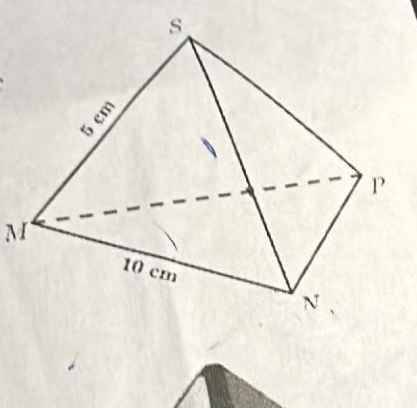
 tính các độ dài các cạnh còn lại của hình chóp . Xác định số đo các của góc tam giác mnp
tính các độ dài các cạnh còn lại của hình chóp . Xác định số đo các của góc tam giác mnp
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

4(x-2)-3(x+1)=5
=>\(4x-8-3x-3=5\)
=>\(x-11=5\)
=>x=11+5=16
\(4\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x+1\right)=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-8-3x-3=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x-3x\right)=5+8+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=16\)
Vậy \(x=16\)

\(\text{Sửa đề }:x^4-3x+2=(x-1)(x^3+ax^2+bx-2)\\\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^3+x^3-x^2+x^2-x-2x+2=(x-1)(x^3+ax^2+bx-2)\\\Leftrightarrow x^3(x-1)+x^2(x-1)+x(x-1)-2(x-1)=(x-1)(x^3+ax^2+bx-2)\\\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(x^3+x^2+x-2)=(x-1)(x^3+ax^2+bx-2)\\\Rightarrow a=b=1\)

Bài 2:
Độ dài của `1/3` quãng đường đầu là:
`1/3*600=200` (km)
Thời gian xe đi trên `1/3` quãng đường đầu là:
\(\dfrac{200}{x}\left(h\right)\)
Quãng đường còn lại là: `600 - 200 = 400`(km)
Vận tốc của xe khi đi trên quãng đường còn lại: `x+10` (km/h)
Thời gian xe đi trên quãng đường còn lại là:
\(\dfrac{400}{x+10}\left(h\right)\)
Biểu thức thể hiện thời gian xe đi từ Hà Nội đến Quãng Ngãi là:
\(\dfrac{200}{x}+\dfrac{400}{x+10}=\dfrac{200\left(x+10\right)}{x\left(x+10\right)}+\dfrac{400x}{x\left(x+10\right)}=\dfrac{200x+2000+400x}{x\left(x+10\right)}=\dfrac{600x+2000}{x\left(x+10\right)}\)

a) \(x^2-36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)\left(x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: ...
b) \(x^2-10x+25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2\cdot x\cdot5+5^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
Vậy: ...
a) \(x^2-36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=36\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=\left(\pm6\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{6;-6\right\}\)
b) \(x^2-10x+25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2.x.5+5^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
Vậy \(x=5\)

a) \(\left(3x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x+2\right)^2\)
\(=\left(3x^2+6x-x-2\right)-\left(x+2\right)^2\)
\(=\left(3x^2+5x-2\right)-\left(x^2+4x+4\right)\)
\(=3x^2+5x-2-x^2-4x-4\)
\(=2x^2+x-6\)
b) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-1\right)-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(=x^2-1-x^2+2x-1\)
\(=2x-2\)
c) \(\left(x-4\right)\left(4+x\right)+2x\left(x-3\right)\)
\(=\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)+2x\left(x-3\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-16\right)+2x^2-6x\)
\(=x^2-16+2x^2-6x\)
\(=3x^2-6x-16\)
d) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-1\right)+\left(x+2\right)^3\)
\(=\left(x^3-x-x^2+1\right)+\left(x^3+6x^2+12x+8\right)\)
\(=x^3-x-x^2+1+x^3+6x^2+12x+8\)
\(=2x^3+5x^2+11x+9\)
e) \(\left(2x-1\right)^2-\left(2x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)\)
\(=\left(4x^2-4x+1\right)-\left(2x^2+10x-5x-25\right)\)
\(=\left(4x^2-4x+1\right)-\left(2x^2+5x-25\right)\)
\(=4x^2-4x+1-2x^2-5x+25\)
\(=2x^2-9x+26\)
f) \(\left(3x+1\right)^2-\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)\)
\(=\left(9x^2+6x+1\right)-\left(x^4+2x^2-x^2-2\right)\)
\(=\left(9x^2+6x+1\right)-\left(x^4+x^2-2\right)\)
\(=9x^2+6x+1-x^4-x^2+2\)
\(=-x^4+8x^2+6x+3\)
g) \(\left(x^2+1\right)^2-\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)\)
\(=\left(x^4+2x^2+1\right)-\left(x^4+2x^2-x^2-2\right)\)
\(=\left(x^4+2x^2+1\right)-\left(x^4+x^2-2\right)\)
\(=x^4+2x^2+1-x^4-x^2+2\)
\(=x^2+3\)
h) \(\left(2x^2-4\right)^2-\left(2x^2+4\right)^2\)
\(=\left(4x^4-16x^2+16\right)-\left(4x^4+16x^2+16\right)\)
\(=4x^4-16x^2+16-4x^4-16x^2-16\)
\(=-32x^2\)

Xét ΔABC vuông tại A có \(sinACB=\dfrac{AB}{BC}\)
=>\(\dfrac{5}{BC}=sin30=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
=>BC=10(cm)
ΔABC vuông tại A
=>\(AB^2+AC^2=BC^2\)
=>\(AC=\sqrt{10^2-5^2}=5\sqrt{3}\left(cm\right)\)

x=2024 nên x-1=2023
\(H=x^{14}-2023x^{13}-2023x^{12}-...-2023x-2023\)
\(=x^{14}-x^{13}\left(x-1\right)-x^{12}\left(x-1\right)-...-x\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\)
\(=x^{14}-x^{14}+x^{13}-x^{13}+x^{12}-...-x^2+x-x+1\)
=1

a)
\(\dfrac{x^4+12x^2-5x}{-x}=-\dfrac{x^4}{x}-\dfrac{12x^2}{x}+\dfrac{-5x}{-x}=-x^3-12x+5\)
b)
\(\dfrac{15x^5y^9-10x^3y^5+25x^4y^4}{5x^2y^2}=\dfrac{15x^5y^9}{5x^2y^2}-\dfrac{10x^3y^5}{5x^2y^2}+\dfrac{25x^4y^4}{5x^2y^2}=3x^3y^7-2xy^3+5x^2y^2\)
`a)`
`(x^4 + 12x^2 -5x):(-x)`
`=[x^4 : (-x)] + [12x^2 : (-x)] - [5x:(-x)]`
`=-x^3 - 12x + 5`
`b)`
`(15 x^5 y^9 - 10 x^3 y^5 + 25 x^4 y^4) : 5x^2 y^2`
`=(15 x^5 y^9 : 5 x^2 y^2) - (10 x^3 y^5 : 5x^2 y^2) + (25 x^4 y^4 : 5 x^2 y^2)`
`=3 x^3 y^7 - 2 x y^3 + 5 x^2 y^2`

Xét ΔMNP có
A,D lần lượt là trung điểm của MN,MP
=>AD là đường trung bình của ΔMNP
=>AD//NP và \(AD=\dfrac{NP}{2}\)
Xét ΔHNP có
B,C lần lượt là trung điểm của HN,HP
=>BC là đường trung bình của ΔHNP
=>BC//NP và \(BC=\dfrac{NP}{2}\)
Ta có: AD//NP
BC//NP
Do đó: AD//BC
Ta có: \(AD=\dfrac{NP}{2}\)
\(BC=\dfrac{NP}{2}\)
Do đó: AD=BC
Xét tứ giác ABCD có
AD//BC
AD=BC
Do đó: ABCD là hình bình hành

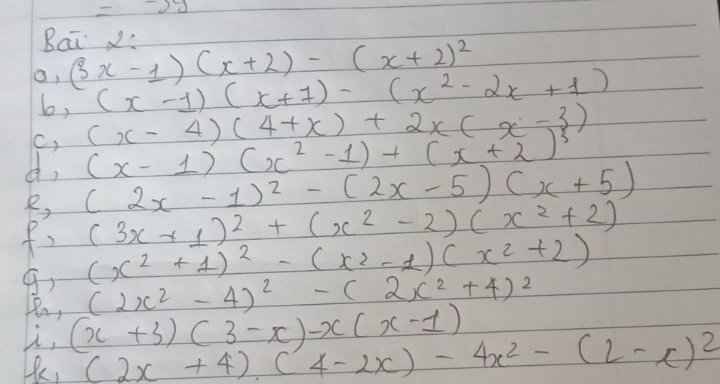
Vì \(S.MNP\) là hình chóp tam giác đều
nên \(SM=SN=SP=5\left(cm\right)\) và \(\triangle MNP\) đều (t/c)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}MN=NP=PM=10\left(cm\right)\\\widehat{MNP}=\widehat{NPM}=\widehat{PMN}=60^{\circ}\end{matrix}\right.\)