tính diện tích 1 mảnh đất hình vuông. biết rằng nếu mở rộng mảnh đất về 2 phía, 1 phía là 4m, một phía là 8m thì mảnh đất đó tăng lên 360 m2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\left(x+y\right)+3\left(x-y\right)=4\\x+y+2\left(x-y\right)=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+2y+3x-3y=4\\x+y+2x-2y=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5x-y=4\\3x-y=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5x-y-3x+y=4-5\\3x-y=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=-1\\y=3x-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\y=3\cdot\dfrac{-1}{2}-5=-\dfrac{3}{2}-5=-\dfrac{13}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x+1\right)\left(y-1\right)=xy-1\\\left(x-3\right)\left(y+3\right)=xy-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}xy-x+y-1=xy-1\\xy+3x-3y-9=xy-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x+y=0\\3x-3y=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-y=0\\x-y=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-y-x+y=0-2\\x-y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}0y=-2\\x-y=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left(x;y\right)\in\varnothing\)

ΔABC=ΔDEF
=>\(\widehat{A}=\widehat{D}\)
=>\(\widehat{D}=55^0\)
ΔABC=ΔDEF
=>\(\widehat{B}=\widehat{E}\)
=>\(\widehat{B}=75^0\)
Xét ΔABC có \(\widehat{A}+\widehat{B}+\widehat{C}=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{C}=180^0-55^0-75^0=50^0\)
=>\(\widehat{F}=\widehat{C}=50^0\)

\(\dfrac{11}{3}+\left|x\right|=\dfrac{9}{4}\)
=>\(\left|x\right|=\dfrac{9}{4}-\dfrac{11}{3}=\dfrac{27}{12}-\dfrac{44}{12}=-\dfrac{17}{12}\)
mà \(\left|x\right|>=0\forall x\)
nên \(x\in\varnothing\)

\(\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{x+2}=16^{4-2x}\)
=>\(2^{-x-2}=2^{4\left(4-2x\right)}\)
=>-x-2=4*(4-2x)
=>-x-2=16-8x
=>-x+8x=16+2
=>7x=18
=>\(x=\dfrac{18}{7}\)

a: \(\dfrac{x}{y}+\dfrac{y}{x}>=2\cdot\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{y}\cdot\dfrac{y}{x}}=2\)
b: \(\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}>=\dfrac{4}{x+y}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+y}{xy}>=\dfrac{4}{x+y}\)
=>\(\left(x+y\right)^2>=4xy\)
=>\(x^2+2xy+y^2-4xy>=0\)
=>\(x^2-2xy+y^2>=0\)
=>\(\left(x-y\right)^2>=0\)(luôn đúng)

Bài 2:
a) \(\dfrac{-7}{-13}=\dfrac{7}{13}\) là số hưu tỉ dương
b) \(\dfrac{2}{-17}=-\dfrac{2}{17}\) là số hưu tỉ âm
c) \(-\dfrac{-6}{5}=\dfrac{6}{5}\) là số hưu tỉ dương
Bài 3:
a) \(-2\dfrac{1}{4}=-\left(2+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)=-\dfrac{9}{4}\)
b) \(6\dfrac{2}{3}=6+\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{20}{3}\)
c) \(-3\dfrac{1}{4}=-\left(3+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)=-\dfrac{13}{4}\)

a: \(x^2+y^2>=2xy\)
=>\(x^2-2xy+y^2>=0\)
=>\(\left(x-y\right)^2>=0\)(luôn đúng)
b: \(x^2+4xy>=-4y^2\)
=>\(x^2+4xy+4y^2>=0\)
=>\(\left(x+2y\right)^2>=0\)(luôn đúng)
c: \(2\left(x^2+y^2\right)>=\left(x+y\right)^2\)
=>\(2x^2+2y^2-x^2-2xy-y^2>=0\)
=>\(x^2-2xy+y^2>=0\)
=>\(\left(x-y\right)^2>=0\)(luôn đúng)

d: A={11;12;13;14;15;16;17;18;19;20}
A={x\(\in\)N|11<=x<=20}
Số phần tử của tập hợp A là 20-11+1=20-10=10(phần tử)
e: D={10;11;12;13;14;15}
D={x\(\in\)N|9<x<=15}
D có 15-10+1=5+1=6 phần tử
f: F={1;2;3;...;30}
F={x\(\in Z^+\)|x<=30}
Số phần tử của tập hợp F là 30-1+1=30(phần tử)
g: G={x\(\in\)N|x>5}
G={6;7;8;...}
G có vô số phần tử
h: C={18;19;...;100}
C={x\(\in\)N|18<=x<=100}
Số phần tử của tập hợp C là 100-18+1=83(phần tử)
i: B={102;105;...;999}
B={x\(\in\)N|100<=x<=999;x\(⋮\)3}
Số phần tử của tập hợp B là \(\left(999-102\right):3+1=300\)(phần tử)

a: 2a+3>2b+3
=>2a>2b
=>a>b
b: -3a-1>=-3b-1
=>\(-3a>=-3b\)
=>3a<=3b
=>a<=b
c: 5-2a<5-a-b
=>5-2a+a<5-b
=>5-a<5-b
=>a-5>b-5
=>a>b



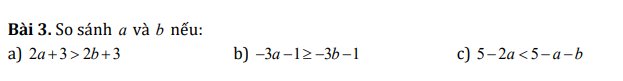
Gọi độ dài mảnh đất ban đầu là x(m)
(Điều kiện: x>0)
Chiều dài mảnh đất mới là x+8(m)
Chiều rộng mảnh đất mới là x+4(m)
Diện tích mảnh đất đó tăng thêm 360m2 nên ta có:
\(\left(x+8\right)\left(x+4\right)-x^2=360\)
=>\(x^2+12x+32-x^2=360\)
=>12x=360-32=328
=>\(x=\dfrac{328}{12}=\dfrac{82}{3}\left(nhận\right)\)
Diện tích mảnh đất ban đầu là \(\left(\dfrac{82}{3}\right)^2=\dfrac{6724}{9}\left(m^2\right)\)