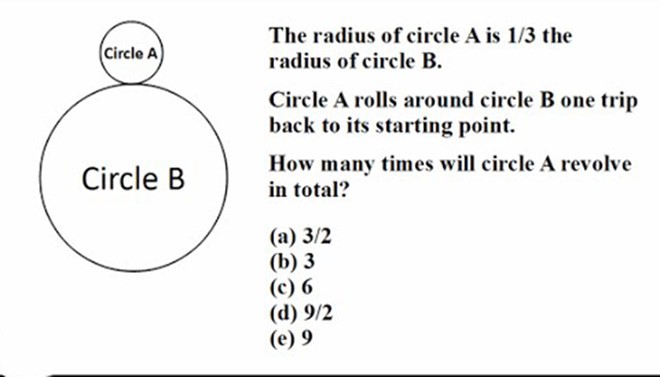
Bán kính hình tròn B gấp 3 lần bán kính hình tròn A. Nếu hình A lăn xung quanh hình B, nó phải thực hiện bao nhiêu vòng quay để trở lại điểm xuất phát?
=> Các phương án được đưa ra là 3/2, 3, 6, 9/2, 9 vòng
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a, \(P=\left(\frac{x^2+9}{x^2+5x}+\frac{x-1}{x}-\frac{x}{x+5}\right)\left(1+\frac{2}{x}\right)\)đk : x khác 0 ; -5
\(=\left(\frac{x^2+9+x^2+4x-5-x^2}{x\left(x+5\right)}\right)\left(\frac{x+2}{x}\right)\)
\(=\frac{x^2+4x+4}{x\left(x+5\right)}\left(\frac{x+2}{x}\right)=\frac{\left(x+2\right)^3}{x^2\left(x+5\right)}\)
b, Ta có \(\left(x+2\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=-2;x=\frac{2}{3}\)
Với x = -2 => P = 0
Với x = 2/3 => \(P=\frac{\left(\frac{2}{3}+2\right)^3}{\frac{4}{9}\left(\frac{2}{3}+5\right)}=\frac{128}{17}\)
-mình nghĩ bạn nên đặt dấu chia giữa 2 đa thức kia thì kq sẽ đẹp hơn

Gọi vân tốc xe máy là x ( x >0 )
vận tốc ô tô là x + 10
Theo bài ra ta có pt \(\left(\frac{1}{3}+3\right)x+3\left(x+10\right)=220\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{10}{3}x+3x=190\Rightarrow x=30\)(tm)
Vậy vân tốc xe máy là 30 km/h
vận tốc ô tô là 40 km/h

Gọi quãng đường xe máy đi từ A đến B là x ( x > 0 )
quãng đường ô tô đi từ A đến B là x + 10
Theo bài ra ta có pt \(\frac{x+10}{3}-\frac{x}{3,5}=10\Rightarrow x=140\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy vân tốc xe máy là \(\frac{140}{3,5}=40\)km/h
vận tốc ô tô là 40 + 10 = 50 km/h

\(\left|x-1\right|=\left|3x-5\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=3x-5\\x-1=5-3x\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=4\\4x=6\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=\frac{3}{2}\end{cases}}\)
gfvfvfvfvfvfvfv555