a) Cho p là số nguyên tố lớn hơn 3 chứng minh rằng 25 - p ^ 2 chỉ hết cho 24.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Giải:
Theo bài ra ta có:
\(\overline{ba}\) = 2 x \(\overline{ab}\) + 18
10b + a = 20a + 2b + 18
10b - 2b = 20a - a + 18
8b = 19a + 8
8b + 19b = 19b + 19a + 8
27b = 19.(a + b) + 18 (1)
Thay a + b = 9 vào (1)
27b = 19.9 + 18
27b = 171 + 18
27b = 189
b = 189 : 27
b = 7
a = 9 - b
a = 9 - 7
a = 2
Vậy \(\overline{ab}\) = 27

\(x^2+2,5x+5\)
\(=x^2+2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{5}{4}+\dfrac{25}{16}+\dfrac{55}{16}\)
\(=\left(x+\dfrac{5}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{55}{16}>=\dfrac{55}{16}>0\forall x\)
=>ĐPCM

Ta có: \(\dfrac{x-1}{3}=\dfrac{x-2}{2}\)
=>3(x-2)=2(x-1)
=>3x-6=2x-2
=>3x-2x=-2+6
=>x=4

\(x\times\) 2 = 5
\(x=5:2\)
\(x=\frac52\)
Vậy \(x=\frac52\)

Đổi 5h 24 phút = 27/5 giờ
Gọi độ dài quãng đường AB là x (km) với x>0
Thời gian xe đi từ A đến B là: \(\dfrac{x}{50}\) giờ
Thời gian xe đi từ B về A là: \(\dfrac{x}{40}\) giờ
Tổng thời gian cả đi và về là: \(\dfrac{x}{50}+\dfrac{x}{40}=\dfrac{9x}{200}\) giờ
Do cả đi và về mất 27/5 giờ nên ta có pt:
\(\dfrac{9x}{200}=\dfrac{27}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=120\left(km\right)\)

3. Chứng minh công thức:
AF/AB + BE/BC + CN/CA = 1 trong tam giác ABC
Giả thiết:
- Tam giác ABC.
- Các điểm F, E, N lần lượt nằm trên các cạnh AB, BC, CA.
Cách chứng minh:
Trường hợp đặc biệt:
Nếu F, E, N là các điểm chia các cạnh theo cùng một tỉ lệ (ví dụ: F chia AB theo tỉ lệ x, E chia BC theo tỉ lệ y, N chia CA theo tỉ lệ z sao cho x + y + z = 1).
Chứng minh tổng quát:
- Gọi AF = x·AB, BE = y·BC, CN = z·CA, với x, y, z ∈ (0;1).
- Khi đó:
\(\frac{A F}{A B} + \frac{B E}{B C} + \frac{C N}{C A} = x + y + z\) - Nếu ba điểm F, E, N chia ba cạnh theo tỉ lệ x, y, z sao cho x + y + z = 1, thì tổng trên bằng 1.
Trường hợp đặc biệt:
Nếu F, E, N là trung điểm các cạnh, thì mỗi phân số đều bằng 1/2, tổng lại là 3/2 ≠ 1.
Vậy công thức đúng khi ba điểm chia ba cạnh theo tỉ lệ x, y, z với x + y + z = 1.

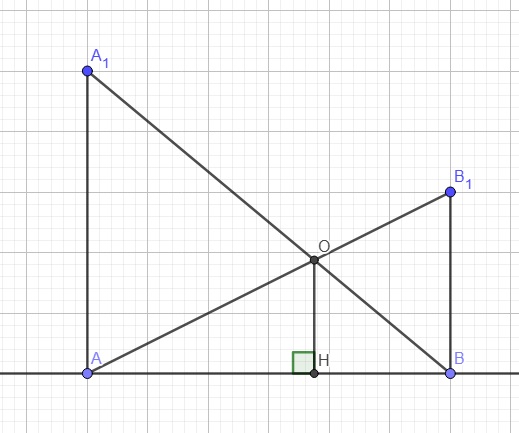
Gọi H là hình chiếu vuông góc của O lên d
\(\Rightarrow AA_1||OH||BB_1\)
Áp dụng định lý Thales trong tam giác \(ABA_1\)
\(\dfrac{OH}{AA_1}=\dfrac{BH}{AB}\)
Áp dụng định lý Thales trong tam giác \(ABB_1\)
\(\dfrac{OH}{BB1}=\dfrac{AH}{AB}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{OH}{AA_1}+\dfrac{OH}{BB_1}=\dfrac{BH}{AB}+\dfrac{AH}{AB}\)
\(\Rightarrow OH.\left(\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{b}\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow OH=\dfrac{a.b}{a+b}\)
Do a, b không đổi \(\Rightarrow OH\) không đổi
Hay khoảng cách từ O đến d không đổi khi A, B chạy trên d

Giải chi tiết:
Bước 1: Xác định phương trình đường thẳng CD
Giả sử:
- Tọa độ của điểm A và B thay đổi, nhưng luôn thỏa mãn điều kiện bài toán.
- Điểm C và D được xác định dựa trên A và B qua một quy tắc cụ thể (ví dụ: trung điểm, hình chiếu, giao điểm đường phân giác...).
- Gọi phương trình đường thẳng CD có dạng:
\(a x + b y + c = 0 (\text{ph}ụ\&\text{nbsp};\text{thu}ộ\text{c}\&\text{nbsp};\text{v} \overset{ˋ}{\text{a}} \text{o}\&\text{nbsp};\text{t}ọ\text{a}\&\text{nbsp};độ\&\text{nbsp};\text{A},\&\text{nbsp};\text{B})\)
Bước 2: Tìm điểm cố định mà CD luôn đi qua
- Giả định tồn tại điểm cố định \(M \left(\right. x_{0} , y_{0} \left.\right)\) sao cho CD luôn đi qua \(M\) với mọi vị trí của A và B (\(A \neq B\)).
- Thay \(M \left(\right. x_{0} , y_{0} \left.\right)\) vào phương trình CD:
\(a \left(\right. x_{0} , y_{0} , A , B \left.\right) \cdot x_{0} + b \left(\right. x_{0} , y_{0} , A , B \left.\right) \cdot y_{0} + c \left(\right. x_{0} , y_{0} , A , B \left.\right) = 0 \forall A , B\) - Phân tích phương trình:
Biến đổi phương trình về dạng đa thức theo tham số liên quan đến A và B. Để phương trình đúng với mọi A, B, hệ số của các hạng tử chứa tham số phải bằng 0.
Bước 3: Giải hệ phương trình
- Ví dụ: Nếu phương trình có dạng:
\(\left(\right. m + 1 \left.\right) x_{0} - \left(\right. 2 m - 3 \left.\right) y_{0} + 5 = 0 \forall m\) - Tách hệ số của \(m\):
\(m \left(\right. x_{0} - 2 y_{0} \left.\right) + \left(\right. x_{0} + 3 y_{0} + 5 \left.\right) = 0 \forall m\) - Đồng nhất hệ số:
\(\left{\right. x_{0} - 2 y_{0} = 0 \\ x_{0} + 3 y_{0} + 5 = 0\) - Giải hệ:
\(x_{0} = 2 y_{0} 2 y_{0} + 3 y_{0} + 5 = 0 \textrm{ }\textrm{ } \Longrightarrow \textrm{ }\textrm{ } y_{0} = - 1 \textrm{ }\textrm{ } \Longrightarrow \textrm{ }\textrm{ } x_{0} = - 2\) - Kết luận: Điểm cố định là \(M \left(\right. - 2 , - 1 \left.\right)\).
- Tách hệ số của \(m\):
Bước 4: Kiểm tra lại
- Thay \(M \left(\right. x_{0} , y_{0} \left.\right)\) vào phương trình CD với các vị trí khác nhau của A, B để xác nhận tính đúng đắn.
Ví dụ minh họa:
Cho tam giác ABC cố định. Trên AB lấy điểm D di động, trên AC lấy điểm E di động sao cho \(A D = C E\). Chứng minh DE luôn đi qua một điểm cố định.
Giải:
- Bước 1: Chọn hệ trục tọa độ, giả sử \(A \left(\right. 0 , 0 \left.\right)\), \(B \left(\right. 1 , 0 \left.\right)\), \(C \left(\right. 0 , 1 \left.\right)\).
- Bước 2: Gọi \(D \left(\right. t , 0 \left.\right)\) trên AB và \(E \left(\right. 0 , t \left.\right)\) trên AC (vì \(A D = C E = t\)).
- Bước 3: Phương trình DE:
\(\frac{x - t}{- t} = \frac{y}{t - 0} \textrm{ }\textrm{ } \Longrightarrow \textrm{ }\textrm{ } x + y = t\) - Bước 4: Phương trình \(x + y = t\) phụ thuộc vào \(t\). Để DE đi qua điểm cố định \(M \left(\right. x_{0} , y_{0} \left.\right)\):
\(x_{0} + y_{0} = t \forall t \textrm{ }\textrm{ } \Longrightarrow \textrm{ }\textrm{ } x_{0} + y_{0} = 0\)
Chọn \(M \left(\right. 1 , - 1 \left.\right)\) (nằm trên đường thẳng \(x + y = 0\)).
Kết luận: DE luôn đi qua điểm cố định \(M \left(\right. 1 , - 1 \left.\right)\).
Đáp án:
Đường thẳng CD luôn đi qua điểm cố định \(M \left(\right. x_{0} , y_{0} \left.\right)\) được xác định bằng cách giải hệ phương trình từ phương trình tổng quát của CD145.
Giải chi tiết:
Bước 1: Xác định vị trí các điểm P, I, K, Q
Giả thiết:
- P là trung điểm của AB.
- Q là trung điểm của AC.
- I và K lần lượt là trung điểm của BC và CA.
Bước 2: Tính chất hình học
- Đường trung bình PQ của tam giác ABC song song với BC và có độ dài bằng \(\frac{1}{2} B C\).
- Tứ giác PIKQ là hình bình hành (do PQ // IK và PI // QK).
Bước 3: Tính diện tích PIKQ
- Diện tích hình bình hành PIKQ = \(\frac{1}{2} \times \text{Di}ệ\text{n}\&\text{nbsp};\text{t} \overset{ˊ}{\imath} \text{ch}\&\text{nbsp};\text{tam}\&\text{nbsp};\text{gi} \overset{ˊ}{\text{a}} \text{c}\&\text{nbsp};\text{ABC}\).
- Giả sử tam giác ABC có diện tích \(S_{A B C}\), khi đó:
\(S_{P I K Q} = \frac{1}{2} S_{A B C}\)
Ví dụ minh họa:
Cho tam giác ABC có diện tích \(20 \textrm{ } \text{cm}^{2}\).
- Diện tích tứ giác PIKQ là:
\(S_{P I K Q} = \frac{1}{2} \times 20 = 10 \textrm{ } \text{cm}^{2}\)
Kết luận:
Diện tích tứ giác PIKQ bằng một nửa diện tích tam giác ABC nếu các điểm P, I, K, Q là trung điểm của các cạnh134.
Công thức tổng quát:
\(S_{P I K Q} = \frac{1}{2} S_{A B C}\)
Đáp án:
Diện tích tứ giác PIKQ là \(\boxed{\frac{1}{2} S_{A B C}}\).
p là số nguyên tố lớn hơn 3
=>p là số lẻ và p không chia hết cho 3
p không chia hết cho 3 nên p=3k+1 hoặc p=3k+2
TH1: p=3k+1
\(25-p^2=25-\left(3k+1\right)^2\)
\(=\left(4-3k-1\right)\left(4+3k+1\right)\)
\(=\left(-3k+3\right)\left(3k+5\right)=-3\left(k-1\right)\left(3k+5\right)⋮3\)(1)
TH2: p=3k+2
\(25-p^2=25-\left(3k+2\right)^2\)
\(=\left(5-3k-2\right)\left(5+3k+2\right)=\left(-3k+3\right)\left(3k+7\right)\)
\(=-3\left(k+1\right)\left(3k+7\right)⋮3\)(2)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra \(25-p^2⋮3\)
p là số lẻ nên p=2k+1
\(25-p^2=25-\left(2k+1\right)^2\)
\(=\left(5-2k-1\right)\left(5+2k+1\right)\)
\(=\left(-2k+4\right)\left(2k+6\right)\)
\(=-4\left(k-2\right)\left(k+3\right)\)
Vì k-2;k+3 có khoảng cách là 5 đơn vị nên (k-2)(k+3)\(⋮\)2
=>\(-4\left(k-2\right)\left(k+3\right)⋮4\cdot2=8\)
=>\(25-p^2⋮8\)
mà \(25-p^2⋮3\)
và ƯCLN(3;8)=1
nên \(25-p^2⋮\left(8\cdot3\right)\)
=>\(25-p^2⋮24\)