Tính giá trị của biểu thức sau :
sin^2 10+sin^2 20+sin^2 45+sin^2 70+sin^2 80=?
SOS cíu mik vs
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(sin^210^0+sin^220^0+sin^245^0+sin^270^0+sin^280^0\)
\(=\left(sin^210^0+sin^280^0\right)+\left(sin^220^0+sin^270^0\right)+\left(sin^245^0\right)\)
\(=\left(sin^210^0+cos^210^0\right)+\left(sin^220^0+cos^220^0\right)+\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\)
\(=1+1+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{5}{2}\)

\(x^3+5x^2+8x+4\)
\(=x^3+x^2+4x^2+4x+4x+4\)
\(=x^2\left(x+1\right)+4x\left(x+1\right)+4\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+4x+4\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)^2\)

\(\text{Sửa đề }:x^4-3x+2=(x-1)(x^3+ax^2+bx-2)\\\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^3+x^3-x^2+x^2-x-2x+2=(x-1)(x^3+ax^2+bx-2)\\\Leftrightarrow x^3(x-1)+x^2(x-1)+x(x-1)-2(x-1)=(x-1)(x^3+ax^2+bx-2)\\\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(x^3+x^2+x-2)=(x-1)(x^3+ax^2+bx-2)\\\Rightarrow a=b=1\)

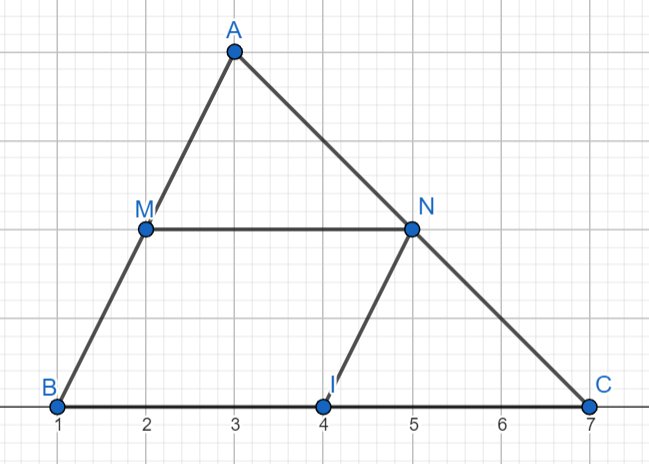
Đề sai rồi bạn, theo đề thì \(MN\) là đường trung bình của \(\triangle ABC\)
nên \(MN//BC\Rightarrow\widehat {AMN}=\widehat{NIC}\) (hai góc đồng vị)
Vì vậy nếu \(\widehat{AMN}=\widehat{INC}\) thì \(\widehat{NIC}=\widehat{INC}\)
\(\Rightarrow\triangle INC\) cân tại C
Từ đây xảy ra trường hợp đặc biệt \(\rightarrow\) đề sai

Bài 4:
a: Đặt 2x+10=0
=>2x=-10
=>x=-5
b: Đặt 4(x-1)+3x-5=0
=>4x-4+3x-5=0
=>7x=9
=>\(x=\dfrac{9}{7}\)
c: Đặt \(-1\dfrac{1}{3}x^2+x=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{4}{3}x^2-x=0\)
=>\(x\left(\dfrac{4}{3}x-1\right)=0\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\\dfrac{4}{3}x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{3}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 5:
a: Xét ΔBAD vuông tại A và ΔBMD vuông tại M có
BD chung
\(\widehat{ABD}=\widehat{MBD}\)
Do đó: ΔBAD=ΔBMD
b: ΔBAD=ΔBMD
=>BA=BM và DA=DM
ta có: BA=BM
=>B nằm trên đường trung trực của AM(1)
Ta có: DA=DM
=>D nằm trên đường trung trực của AM(2)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra BD là đường trung trực của AM
c: Xét ΔBKC có
KM,CA là các đường cao
KM cắt CA tại D
Do đó: D là trực tâm của ΔBKC
=>BD\(\perp\)KC tại N

Bài 2:
Độ dài của `1/3` quãng đường đầu là:
`1/3*600=200` (km)
Thời gian xe đi trên `1/3` quãng đường đầu là:
\(\dfrac{200}{x}\left(h\right)\)
Quãng đường còn lại là: `600 - 200 = 400`(km)
Vận tốc của xe khi đi trên quãng đường còn lại: `x+10` (km/h)
Thời gian xe đi trên quãng đường còn lại là:
\(\dfrac{400}{x+10}\left(h\right)\)
Biểu thức thể hiện thời gian xe đi từ Hà Nội đến Quãng Ngãi là:
\(\dfrac{200}{x}+\dfrac{400}{x+10}=\dfrac{200\left(x+10\right)}{x\left(x+10\right)}+\dfrac{400x}{x\left(x+10\right)}=\dfrac{200x+2000+400x}{x\left(x+10\right)}=\dfrac{600x+2000}{x\left(x+10\right)}\)

`#3107.101107`
`a + b + c = 0`
`=> (a + b + c)^3 = 0`
`=> a^3 + b^3 + c^3 + 3a^2b + 3ab^2 + 3b^2c + 3bc^2 + 3a^2c + 3ac^2 + 6abc = 0`
`=> a^3 + b^3 + c^3 + 3a^2b + 3ab^2 + 3b^2c + 3bc^2 + 3a^2c + 3ac^2 + 6abc + 3abc - 3abc = 0`
`=> a^3 + b^3 + c^3 + (3a^2b + 3ab^2 + 3abc) + (3b^2c + 3bc^2 + 3abc) + (3a^2c + 3ac^2 + 3abc) - 3abc = 0`
`=> a^3 + b^3 + c^3 + 3ab(a + b + c) + 3bc(b + c + a) + 3ac(a + c + b) = 3abc`
`=> a^3 + b^3 + c^3 + (3ab + 3bc + 3ac)(a + b + c) = 3abc`
Mà `a + b + c = 0`
`=> a^3 + b^3 + c^3 = 3abc` (đpcm).

a) \(x^2-36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)\left(x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: ...
b) \(x^2-10x+25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2\cdot x\cdot5+5^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
Vậy: ...
a) \(x^2-36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=36\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=\left(\pm6\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{6;-6\right\}\)
b) \(x^2-10x+25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2.x.5+5^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
Vậy \(x=5\)

a) \(\left(3x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x+2\right)^2\)
\(=\left(3x^2+6x-x-2\right)-\left(x+2\right)^2\)
\(=\left(3x^2+5x-2\right)-\left(x^2+4x+4\right)\)
\(=3x^2+5x-2-x^2-4x-4\)
\(=2x^2+x-6\)
b) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-1\right)-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(=x^2-1-x^2+2x-1\)
\(=2x-2\)
c) \(\left(x-4\right)\left(4+x\right)+2x\left(x-3\right)\)
\(=\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)+2x\left(x-3\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-16\right)+2x^2-6x\)
\(=x^2-16+2x^2-6x\)
\(=3x^2-6x-16\)
d) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-1\right)+\left(x+2\right)^3\)
\(=\left(x^3-x-x^2+1\right)+\left(x^3+6x^2+12x+8\right)\)
\(=x^3-x-x^2+1+x^3+6x^2+12x+8\)
\(=2x^3+5x^2+11x+9\)
e) \(\left(2x-1\right)^2-\left(2x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)\)
\(=\left(4x^2-4x+1\right)-\left(2x^2+10x-5x-25\right)\)
\(=\left(4x^2-4x+1\right)-\left(2x^2+5x-25\right)\)
\(=4x^2-4x+1-2x^2-5x+25\)
\(=2x^2-9x+26\)
f) \(\left(3x+1\right)^2-\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)\)
\(=\left(9x^2+6x+1\right)-\left(x^4+2x^2-x^2-2\right)\)
\(=\left(9x^2+6x+1\right)-\left(x^4+x^2-2\right)\)
\(=9x^2+6x+1-x^4-x^2+2\)
\(=-x^4+8x^2+6x+3\)
g) \(\left(x^2+1\right)^2-\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)\)
\(=\left(x^4+2x^2+1\right)-\left(x^4+2x^2-x^2-2\right)\)
\(=\left(x^4+2x^2+1\right)-\left(x^4+x^2-2\right)\)
\(=x^4+2x^2+1-x^4-x^2+2\)
\(=x^2+3\)
h) \(\left(2x^2-4\right)^2-\left(2x^2+4\right)^2\)
\(=\left(4x^4-16x^2+16\right)-\left(4x^4+16x^2+16\right)\)
\(=4x^4-16x^2+16-4x^4-16x^2-16\)
\(=-32x^2\)



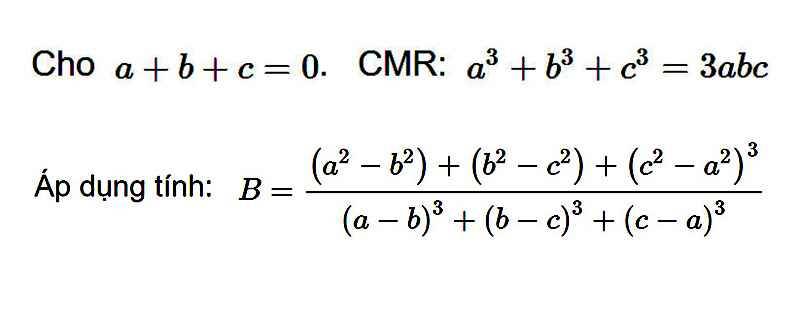
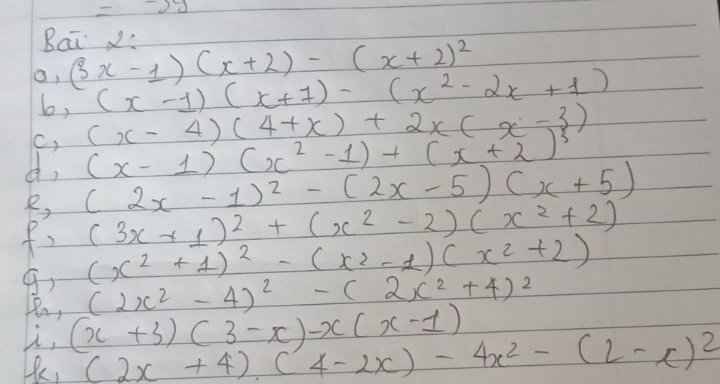
\(sin^210+sin^220+sin^245+sin^270+sin^280\)
\(=sin^210+sin^220+sin^245+cos^220+cos^210=1+1+sin^245=2+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{5}{2}\)