợi nhắc về vai trò quan trọng của gia đình trong cuộc sống. Gia đình là nơi đầu tiên mang đến cho chúng ta yêu thương và sự chăm sóc. Từ những cái ôm của cha mẹ đến lời dạy từ ông bà, tình cảm này nuôi dưỡng tâm hồn và xây dựng niềm tin cho mỗi cá nhân.
Tình yêu trong gia đình không bao giờ kết thúc, dù ta có trưởng thành và rời xa. Gia đình luôn là chốn trở về, nơi chúng ta tìm kiếm sự an ủi và hỗ trợ khi gặp khó khăn. Những kỷ niệm sẽ mãi theo ta, tạo nên sự kết nối bền chặt giữa các thành viên.
Ngoài ra, gia đình dạy cho chúng ta về trách nhiệm và sự hy sinh, làm cho tình yêu thêm sâu sắc qua những trải nghiệm chung. Gia đình chính là bến đỗ vững chắc, nơi tình yêu bắt đầu và luôn luôn tồn tại, bất chấp thời gian và khoảng cách. Trân trọng tình cảm gia đình là điều cần thiết, vì đó là nguồn sức mạnh quý giá nhất trong cuộc đời.
Câu hỏi này của em đăng không đúng môn học. lần sau, em muốn được trợ giúp tốt nhất thì phải đăng câu hỏi đúng với môn học em nhé. Vì ai cũng có chuyên môn riêng nên họ sẽ chọn theo chuyên môn của mình để trả lời.

a: \(-\dfrac{15}{45}=\dfrac{-15:45}{45:15}=\dfrac{-1}{3};\dfrac{-0,09}{\dfrac{27}{100}}=\dfrac{-0,09}{0,27}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Do đó: \(\dfrac{-15}{45}=\dfrac{-0,09}{\dfrac{27}{100}}\)
=>Cặp tỉ số này có thể lập thành tỉ lệ thức
b: \(\dfrac{36}{7}:0,25=\dfrac{36}{7}:\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{36}{7}\cdot4=\dfrac{144}{7}\)
\(2:\left(-7\right)=\dfrac{-2}{7}\)
Do đó: \(2:\left(-7\right)\ne\dfrac{36}{7}:0,25\)
=>Cặp tỉ số này không thể lập thành tỉ lệ thức

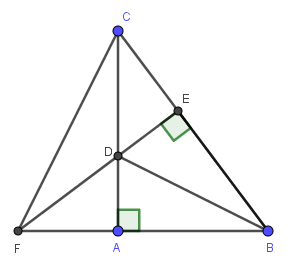
a) Do \(BD\) là tia phân giác của \(\widehat{ABC}\left(gt\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{ABD}=\widehat{CBD}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{ABD}=\widehat{EBD}\)
Xét hai tam giác vuông: \(\Delta BAD\) và \(\Delta BED\) có:
\(BD\) là cạnh chung
\(\widehat{ABD}=\widehat{EBD}\left(cmt\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta BAD=\Delta BED\) (cạnh huyền - góc nhọn)
b) Do \(\Delta BAD=\Delta BED\left(cmt\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow AD=ED\) (hai cạnh tương ứng)
Xét hai tam giác vuông: \(\Delta ADF\) và \(\Delta EDC\) có:
\(AD=ED\left(cmt\right)\)
\(\widehat{ADF}=\widehat{EDC}\) (đối đỉnh)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ADF=\Delta EDC\) (cạnh góc vuông - góc nhọn kề)
\(AF=EC\) (hai cạnh tương ứng)
c) Do \(\Delta BAD=\Delta BED\left(cmt\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow BA=BD\) (hai cạnh tương ứng)
Lại có:
\(AF=CE\left(cmt\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow BA+AF=BE+EC\)
\(\Rightarrow BF=BC\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta BCF\) cân tại B
a)
Xét △BAD và △BED , ta có :
góc BAD = góc BED ( cùng bằng 90°)
BD là cạnh chung
∠ABD = ∠EBD (BD là tia phân giác)
⇒ △BAD = △BED (cạnh huyền - góc nhọn)
b)
Từ △BAD = △BED ⇒ BA = BE và DA = DE
Xét △ADF và △EDC:
DA = DE
gócADF = góc EDC (đối đỉnh)
∠FAD = ∠CED = 90°
⇒ △ADF = △EDC (g. c .g)
⇒ AF = EC
c) Từ BA = BE ⇒ △BAE cân tại B
⇒ gócBAE = gócBEA
Từ △ADF = △EDC ⇒ góc AFD = góc ECD
Mà gócAFD = ∠BFC (đối đỉnh) ⇒ góc BFC = gócECD
Ta có:
gócBCF = góc BCE + gócECF
gócBFC = gócECD
Suy ra: gócBCF = gócBFC
⇒ △BCF cân tại B

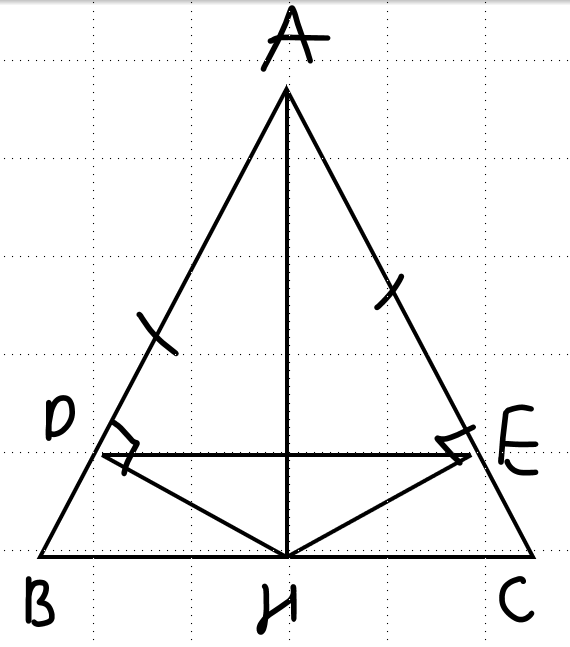
a. xét ΔABH và ΔACH, có:
AB = AC (ΔABC cân tại A)
\(\widehat{ABC}=\widehat{ACB}\left(\text{Δ}ABC\text{ cân tại A}\right)\)
HB = HC (H là trung điểm BC)
=> ΔABH = ΔACH (c-g-c)
b. trong ΔABC cân tại A có AH là đường trung tuyến
=> AH cũng là đường phân giác
\(=>\widehat{DAH}=\widehat{EAH}\) (1)
xét Δ vuông DAH và Δ vuông EAH có:
AH là cạnh chung; \(\widehat{DAH}=\widehat{EAH}\) (từ (1))
=> Δ DAH = Δ EAH (ch-gn)
=> HD = HE (2 cạnh tương ứng)
=> ΔHDE là Δ cân (tại H)
c. ta có Δ DAH = Δ EAH (câu b)
=> AD = AE (2 cạnh tương ứng)
=> ΔDEA là Δ cân tại A
xét ΔDEA cân tại A có: \(\widehat{ADE}=\dfrac{180^0-\widehat{A}}{2}\left(2\right)\)
xét ΔABC cân tại A có: \(\widehat{ABC}=\dfrac{180^0-\widehat{A}}{2}\left(3\right)\)
từ (2) và (3) => \(\widehat{ADE}=\widehat{ABC}\)
mà 2 góc này ở vị trí đồng vị
=> DE // BC