n mũ 2 +n+4 chia hết n+1
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\left(27+11\right)\cdot\left(512-\left[14\cdot\left(64-4^2\right):2\right]\right)\\ =33\cdot\left[512-\left[14\cdot\left(64-16\right):2\right]\right]\\ =33\cdot\left(512-14\cdot48:2\right)\\ =33\cdot\left(512-14\cdot24\right)\\ =33\cdot\left(512-336\right)\\ =33\cdot176\\ =5808\)

Ta có: QE\(\perp\)OM
NP\(\perp\)OM
Do đó: QE//NP
Ta có: PQ\(\perp\)Ox
MN\(\perp\)Ox
Do đó: PQ//MN

Gọi số cần tìm có dạng là \(X=\overline{ab}\)
Khi viết thêm chữ số 0 vào giữa hai chữ số thì ta được số mới gấp 6 lần số cũ nên \(\overline{a0b}=6\cdot\overline{ab}\)
=>\(100a+b=6\left(10a+b\right)\)
=>100a+b=60a+6b
=>40a=5b
=>8a=b
=>b=8; a=1
Vậy: Số cần tìm là 18

Bài 8:
1: \(\left(x+y\right)^2-\left(x-y\right)^2\)
\(=\left(x+y+x-y\right)\left(x+y-x+y\right)\)
\(=2x\cdot2y=4xy\)
2: \(\left(2x+3\right)^2-3x\left(2x+1\right)\)
\(=4x^2+12x+9-6x^2-3x\)
\(=-2x^2+9x+9\)
3: \(\left(4-2x\right)\left(4+2x\right)-4x\left(2x+3\right)\)
\(=4^2-\left(2x\right)^2-8x^2-12x\)
\(=16-4x^2-8x^2-12x=-12x^2-12x+16\)
4: \(2\left(x+y\right)\left(x-y\right)+\left(x+y\right)^2-2x^2\)
\(=2\left(x^2-y^2\right)+x^2+2xy+y^2-2x^2\)
\(=2x^2-2y^2-x^2+2xy+y^2=x^2+2xy-y^2\)
5: \(\left(3x+4\right)\left(3x-2\right)-\left(3x+1\right)^2\)
\(=9x^2-6x+12x-8-9x^2-6x-1\)
=-9
6: \(4x\left(x-3\right)-\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)\)
\(=4x^2-12x-\left(4x^2-1\right)\)
\(=4x^2-12x-4x^2+1=-12x+1\)
7: \(\dfrac{3}{2}x^2-\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+3x\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{2}x^2+3x-\left(x^2-1\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{2}x^2+3x-x^2+1=\dfrac{1}{2}x^2+3x+1\)
8: \(2\left(5-x\right)\left(5+x\right)-\left(2x+3\right)^2-x\left(3x+2\right)\)
\(=2\left(25-x^2\right)-4x^2-12x-9-3x^2-2x\)
\(=2\left(25-x^2\right)-7x^2-14x-9\)
\(=50-2x^2-7x^2-14x-9=-9x^2-14x+41\)

Bài 8:
\(1)\left(x+y\right)^2-\left(x-y\right)^2\\ =\left(x^2+2xy+y^2\right)-\left(x^2-2xy+y^2\right)\\ =x^2+2xy+y^2-x^2+2xy-y^2\\ =4xy\\ 2)\left(2x+3\right)^2-3x\left(2x+1\right)\\ =\left(4x^2+12x+9\right)-\left(6x^2+3x\right)\\ =4x^2+12x+9-6x^2-3x\\ =-2x^2+9x+9\\ 3)\left(4-2x\right)\left(4+2x\right)-4x\left(2x+3\right)\\ =\left[4^2-\left(2x\right)^2\right]-\left(8x^2+12x\right)\\ =16-4x^2-8x^2-12x\\ =16-12x^2-12x\\ 4)2\left(x+y\right)\left(x-y\right)+\left(x+y\right)^2-2x^2\\ =2\left(x^2-y^2\right)+\left(x^2+2xy+y^2\right)-2x^2\\ =2x^2-2y^2+x^2+2xy+y^2-2x^2\\ =x^2+2xy-y^2\)
Bài 8:
1: \(\left(x+y\right)^2-\left(x-y\right)^2\)
\(=\left(x+y+x-y\right)\left(x+y-x+y\right)\)
\(=2x\cdot2y=4xy\)
2: \(\left(2x+3\right)^2-3x\left(2x+1\right)\)
\(=4x^2+12x+9-6x^2-3x\)
\(=-2x^2+9x+9\)
3: \(\left(4-2x\right)\left(4+2x\right)-4x\left(2x+3\right)\)
\(=4^2-\left(2x\right)^2-8x^2-12x\)
\(=16-4x^2-8x^2-12x=-12x^2-12x+16\)
4: \(2\left(x+y\right)\left(x-y\right)+\left(x+y\right)^2-2x^2\)
\(=2\left(x^2-y^2\right)+x^2+2xy+y^2-2x^2\)
\(=2x^2-2y^2-x^2+2xy+y^2=x^2+2xy-y^2\)
5: \(\left(3x+4\right)\left(3x-2\right)-\left(3x+1\right)^2\)
\(=9x^2-6x+12x-8-9x^2-6x-1\)
=-9
6: \(4x\left(x-3\right)-\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)\)
\(=4x^2-12x-\left(4x^2-1\right)\)
\(=4x^2-12x-4x^2+1=-12x+1\)
7: \(\dfrac{3}{2}x^2-\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+3x\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{2}x^2+3x-\left(x^2-1\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{2}x^2+3x-x^2+1=\dfrac{1}{2}x^2+3x+1\)
8: \(2\left(5-x\right)\left(5+x\right)-\left(2x+3\right)^2-x\left(3x+2\right)\)
\(=2\left(25-x^2\right)-4x^2-12x-9-3x^2-2x\)
\(=2\left(25-x^2\right)-7x^2-14x-9\)
\(=50-2x^2-7x^2-14x-9=-9x^2-14x+41\)

11.
a)
\(A=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\\=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x\cdot1+1^2\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x\cdot1+1^2\right)\\ =\left(x^3+1^3\right)-\left(x^3-1^3\right)\\ =x^3+1-x^3+1\\ =2\)
=> Giá trị của bt không phụ thuộc vào biến
b)
\(B=\left(2x+6\right)\left(4x^2-12x+36\right)-8x^3+10\\ =\left(2x+6\right)\left[\left(2x\right)^2-2x\cdot6+6^2\right]-8x^3+10\\ =\left[\left(2x\right)^3+6^3\right]-8x^3+10\\ =\left(8x^3+216\right)-8x^3+10\\ =8x^3+216-8x^3+10\\ =226\)
=> Giá trị của bt không phụ thuộc vào biến
6.
\(a)\left(x+1\right)^3=x^3+3\cdot x^2\cdot1+3\cdot x\cdot1^2+1^3=x^3+3x^2+3x+1\\ b)\left(2x+3\right)^3=\left(2x\right)^3+3\cdot\left(2x\right)^2\cdot3+3\cdot2x\cdot3^2+3^3=8x^3+36x^2+54x+27\\ c)\left(x^2+2\right)^3=\left(x^2\right)^3+3\cdot\left(x^2\right)^2\cdot2+3\cdot x^2\cdot2^2+2^3=x^6+6x^4+12x^2+8\\ d)\left(2x+5y\right)^3=\left(2x\right)^3+3\cdot\left(2x\right)^2\cdot5y+3\cdot2x\cdot\left(5y\right)^2+\left(5y\right)^3=8x^3+60x^2y+150xy^2+125y^3\\ e.\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3=x^3+3\cdot x^2\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+3\cdot x\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3=x^3+\dfrac{3}{2}x^2+\dfrac{3}{4}x+\dfrac{1}{8}\\ g.\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x+y^2\right)=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x\right)^3+3\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x\right)^2\cdot y^2+3\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}x\cdot\left(y^2\right)^2+\left(y^2\right)^3\\ =\dfrac{x^3}{8}+\dfrac{3}{4}x^2y^2+\dfrac{3}{2}xy^4+y^6\\ h.\left(x^2-2\right)^3=\left(x^2\right)^3-3\cdot\left(x^2\right)^2\cdot2+3\cdot x^2\cdot2^2-2^3=x^6-6x^4+12x^2-8\)

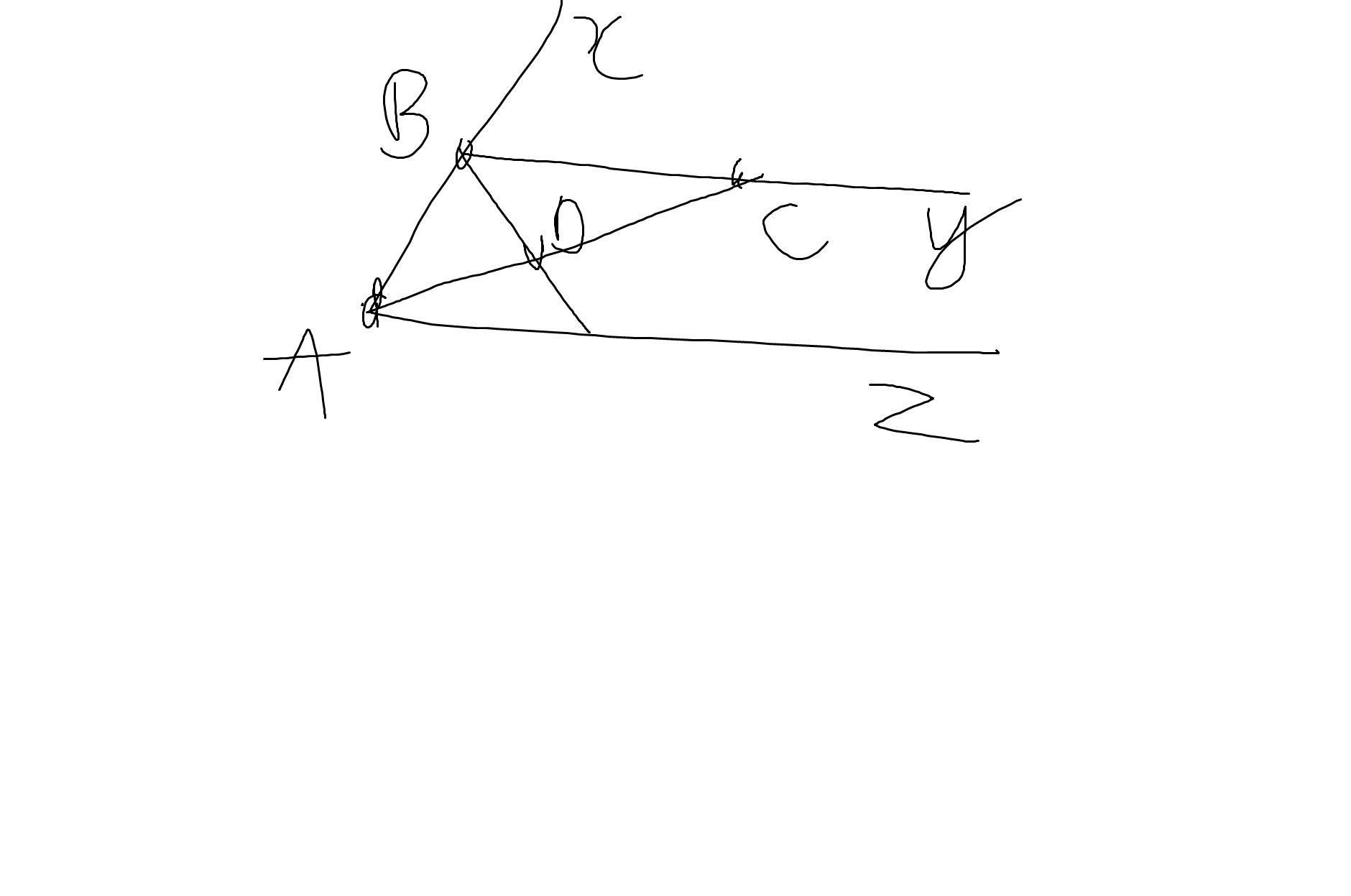
a: Ta có: \(\widehat{xBy}=\widehat{xAz}\left(=60^0\right)\)
mà hai góc này là hai góc ở vị trí đồng vị
nên By//Az
b: Ta có: \(\widehat{ABC}+\widehat{xBC}=180^0\)(hai góc kề bù)
=>\(\widehat{ABC}+60^0=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{ABC}=120^0\)
AC là phân giác của góc zAB
=>\(\widehat{BAC}=\dfrac{\widehat{xAB}}{2}=30^0\)
Xét ΔBAC có \(\widehat{ABC}+\widehat{BAC}+\widehat{BCA}=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{BCA}+120^0+30^0=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{BCA}=30^0\)
c: Ta có: BD là phân giác của góc ABC
=>\(\widehat{ABD}=\dfrac{\widehat{ABC}}{2}=60^0\)
Xét ΔDBA có \(\widehat{DBA}+\widehat{DAB}=60^0+30^0=90^0\)
nên ΔBDA vuông tại D
=>BD\(\perp\)AC

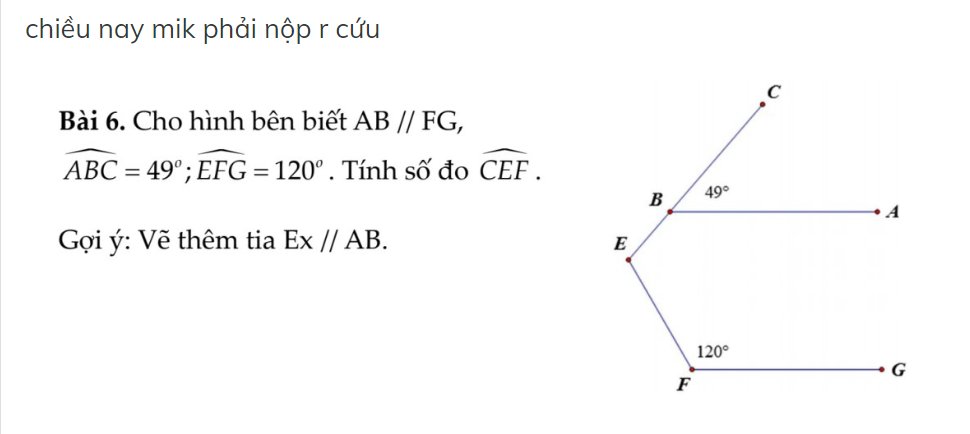
Kẻ Ex // AB
\(\widehat{BEx}\) = \(\widehat{CBA}\) = 490 (đồng vị)
\(\widehat{xEF}\) + \(\widehat{EFG}\) = 1800 (hai góc trong cùng phía)
⇒ \(\widehat{xEF}\) = 1800 - \(\widehat{EFG}\) = 1800 - 1200 = 600
\(\widehat{BEF}\) = \(\widehat{BEx}\) + \(\widehat{xEF}\) = 490 + 600 = 1090
Kết luận: góc BEF là 1090
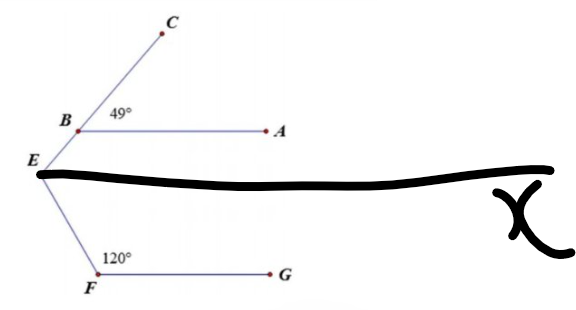
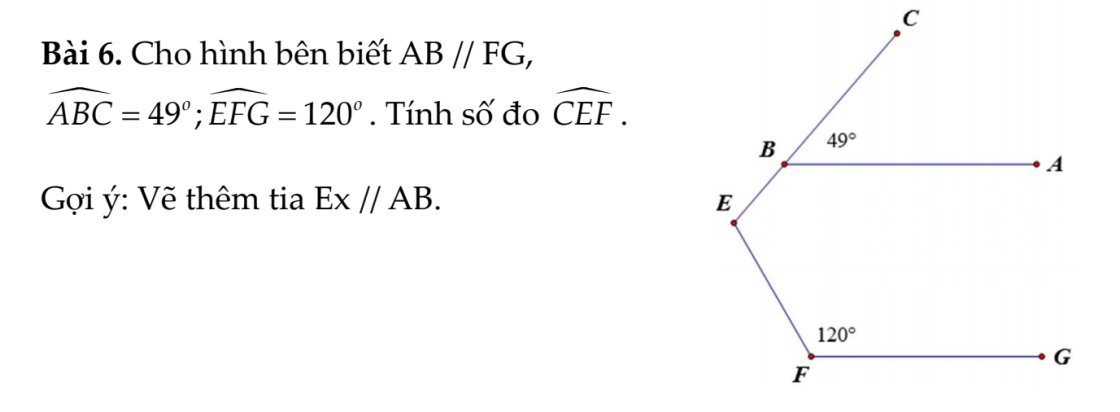
Kẻ Ex//AB(Ex và AB nằm trên cùng mặt phẳng bờ chứa tia BE)
Ta có: Ex//AB
AB//FG
Do đó: Ex//FG
Ex//AB
=>\(\widehat{BEx}=\widehat{CBA}\)(hai góc đồng vị)
=>\(\widehat{xEB}=49^0\)
Ta có: Ex//FG
=>\(\widehat{xEF}+\widehat{EFG}=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{xEF}=180^0-120^0=60^0\)
\(\widehat{BEF}=\widehat{xEB}+\widehat{xEF}=49^0+60^0=109^0\)

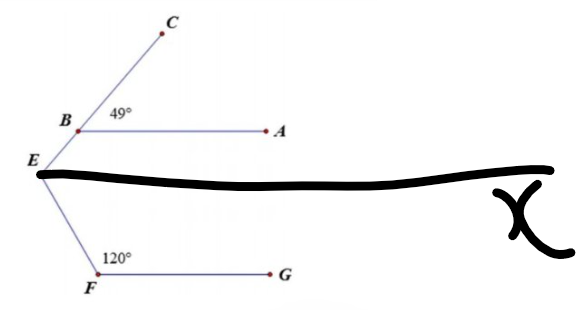
Kẻ Ex//AB(Ex và AB nằm trên cùng mặt phẳng bờ chứa tia BE)
Ta có: Ex//AB
AB//FG
Do đó: Ex//FG
Ex//AB
=>\(\widehat{BEx}=\widehat{CBA}\)(hai góc đồng vị)
=>\(\widehat{xEB}=49^0\)
Ta có: Ex//FG
=>\(\widehat{xEF}+\widehat{EFG}=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{xEF}=180^0-120^0=60^0\)
\(\widehat{BEF}=\widehat{xEB}+\widehat{xEF}=49^0+60^0=109^0\)


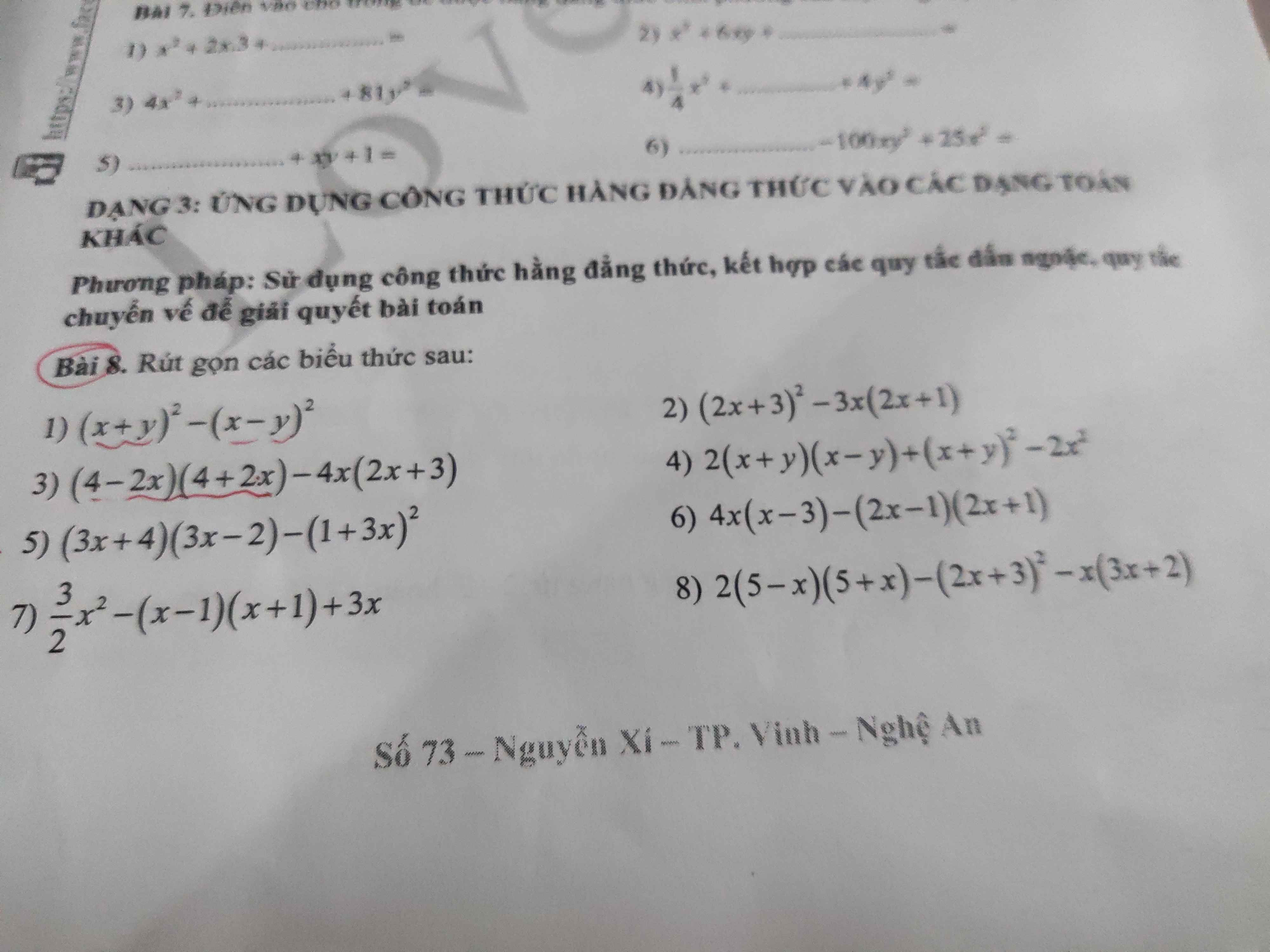
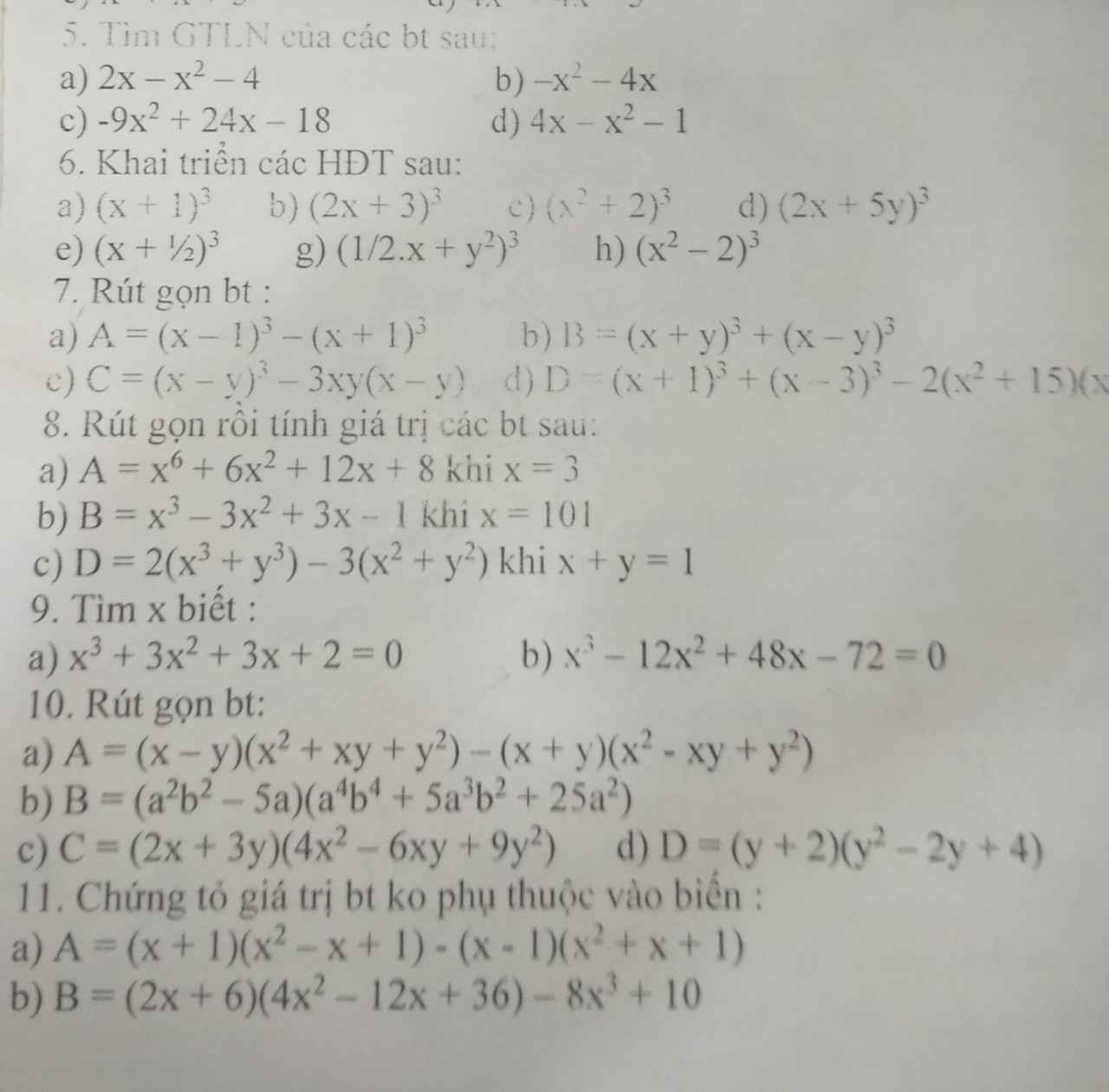

`n^2+n+4` chia hết cho n + 1
`=>(n^2+n) +4` chia hết cho n + 1
`=> n(n+1)+4` chia hết cho n + 1
Mà: `n(n+1)` chia hết cho n + 1
=> 4 chia hết cho n + 1
=> n + 1 ∈ Ư(4) = {1; -1; 2; -2; 4; -4}
=> n ∈ {0; -2; 1; -3; 3; -5}