giải phương trình sau x^2 - 5 x + 3 = 0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\left(x^2-y^2\right)^2+4x^2y^2+x^2-2y^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^4+y^4-2x^2y^2+4x^2y^2+x^2-2y^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^4+y^4+2x^2y^2+x^2-2y^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x^2+y^2\right)^2-2\left(x^2+y^2\right)+3x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+y^2-1\right)^2=1-3x^2\le1\)
\(\Rightarrow-1\le x^2+y^2-1\le1\)
\(\Rightarrow0\le x^2+y^2\le2\)
\(\Rightarrow A_{min}=0\) khi \(x=y=0\)
\(A_{max}=2\) khi \(x=0;y=\pm\sqrt{2}\)

\(P=\dfrac{x+1}{x^3-1}\left[\left(4x^2-1\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{2x-1}-\dfrac{1}{2x+1}+1\right)-5\right]\)
\(=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\cdot\left[\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)\cdot\dfrac{2x+1-2x+1+4x^2-1}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}-5\right]\)
\(=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\cdot\left(4x^2+1-5\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\cdot\left(4x^2-4\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\cdot4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{4\left(x+1\right)^2}{x^2+x+1}\)

\(B=-3x^2+4x+1\)
\(=-3\left(x^2-\dfrac{4}{3}x-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\)
\(=-3\left(x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{4}{9}-\dfrac{7}{9}\right)\)
\(=-3\left(x-\dfrac{2}{3}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{3}< =\dfrac{7}{3}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi \(x-\dfrac{2}{3}=0\)
=>\(x=\dfrac{2}{3}\)

Đặt \(x^2+4=a;1-6x=b\)
=>\(a+b=x^2+4+1-6x=x^2-6x+5\)
\(\left(x^2+4\right)^3+\left(1-6x\right)^3=\left(x^2-6x+5\right)^3\)
=>\(a^3+b^3=\left(a+b\right)^3\)
=>\(\left(a+b\right)^3-\left(a+b\right)^3+3ab\left(a+b\right)=0\)
=>3ab(a+b)=0
=>ab(a+b)=0
=>\(\left(x^2+4\right)\left(1-6x\right)\left(x^2-6x+5\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(1-6x\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x-5\right)=0\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}1-6x=0\\x-1=0\\x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{6}\\x=1\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)


Bài 5:
a: \(D=\dfrac{6x}{4x^2-9}-\dfrac{x}{3-2x}+\dfrac{x}{2x+3}-1\)
\(=\dfrac{6x}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)}+\dfrac{x}{2x-3}+\dfrac{x}{2x+3}-1\)
\(=\dfrac{6x+x\left(2x+3\right)+x\left(2x-3\right)-4x^2+9}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{6x+x\left(2x+3+2x-3\right)-4x^2+9}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{6x+9}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)}=\dfrac{3}{2x-3}\)
b: \(D=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
=>\(\dfrac{3}{2x-3}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
=>2x-3=-6
=>2x=-3
=>\(x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\left(loại\right)\)
c: Để D nguyên thì \(3⋮2x-3\)
=>\(2x-3\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{2;1;3;0\right\}\)
Bài 6:
a: \(P=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}+\dfrac{x}{x-2}+\dfrac{2x+4}{4-x^2}\right)\cdot\left(1+\dfrac{5}{x-3}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}+\dfrac{x}{x-2}-\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x-3+5}{x-3}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}+\dfrac{x}{x-2}-\dfrac{2}{x-2}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}+1\right)\cdot\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}=\dfrac{x-2+x+2}{x+2}\cdot\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}=\dfrac{2x}{x-3}\)
b: Khi x=-1 thì \(P=\dfrac{2\cdot\left(-1\right)}{-1-3}=\dfrac{-2}{-4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c: \(P=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x}{x-3}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x}{x-3}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
=>3x=x-3
=>2x=-3
=>\(x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)(nhận)
d: Để P là số tự nhiên thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x⋮x-3\\\dfrac{2x}{x-3}>=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-6+6⋮x-3\\\dfrac{x}{x-3}>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6⋮x-3\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>3\\x< =0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;3;-3;6;-6\right\}\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>3\\x< =0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x\in\left\{4;5;6;0;9;-3\right\}\)


Chắc em ghi đề sai
Nếu \(a+b+c=1\) thì \(\dfrac{a}{1+a^2}+\dfrac{b}{1+b^2}+\dfrac{c}{1+c^2}\le\dfrac{9}{10}\)
Còn \(a+b+c=3\) thì \(\dfrac{a}{1+a^2}+\dfrac{b}{1+b^2}+\dfrac{c}{1+c^2}\le\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Chứng minh BĐT dưới quá đơn giản chỉ bằng 1 dòng AM-Gm cho mẫu.
Còn BĐT trên thì sử dụng đánh giá (thông qua kĩ thuật UCT):
\(\dfrac{x}{1+x^2}\le\dfrac{36x+3}{50}\)
Nhân chéo quy đồng thì BĐT này tương đương:
\(\left(3x-1\right)^2\left(4x+3\right)\ge0\) (luôn đúng với x dương)
Áp dụng cho a;b;c rồi cộng vế là xong

Xét tứ giác BFHD có \(\widehat{BFH}+\widehat{BDH}=90^0+90^0=180^0\)
nên BFHD là tứ giác nội tiếp
Xét tứ giác CEHD có \(\widehat{CEH}+\widehat{CDH}=90^0+90^0=180^0\)
nên CEHD là tứ giác nội tiếp
Xét tứ giác AEHF có \(\widehat{AEH}+\widehat{AFH}=90^0+90^0=180^0\)
nên AEHF là tứ giác nội tiếp
Ta có: \(\widehat{FDH}=\widehat{FBH}\)(BFHD nội tiếp)
\(\widehat{EDH}=\widehat{ECH}\)(EHDC nội tiếp)
mà \(\widehat{FBH}=\widehat{ECH}\left(=90^0-\widehat{BAC}\right)\)
nên \(\widehat{FDH}=\widehat{EDH}\)
=>DH là phân giác của góc FDE
Ta có: \(\widehat{EFH}=\widehat{EAH}\)(AEHF nội tiếp)
\(\widehat{DFH}=\widehat{DBH}\)(BFHD nội tiếp)
mà \(\widehat{EAH}=\widehat{DBH}\left(=90^0-\widehat{ACD}\right)\)
nên \(\widehat{EFH}=\widehat{DFH}\)
=>FH là phân giác của góc EFD
Xét ΔEFD có
DH,FH là các đường phân giác
DH cắt FH tại H
Do đó: H là tâm đường tròn nội tiếp của ΔEFD
hay H cách đều ba cạnh của ΔEFD
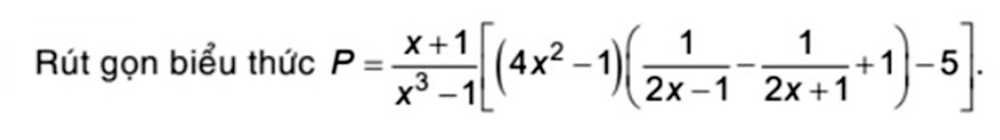

\(x^2-5x+3=0\\ \Delta=b^2-4ac=\left(-5\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot3=13>0\\ x_1=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-\left(-5\right)-\sqrt{13}}{2\cdot1}=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{13}}{2}\\ x_2=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-\left(-5\right)+\sqrt{13}}{2\cdot1}=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{13}}{2}\\ \text{vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm là }x_1=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{13}}{2};x_2=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{13}}{2}\)