Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a)
\(8,4-1,2x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow1,2x=8,4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{8,4}{1,2}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=7\)
b)
\(8x-5=2x+13\\ \Leftrightarrow8x-2x=13+5\\ \Leftrightarrow6x=18\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{18}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3\)
c)
\(7-3x=25-9x\\ \Leftrightarrow-3x+9x=25-7\\ \Leftrightarrow6x=18\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{18}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3\)
d)
\(6x-4+x=3\left(x+4\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow7x-4=3x+12\\ \Leftrightarrow7x-3x=12+4\\ \Leftrightarrow4x=16\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{16}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=4\)
e)
\(5\left(1-3x\right)=-2\left(4x+5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow5-15x=-8x-10\\ \Leftrightarrow-8x+15x=5+10\\ \Leftrightarrow7x=15\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{15}{7}\)
f)
\(-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(x+1\right)+1=2x+\dfrac{1}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{1}{2}x-\dfrac{1}{2}+1=2x+\dfrac{1}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{1}{2}=2x+\dfrac{1}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow2x+\dfrac{1}{2}x=\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{2}x=\dfrac{1}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{6}:\dfrac{5}{2}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{15}\)

a) \(-3x+1=0\) là phương trình bậc nhất 1 ẩn
Có hệ số của x là `-3`
Hạng tử tự do là: 1
b) \(2,5x-\dfrac{1}{2}=0\) là phương trình bậc nhất 1 ẩn
Có hệ số của x là `2,5`
Hạng tử tự do là: `-1/2`
c) \(x^2-4\) không phải là phương trình bậc nhất 1 ẩn
d) \(0x+3=0\) không phải là phương trình bậc nhất 1 ẩn
e) \(\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{2}{7}x=0\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{2}{7}x+\dfrac{1}{3}=0\) là phương trình bậc nhất 1 ẩn
Có hệ số của x là: `-2/7`
Hạng tử tự do là: `1/3`
f) \(\dfrac{5}{3}x=0\) là phương trình bậc nhất 1 ẩn
Có hệ số của x là: `5/3`
Hạng tử tự do là: 0

Tổng độ dài của 2 sợi dây là:
\(2\times28=56\left(m\right)\)
Độ dài sợi dây thứ hai là:
\(56-25=31\left(m\right)\)
Đáp số: 31m
☘ Giải :
Tổng độ dài của 2 sợi dây là :
28 x 2 = 56 ( m )
Độ dài của sợi dâu thứ hai là :
56 - 25 = 31 ( m )
Đáp số : 31 m

Sau 12 ngày thì số gạo còn lại đủ cho 50 người ăn trong:
\(30-12=18\) (ngày)
Số gạo còn lại nếu ăn trong 1 ngày thì cần số người là:
\(50\times18=900\) (người)
Sau khi nhận thêm người thì tổng số người có ở đó là:
\(50+10=60\) (người)
Số gạo đó đủ cho 60 người ăn trong:
\(900:60=15\) (ngày)
Đáp số: ...
Số gạo còn lại đủ ăn trong số ngày dự định là:
30 - 12 = 18 (ngày)
Số người sau khi có 10 người đến:
50 + 10 = 60 (người)
Do số người ăn và số ngày ăn là hai đại lượng tỉ lệ nghịch nên số ngày ăn ứng với 60 người là:
18 × 50 : 60 = 15 (ngày)

Đáy bé của hình thang là:
\(8:2=4\left(cm\right)\)
Đổi: \(54m^2=540000cm^2\)
Chiều cao của hình thang là:
\(540000\times2:\left(8+4\right)=90000\left(cm\right)\)
Đáp số: ...
Đáy bé của hình thang là: 8 : 2 = 4(cm)
4cm = 0,04 m
8 cm = 0,08 m
Chiều cao của hình thang là:
54 x 2 : (0,08 + 0,04) = 900 (m)
Đs:..

Lập bảng ta có:
| Số thứ tự của các bông hoa | Số cánh hoa của mỗi bông |
| 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 6 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 8 |
| 5 | 4 |
| 6 | 5 |
| 7 | 6 |
a; Theo bảng trên ta có dãy số mà Loan ghi có 7 số hạng. Số đầu tiên trong dãy số đó là số 5
b; Bông Hoa có nhiều cánh hoa nhất có 8 cánh.
c; Trong số bông hoa mà Loan đếm không có hoa Ý lan vì hoa đó chỉ có 1 cánh, mà trong số bông hoa Loan ghi không có hoa nào có 1 cánh hoa.
a) Dãy trên có 7 số
Số đầu tiên trong dãy là số 5
b) Bông hoa có nhiều cánh hoa nhất có 8 cánh hoa
c) Chưa xác định được vì đề thiếu dữ liệu

a) \(P=\dfrac{x}{\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)}-\dfrac{y}{\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(1+\sqrt{x}\right)}-\dfrac{xy}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)}\)
ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0;y\ge0\\\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\ne0\\\sqrt{x}+1\ne0\\1-\sqrt{y}\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0;y\ge0\\x^2+y^2>0\\y\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(P=\dfrac{x\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}-\dfrac{y\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}-\dfrac{xy\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{x\sqrt{x}+x-y+y\sqrt{y}-xy\sqrt{x}-xy\sqrt{y}}{\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{\left(x\sqrt{x}+y\sqrt{y}\right)+\left(x-y\right)-\left(xy\sqrt{x}+xy\sqrt{y}\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(x-\sqrt{xy}+y\right)+\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}\right)-xy\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(x-\sqrt{xy}+y+\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}-xy\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{\left(x-xy\right)+\left(-\sqrt{y}+y\right)+\left(\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{xy}\right)}{\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{x\left(1-y\right)-\sqrt{y}\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)+\sqrt{x}\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)}{\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{x\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(1+\sqrt{y}\right)-\sqrt{y}\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)+\sqrt{x}\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)}{\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(x+x\sqrt{y}-\sqrt{y}+\sqrt{x}\right)}{\left(1-\sqrt{y}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(P=\dfrac{x+x\sqrt{y}-\sqrt{y}+\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(P=\dfrac{\left(x+\sqrt{x}\right)+\left(x\sqrt{y}-\sqrt{y}\right)}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(P=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)+\sqrt{y}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(P=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{xy}-\sqrt{y}\right)}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(P=\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{xy}-\sqrt{y}\)
b) \(P=2\) khi:
\(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{xy}-\sqrt{y}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{y}+1\right)-\sqrt{y}-1=2-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{y}+1\right)-\left(\sqrt{y}+1\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{y}+1\right)=1\)
Mà: x,y là nguyên \(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}-1,\sqrt{y}+1\inƯ\left(1\right)=\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
Mặt khác: \(\sqrt{y}+1\ge1\) nên ta có:
\(\sqrt{y}+1=1\Leftrightarrow y=0\) (tm)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}-1=1\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=2\Leftrightarrow x=4\) (tm)
Vậy: \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(4;0\right)\)

Trung bình cộng của các số:
\(\left(12+12+14+10+19+67+4+5797+34+3+4444+44346+978964+565\right):14=\dfrac{1034291}{14}\)Đáp số: ...

Tổng số thóc của cả hai kho là:
`1165\times2=2330(kg)`
Số thóc của kho B là:
`2330-1087=1243(kg)`
Tổng số thóc của cả 2 kho là:
\(1165.2=2330\) (kg)
Kho B có số ki-lô-gam thóc là:
\(2330-1087=1243\) (kg)
Đáp số: \(1243\) kg
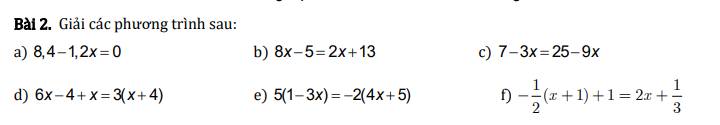

a)
\(\dfrac{4x-5}{3}=\dfrac{1+3x}{2}\\ \Leftrightarrow2\left(4x-5\right)=3\left(1+3x\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow8x-10=3+9x\\ \Leftrightarrow9x-8x=-10-3\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-13\)
b)
\(\dfrac{3x-1}{4}+\dfrac{6x-2}{8}=\dfrac{1-3x}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x-1}{4}+\dfrac{2\left(3x-1\right)}{8}=\dfrac{-\left(3x-1\right)}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x-1}{4}+\dfrac{3x-1}{4}+\dfrac{3x-1}{6}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{6}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3x-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3x=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
c)
\(\dfrac{7x-1}{6}+2x=\dfrac{16-x}{5}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{7x-1+6\cdot2x}{6}=\dfrac{16-x}{5}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{19x-1}{6}=\dfrac{16-x}{5}\\ \Leftrightarrow5\left(19x-1\right)=6\left(16-x\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow95x-5=96-6x\\ \Leftrightarrow95x+6x=96+5\\ \Leftrightarrow101x=101\\ \Leftrightarrow x=1\)
d)
\(\dfrac{5x+9}{3}-\dfrac{7x-9}{4}=\dfrac{3\left(x+3\right)}{4}+\dfrac{1}{2}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5x+9}{3}-\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{3x+9}{4}+\dfrac{7x-9}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(5x+9\right)-3}{6}=\dfrac{3x+9+7x-9}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{10x+15}{6}=\dfrac{10x}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow6\cdot5x=2\cdot\left(10x+15\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow30x=20x+30\\ \Leftrightarrow30x-20x=30\\ \Leftrightarrow10x=30\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{30}{10}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3\)
\(a,\dfrac{4x-5}{3}=\dfrac{1+3x}{2}\\ \Rightarrow2\left(4x-5\right)=3\left(1+3x\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow8x-10=3+9x\\ \Leftrightarrow9x-8x=-3-10\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-13\\ ---\\ b,\dfrac{3x-1}{4}+\dfrac{6x-2}{8}=\dfrac{1-3x}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x-1}{4}+\dfrac{2\left(3x-1\right)}{4.2}=\dfrac{1-3x}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x-1}{4}+\dfrac{3x-1}{4}=\dfrac{1-3x}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x-1+3x-1}{4}=\dfrac{1-3x}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{6x-2}{4}=\dfrac{1-3x}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(3x-1\right)}{2.2}=\dfrac{1-3x}{6}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x-1}{2}=\dfrac{1-3x}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow6\left(3x-1\right)=2\left(1-3x\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow18x-6=2-6x\\ \Leftrightarrow18x+6x=2+6\\ \Leftrightarrow24x=8\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{8}{24}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)