
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Gọi x là số thứ nhất
⇒ Số thứ hai là: 59 - x
Theo đề bài, ta có phương trình:
2x - 3(59 - x) = -7
2x - 177 + 3x = -7
5x = -7 + 177
5x = 170
x = 170 : 5
x = 34
Vậy số thứ nhất là 34
số thứ hai là 59 - 34 = 25

a) `y=(m-4)x+m` có `a=m-4`
Để là hàm số bậc nhất thì `a≠0`
`=>m-4≠0`
`<=>m≠4`
b) `y=5-3mx` có `a=-3m`
Để là hàm số bậc nhất thì `a≠0`
`=>-3m≠0`
`<=>m≠0`
c) `y=(m-2)x+m` có `a=m-2`
Để là hàm số bậc nhất thì `a≠0`
`=>m-2≠0`
`<=>m≠2`
d) `y=7-5mx` có `a=-5m`
Để là hàm số bậc nhất thì `a≠0`
`=>-5m≠0`
`<=>m≠0`

Lời giải:
Hàm bậc nhất là hàm có dạng $y=ax+b$ với $a,b$ là số thực, $a\neq 0$
Căn cứ vào đó thì:
a. Để $y=(m-4)x+m$ là hsbn thì: $m-4\neq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow m\neq 4$
b.
Để $y=-3mx+5$ là hsbn thì $-3m\neq 0\Leftrightarrow m\neq 0$
c.
Để $y=(m-2)x+m$ là hsbn thì $m-2\neq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow m\neq 2$
d.
Để $y=-5mx+7$ là hsbn thì $-5m\neq 0\Leftrightarrow m\neq 0$


Bài 2:
a) ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+3\ne0\\x-3\ne0\\9-x^2\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\ne\pm3\)
b) \(A=\dfrac{3}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x-3}-\dfrac{18}{9-x^2}\)
\(A=\dfrac{3}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x-3}+\dfrac{18}{x^2-9}\)
\(A=\dfrac{3\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{x+3}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{18}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{3x-9+x+3+18}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{4x+12}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{4\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{4}{x-3}\)
c) Thay `x=-1` vào A ta có:
\(A=\dfrac{4}{-1-3}=\dfrac{4}{-4}=-1\)
d) `A=-4` khi: \(\dfrac{4}{x-3}=-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\)
Bài 1:
a: ĐKXĐ: x<>3
\(\dfrac{9}{x-3}+\dfrac{3x}{3-x}\)
\(=\dfrac{9}{x-3}-\dfrac{3x}{x-3}=\dfrac{9-3x}{x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{-3\left(x-3\right)}{x-3}=-3\)
b: \(\dfrac{5}{x+5}+\dfrac{-4}{x+4}\)
\(=\dfrac{5\left(x+4\right)-4\left(x+5\right)}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+4\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x+20-4x-20}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+4\right)}=\dfrac{x}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+4\right)}\)
c: \(\dfrac{x+5}{2x-3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{3-2x}-\dfrac{x+4}{3-2x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+5}{2x-3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{2x-3}+\dfrac{x+4}{2x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+5+2x-7+x+4}{2x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x+2}{2x-3}\)
d: \(\dfrac{x^2-y^2}{10x^3y}:\dfrac{x-y}{5xy}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}{10x^3y}\cdot\dfrac{5xy}{x-y}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+y}{1}\cdot\dfrac{5xy}{10x^3y}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+y}{2x^2}\)
e: \(\dfrac{2x^2-20x+50}{3x+3}\cdot\dfrac{x^2-1}{4\left(x-5\right)^3}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(x^2-10x+25\right)}{3\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}{4\left(x-5\right)^3}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(x-5\right)^2}{4\left(x-5\right)^3}\cdot\dfrac{x-1}{3}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-1}{3\cdot2\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{6x-30}\)
f: \(\dfrac{x-2}{x+1}:\dfrac{x^2-5x+6}{x^2-2x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2}{x+1}:\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2}{x+1}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)}{x-2}=1\)
g: \(\dfrac{x}{x-2y}+\dfrac{x}{x+2y}+\dfrac{4xy}{4y^2-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x}{x-2y}+\dfrac{x}{x+2y}-\dfrac{4xy}{\left(x-2y\right)\left(x+2y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+2y\right)+x\left(x-2y\right)-4xy}{\left(x-2y\right)\left(x+2y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2-4xy}{\left(x-2y\right)\left(x+2y\right)}=\dfrac{2x\left(x-2y\right)}{\left(x-2y\right)\left(x+2y\right)}=\dfrac{2x}{x+2y}\)
h: \(\dfrac{1}{x-y}+\dfrac{3xy}{y^3-x^3}+\dfrac{x-y}{x^2+xy+y^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x-y}-\dfrac{3xy}{\left(x-y\right)\cdot\left(x^2+xy+y^2\right)}+\dfrac{x-y}{x^2+xy+y^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+xy+y^2-3xy+\left(x-y\right)^2}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x^2+xy+y^2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(x-y\right)^2}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x^2+xy+y^2\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x-y\right)}{x^2+xy+y^2}\)
i: \(\left(\dfrac{2}{x+2}+\dfrac{2}{x-1}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x^2-4}{4x^2-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)+2\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(2x+1\right)}{x-1}\cdot\dfrac{x+1}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
j: \(1+\dfrac{x^3-x}{x^2+1}\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{1-x}-\dfrac{1}{1-x^2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x^2+1}\cdot\left(\dfrac{-1}{x-1}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x^2+1}\cdot\dfrac{-x-1+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=1+\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x^2+1}\cdot\dfrac{-x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=1-\dfrac{x^2}{x^2+1}=\dfrac{1}{x^2+1}\)

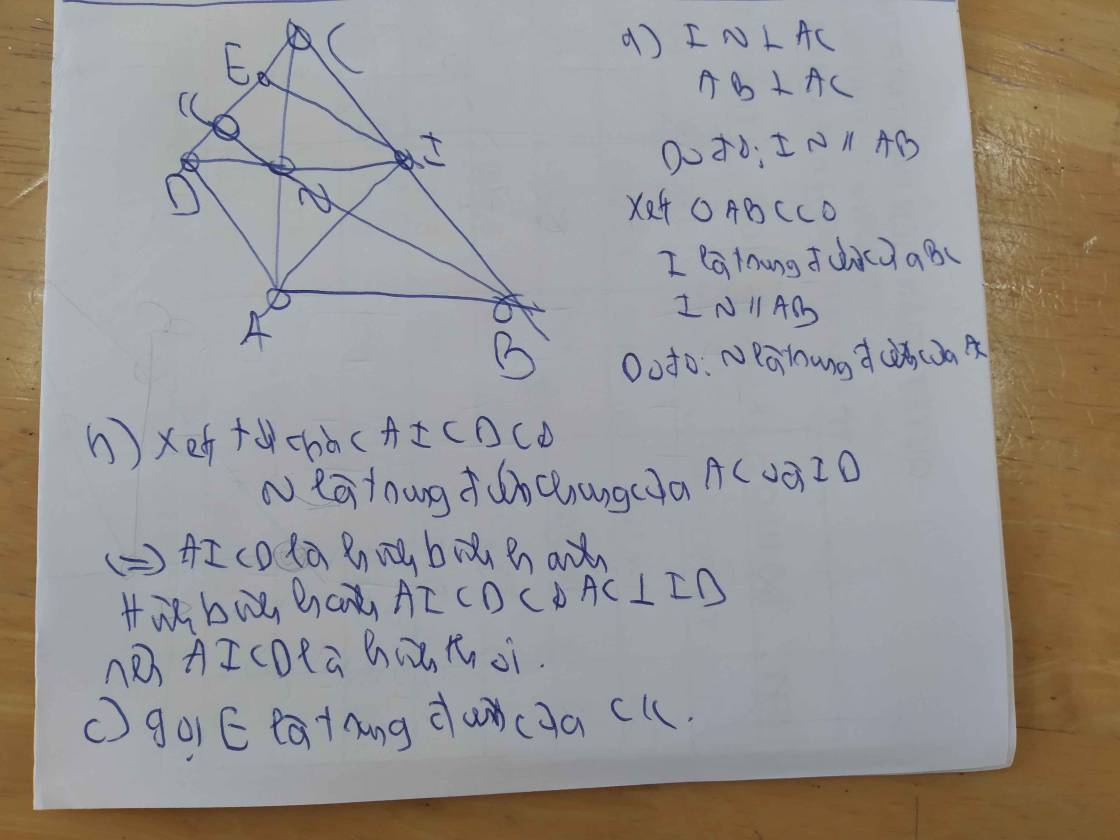

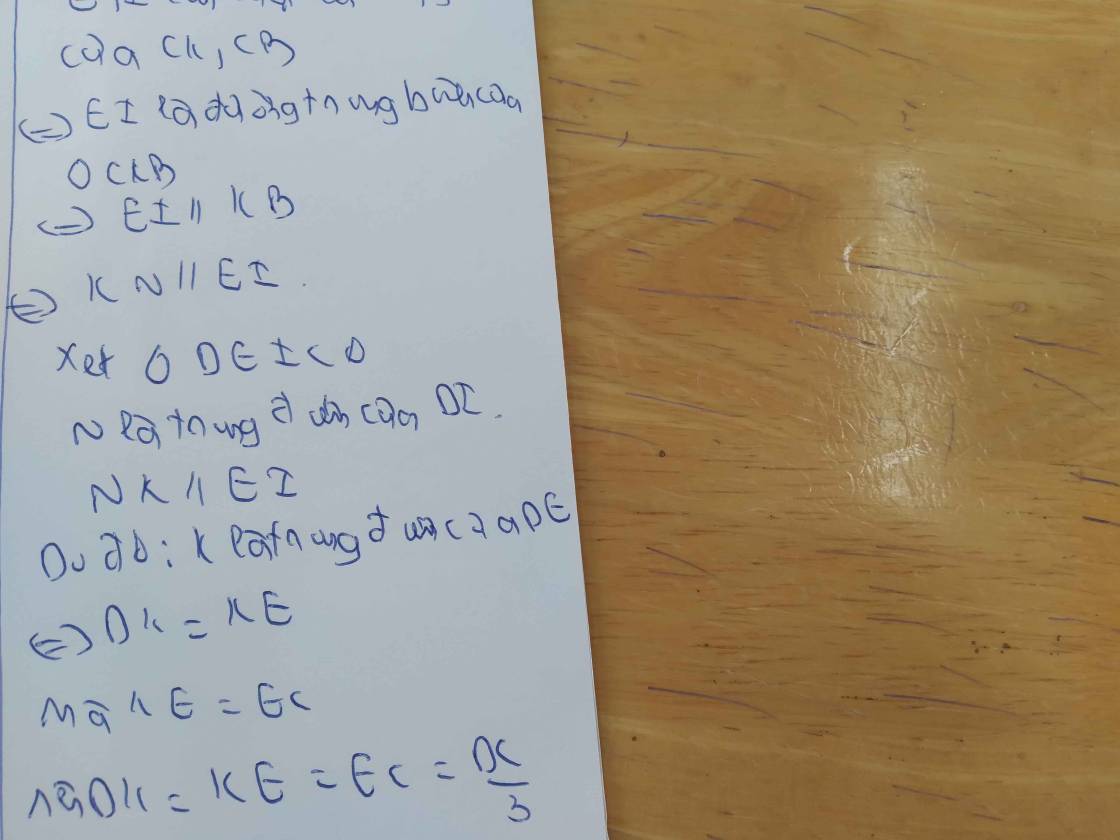

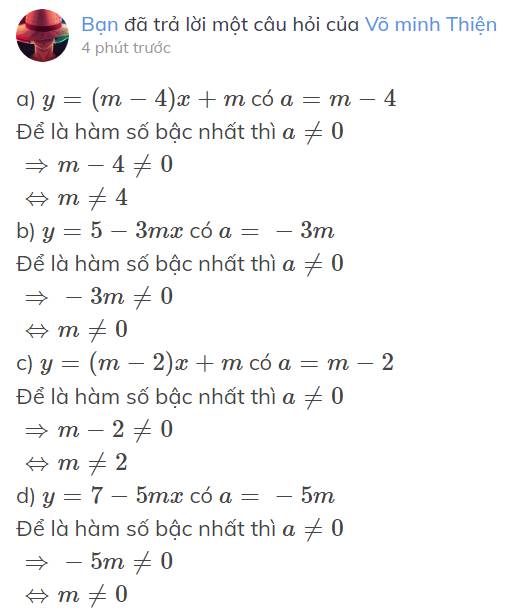
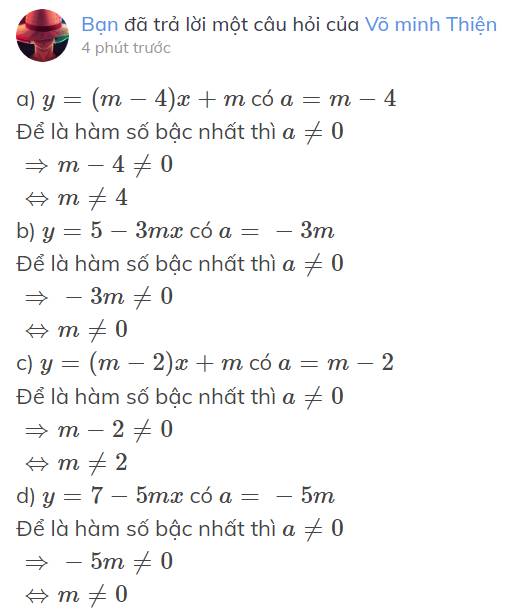


Gọi độ dài quãng đường AB là x (km) với x>0
Thời gian người đó đi từ A đến B là: \(\dfrac{x}{35}\) giờ
Do lúc về đi con đường khác dài hơn đường cũ 8km nên độ dài quãng đường về là: \(x+8\) (km)
Vận tốc lúc về lớn hơn lúc đi là 5km/h nên vận tốc lúc về là: \(35+5=40\) (km/h)
Thời gian về là: \(\dfrac{x+8}{40}\) gờ
Do thời gian về ít hơn thời gian đi là 3 phút =1/20 giờ nên ta có pt:
\(\dfrac{x}{35}-\dfrac{x+8}{40}=\dfrac{1}{20}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(\dfrac{1}{35}-\dfrac{1}{40}\right)=\dfrac{8}{40}+\dfrac{1}{20}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{280}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{280}{4}=70\left(km\right)\)