Cho tam giác ABC, D thuộc đường trung tuyến AM. Trên tia DM lấy điểm K sao cho MD=MK. Qua D kẻ đường thẳng song song với AB, cắt AC và BC theo thứ tự tại E và F. a) Chứng minh FK song song với AC b) Gọi I là giao điểm của KF và AB. Chứng minh IK=EC c) Chứng minh tứ giác BIED là hình bình hành
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 2:
a: Khi x=4 thì \(M=\dfrac{4+3}{4-2}=\dfrac{7}{2}\)
b: \(M=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+3}{x-2}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
=>3(x+3)=2(x-2)
=>3x+9=2x-4
=>3x-2x=-4-9
=>x=-13(nhận)
c: Để M là số nguyên dương thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+3⋮x-2\\M>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2+5⋮x-2\\\dfrac{x+3}{x-2}>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5⋮x-2\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>2\\x< -3\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2\in\left\{1;-1;5;-5\right\}\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>2\\x< -3\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x\in\left\{3;7\right\}\)
Bài 3:
ΔMIN vuông tại I
=>\(IM^2+IN^2=MN^2\)
=>\(x=MI=\sqrt{12^2-5^2}=\sqrt{144-25}=\sqrt{119}\left(cm\right)\)
ΔMIP vuông tại I
=>\(IM^2+IP^2=PM^2\)
=>\(y=\sqrt{119+100}=\sqrt{219}\left(cm\right)\)
Bài 4:
a: Xét ΔBAC vuông tại A và ΔBHA vuông tại H có
\(\widehat{ABC}\) chung
Do đó: ΔBAC~ΔBHA
b: Xét ΔHBA vuông tại H và ΔHAC vuông tại H có
\(\widehat{HBA}=\widehat{HAC}\left(=90^0-\widehat{HAB}\right)\)
Do đó: ΔHBA~ΔHAC
=>\(\dfrac{HB}{HA}=\dfrac{HA}{HC}\)
=>\(HA^2=HB\cdot HC\)
c: Xét tứ giác AIHK có \(\widehat{AIH}=\widehat{AKH}=\widehat{KAI}=90^0\)
nên AIHK là hình chữ nhật
=>\(\widehat{AKI}=\widehat{AHI}\)
mà \(\widehat{AHI}=\widehat{ABC}\left(=90^0-\widehat{HAB}\right)\)
nên \(\widehat{AKI}=\widehat{ABC}\)
ΔABC vuông tại A
mà AM là đường trung tuyến
nên MA=MC
=>ΔMAC cân tại M
=>\(\widehat{MAC}=\widehat{MCA}\)
\(\widehat{AKI}+\widehat{MAC}=\widehat{ABC}+\widehat{ACB}=90^0\)
=>AM\(\perp\)IK

Gọi biểu thức cần tìm GTLN là P
Bunhiacopxki:
\(\left(x^2+y+z\right)\left(1+y+z\right)\ge\left(x+y+z\right)^2=9\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{x^2+y+z}\le\dfrac{1+y+z}{9}\)
Tương tự:
\(\dfrac{1}{y^2+x+z}\le\dfrac{1+x+z}{9}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{z^2+x+y}\le\dfrac{1+x+y}{9}\)
Cộng vế:
\(P\le\dfrac{1+y+z}{9}+\dfrac{1+x+z}{9}+\dfrac{1+x+y}{9}=1\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(x=y=z=1\)

nửa chu vi HCN là: 80 : 2 = 40 (cm)
gọi x; y (cm) lần lượt là chiều dài và chiều rộng (đk: 0 < y < x < 40)
nửa chu vi HCN là 40cm nên: x + y = 40 (cm) ⇒ x = 40 - y (1)
mà 5 lần chiều dài hơn 2 lần chiều rộng là 130cm nên: 5x - 2y = 130 (2)
thay (1) vào (2) ta được: \(5\cdot\left(40-y\right)-2y=130\)
\(\Rightarrow200-5y-2y=130\\ \Rightarrow-7y=-70\\ \Rightarrow y=10\\ \Rightarrow x=40-10=30\)
diện tích hình chữ nhật: 30 x 10 = 300 (cm²)
Xin lỗi vì sự phức tạp, mình sẽ giải thích lại một cách đơn giản hơn nhé!
Bài toán:
- Chu vi của hình chữ nhật là 80 cm.
- 5 lần chiều dài hơn 2 lần chiều rộng là 130 cm.
- Tính diện tích hình chữ nhật.
Bước 1: Gọi chiều dài và chiều rộng
- Gọi chiều dài của hình chữ nhật là l (cm) và chiều rộng là w (cm).
Bước 2: Sử dụng chu vi
Ta có công thức tính chu vi của hình chữ nhật là:
\(\text{Chu}\&\text{nbsp};\text{vi} = 2 \times \left(\right. l + w \left.\right)\)
Đề bài cho chu vi là 80 cm, vậy ta có:
\(2 \times \left(\right. l + w \left.\right) = 80\)
Chia cả hai vế cho 2:
\(l + w = 40\)
(Phương trình này nói rằng tổng chiều dài và chiều rộng là 40 cm)
Bước 3: Dùng mối quan hệ giữa chiều dài và chiều rộng
Đề bài còn cho biết: "5 lần chiều dài hơn 2 lần chiều rộng là 130 cm". Vậy ta có phương trình thứ hai:
\(5 l - 2 w = 130\)
(Mối quan hệ này nói rằng 5 lần chiều dài trừ đi 2 lần chiều rộng thì bằng 130 cm)
Bước 4: Giải hệ phương trình
Phương trình 1: \(l + w = 40\)
Phương trình 2: \(5 l - 2 w = 130\)
Bây giờ ta sẽ giải hệ phương trình này:
- Từ phương trình 1, ta có thể tìm \(l\) (chiều dài):
\(l = 40 - w\) - Thay \(l = 40 - w\) vào phương trình 2:
\(5 \left(\right. 40 - w \left.\right) - 2 w = 130\)
Giải phương trình này:
\(200 - 5 w - 2 w = 130\) \(200 - 7 w = 130\) \(- 7 w = 130 - 200\) \(- 7 w = - 70\) \(w = 10\)
Vậy chiều rộng là \(w = 10\) cm.
Bước 5: Tính chiều dài
Bây giờ ta thay \(w = 10\) vào phương trình \(l + w = 40\):
\(l + 10 = 40\) \(l = 40 - 10 = 30\)
Vậy chiều dài là \(l = 30\) cm.
Bước 6: Tính diện tích
Diện tích của hình chữ nhật là:
\(\text{Di}ệ\text{n}\&\text{nbsp};\text{t} \overset{ˊ}{\imath} \text{ch} = l \times w = 30 \times 10 = 300 \textrm{ } \text{cm}^{2}\)
Vậy diện tích hình chữ nhật là 300 cm².
😊

Ta có �2−4�+9=(�−2)2+5⩾5x2−4x+9=(x−2)2+5⩾5.
Suy ra �=1�2−4�+9=1(�−2)2+5⩽15B=x2−4x+91=(x−2)2+51⩽51.

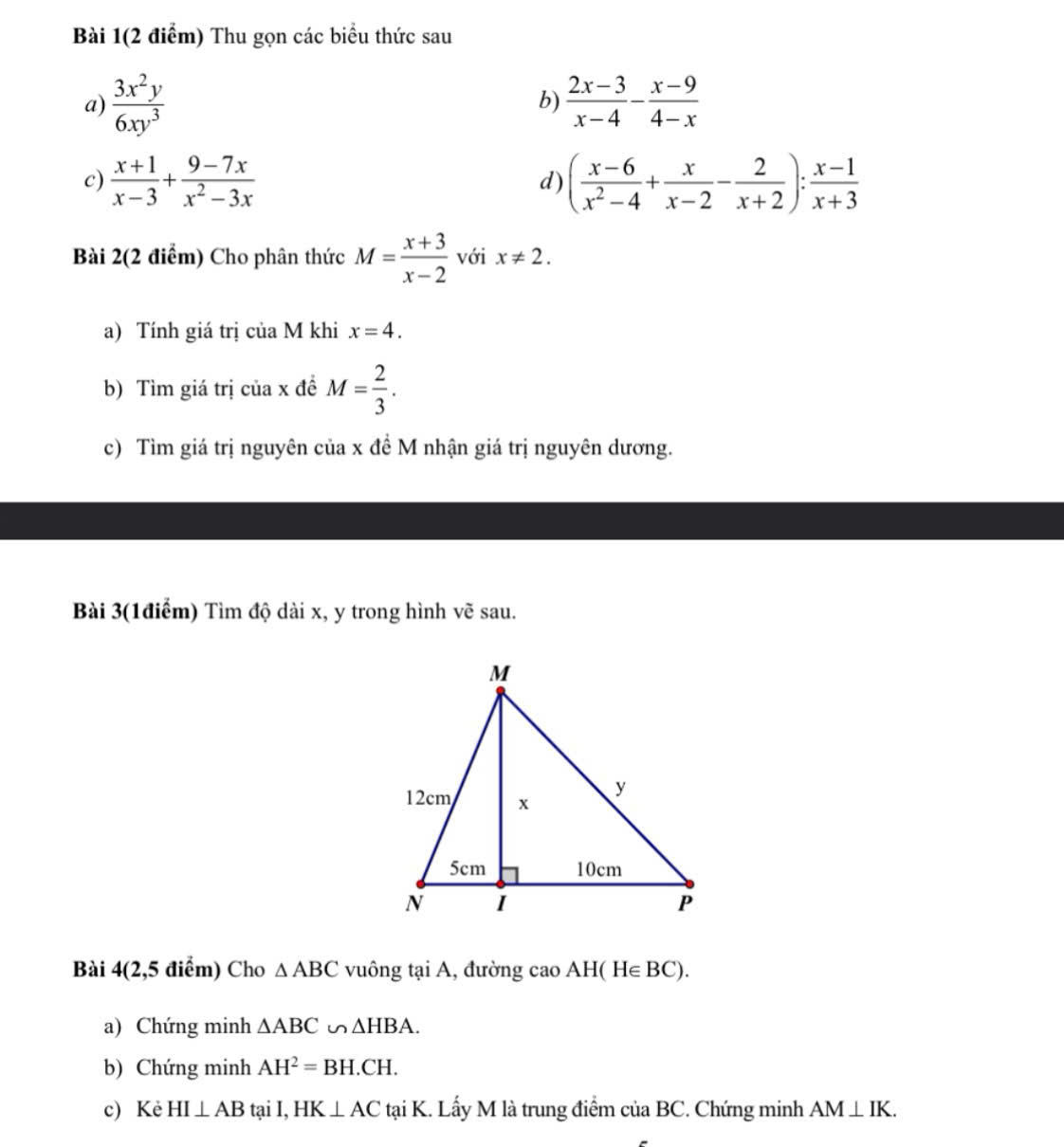
Do \(MNPQ\) là hình bình hành (gt)
\(\Rightarrow MN=PQ\)
Mà \(QI=\dfrac{1}{3}PQ\left(gt\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow QI=\dfrac{1}{3}MN\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{QI}{MN}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Do \(MNPQ\) là hình bình hành (gt)
\(\Rightarrow MN\) // \(PQ\)
\(\Rightarrow MN\) // \(QI\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{QI}{MN}=\dfrac{QE}{EN}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{QE}{EN}=\dfrac{1}{3}\Rightarrow EN=3QE\)
Mà \(EN+QE=NQ=18\left(cm\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow3QE+QE=18\)
\(\Rightarrow4QE=18\)
\(\Rightarrow QE=\dfrac{18}{4}=4,5\left(cm\right)\)

Ta có: MNPQ là hình bình hành
=>MP cắt NQ tại trung điểm của mỗi đường
=>O là trung điểm chung của MP và NQ
Xét ΔMQN có
ND,MO là các đường trung tuyến
ND cắt MO tại H
do đó: H là trọng tâm của ΔMQN
=>\(NH=\frac23ND\)
Xét ΔNQP có
NE,PO là các đường trung tuyến
NE cắt PO tại K
Do đó: K là trọng tâm của ΔNQP
=>\(NK=\frac23NE\)
Xét ΔNDE có \(\frac{NH}{ND}=\frac{NK}{NE}\left(=\frac23\right)\)
nên HK//DE
=>\(\frac{HK}{DE}=\frac{NH}{ND}=\frac23\)
=>\(\frac{28}{DE}=\frac23=\frac{28}{42}\)
=>DE=42(cm)

a: Vẽ đồ thị:
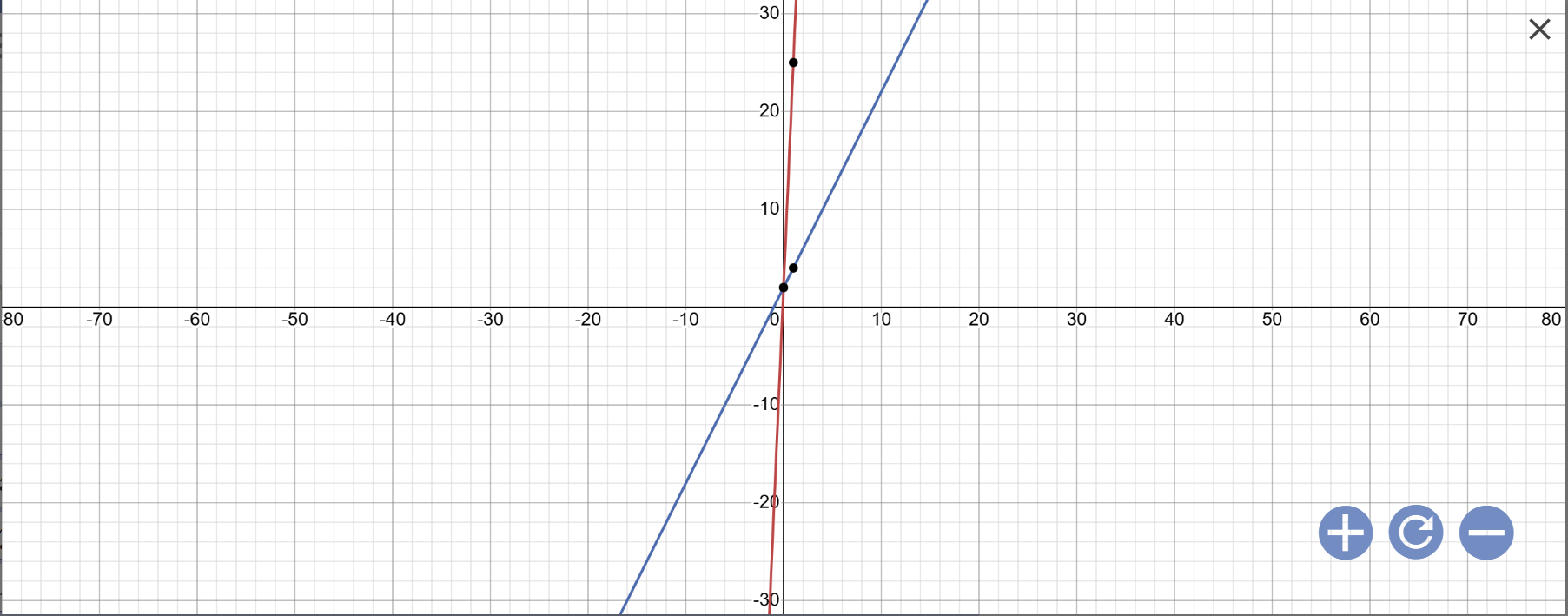
b: Tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) với trục Ox là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\23x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\23x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=-\dfrac{2}{23}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) với trục Oy là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=23x+2=23\cdot0+2=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
23x+2=2x+2
=>23x-2x=0
=>21x=0
=>x=0
Khi x=0 thì \(y=2x+2=2\cdot0+2=2\)
Vậy: (d1) cắt (d2) tại A(0;2)

`(-x^2 + x)/(-2x^2 + 3x - 1) ` `(đkxđ: x ne 1/2; x ne 1)`
`= (x^2 - x)/(2x^2 - 3x + 1) `
`= (x(x-1))/((x-1)(2x - 1))`
`= x/(2x -1)`
\(\dfrac{-x^2+x}{-2x^2+3x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-x}{2x^2-3x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x}{2x-1}\)