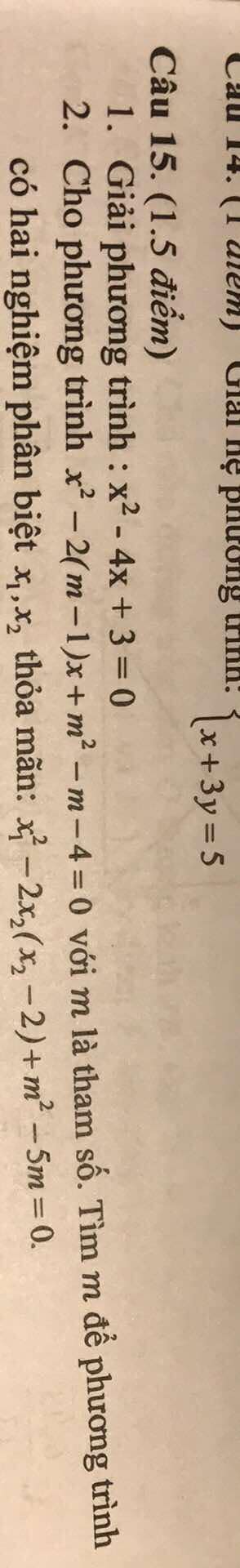 giải giúp tôi phần 2. với
giải giúp tôi phần 2. với
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: Xét (\(O_1\)) có
ΔAEH nội tiếp
AH là đường kính
Do đó: ΔAEH vuông tại E
=>HE\(\perp\)AC tại E
Xét \(\left(O_2\right)\) có
ΔHFB nội tiếp
HB là đường kính
Do đó: ΔHFB vuông tại F
=>HF\(\perp\)CB tại F
Xét ΔCHA vuông tại H có HE là đường cao
nên \(CE\cdot CA=CH^2\left(1\right)\)
Xét ΔCHB vuông tại H có HF là đường cao
nên \(CF\cdot CB=CH^2\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra \(CE\cdot CA=CF\cdot CB\)
=>\(\dfrac{CE}{CB}=\dfrac{CF}{CA}\)
Xét ΔCEF và ΔCBA có
\(\dfrac{CE}{CB}=\dfrac{CF}{CA}\)
\(\widehat{ECF}\) chung
Do đó: ΔCEF~ΔCBA
=>\(\widehat{CEF}=\widehat{CBA}\)
mà \(\widehat{CEF}+\widehat{FEA}=180^0\)(hai góc kề bù)
nên \(\widehat{FEA}+\widehat{FBA}=180^0\)
=>AEFB là tứ giác nội tiếp

`3x^2 + 4x - 4 = 0`
`<=> 3x^2 - 2x + 6x - 4 = 0`
`<=> (3x^2 - 2x) + (6x - 4) = 0`
`<=> x (3x - 2) + 2(3x - 2) = 0`
`<=> (x + 2)(3x - 2) = 0`
`<=> x = -2` hoặc `x = 2/3`
Vậy ...

Bài 17:
a:
Xét tứ giác OBAC có \(\widehat{OBA}+\widehat{OCA}=90^0+90^0=180^0\)
nên OBAC là tứ giác nội tiếp
=>O,B,A,C cùng thuộc một đường tròn
Xét (O) có
AB,AC là các tiếp tuyến
Do đó: AB=AC
=>A nằm trên đường trung trực của BC(1)
Ta có: OB=OC
=>O nằm trên đường trung trực của BC(2)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra OA là đường trung trực của BC
=>OA\(\perp\)BC tại H và H là trung điểm của BC
Xét (O) có
ΔBCD nội tiếp
BD là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBCD vuông tại C
=>BC\(\perp\)CD
mà OA\(\perp\)BC
nên OA//CD
b: Xét (O) có
ΔBED nội tiếp
BD là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBED vuông tại E
=>BE\(\perp\)AD tại E
Xét ΔABD vuông tại B có BE là đường cao
nên \(AE\cdot AD=AB^2\left(3\right)\)
Xét ΔABO vuông tại B có BH là đường cao
nên \(AH\cdot AO=AB^2\left(4\right)\)
Từ (3),(4) suy ra \(AE\cdot AD=AH\cdot AO\)
=>\(\dfrac{AE}{AO}=\dfrac{AH}{AD}\)
Xét ΔAEH và ΔAOD có
\(\dfrac{AE}{AO}=\dfrac{AH}{AD}\)
\(\widehat{EAH}\) chung
Do đó: ΔAEH~ΔAOD
=>\(\widehat{AHE}=\widehat{ADO}\)
Bài 15:
a:
Xét (O) có
ΔBEC nội tiếp
BC là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBEC vuông tại E
=>BE\(\perp\)AC tại E
b:
Xét (O) có
ΔBFC nội tiếp
BC là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBFC vuông tại F
=>CF\(\perp\)AB tại F
Xét ΔABC có
BE,CF là các đường cao
BE cắt CF tại H
Do đó: H là trực tâm của ΔABC
=>AH\(\perp\)BC tại D
Xét tứ giác BFHD có \(\widehat{BFH}+\widehat{BDH}=90^0+90^0=180^0\)
nên BFHD là tứ giác nội tiếp
Xét tứ giác CEHD có \(\widehat{CEH}+\widehat{CDH}=90^0+90^0=180^0\)
nên CEHD là tứ giác nội tiếp
Ta có: \(\widehat{FDH}=\widehat{FBH}\)(BFHD nội tiếp)
\(\widehat{EDH}=\widehat{ECH}\)(CEHD nội tiếp)
mà \(\widehat{FBH}=\widehat{ECH}\left(=90^0-\widehat{BAC}\right)\)
nên \(\widehat{FDH}=\widehat{EDH}\)
=>DA là phân giác của góc FDE

a: Các kết quả có thể xảy ra nằm trong tập hợp sau:
\(\Omega=\left\{\left(1;1\right);\left(1;2\right);...;\left(6;5\right);\left(6;6\right)\right\}\)
=>Có 36 kết quả có thể xảy ra
b: Gọi A là biến cố "Tổng số chấm ở hai con xúc sắc là 7"
=>A={(1;6);(2;5);(3;4);(4;3);(5;2);(6;1)}
=>n(A)=6
=>\(P_A=\dfrac{6}{36}=\dfrac{1}{6}\)
a) Xúc xắc 1 có 6 kết quả (6 mặt)
Xúc xắc 2 có 6 kết quả
Số kết quả xảy ra khi tung 2 xúc xắc là:
`6 xx 6 = 36` (kết quả)

`69^2022`
`= (...9)^2022`
Có cùng chữ số tận cùng với `9^2022`
Ta có: `9^2022 = 9^(1011.2) = (9^2)^1011 = 81^1011` có tận cùng chữ số 1
Vậy ....
\(15^{15^{15^{15}}}\) có tận cùng là chữ số 5 do các chữ số tận cùng là 5 mũ bao nhiêu cũng tận cùng là 5 ngoại từ mũ 0

Để phương trình là phương trình bậc hai thì \(\sqrt{m}>=0\)
=>m>=0
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì \(\left[-2\left(\sqrt{m}+1\right)\right]^2-4\left(\sqrt{m}+1\right)>0\)
=>\(4\left(m+2\sqrt{m}+1\right)-4\left(\sqrt{m}+1\right)>0\)
=>\(4\left(m+\sqrt{m}\right)>0\)(luôn đúng khi m>=0)
Điều kiện: `m >= 0`
Phương trình đã cho có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
`<=> Δ' > 0`
`<=> (sqrt{m} + 1)^2 - (sqrt{m} + 1).1 > 0`
`<=> m^2 + 2sqrt{m} + 1 - sqrt{m} - 1 > 0`
`<=> m^2 + sqrt{m} >= 0` (Thỏa mãn với mọi `m >= 0)`

Thời gian(phút) | [0;5) | [0;5) | [0;5) | [0;5) |
Tần số(n) | 9,375% | 9,375% | 9,375% | 9,375% |
biểu đồ của em là :
Thời gian(phút) | [0;5) | [0;5) | [0;5) | [0;5) |
Tần số(n) | 9,375% | 9,375% | 9,375% | 9,375% |
Câu 1:
x2−4x+3=0x^2 - 4x + 3 = 0x2−4x+3=0
Phương trình này là phương trình bậc hai có dạng chuẩn ax2+bx+c=0ax^2 + bx + c = 0ax2+bx+c=0 với:
Tính biệt số Δ\DeltaΔ:
Δ=b2−4ac=(−4)2−4(1)(3)=16−12=4.\Delta = b^2 - 4ac = (-4)^2 - 4(1)(3) = 16 - 12 = 4.Δ=b2−4ac=(−4)2−4(1)(3)=16−12=4.
Vì Δ>0\Delta > 0Δ>0, phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt:
x=−b±Δ2a=4±22.x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{\Delta}}{2a} = \frac{4 \pm 2}{2}.x=2a−b±Δ=24±2.
Suy ra hai nghiệm:
x1=4−22=1,x2=4+22=3.x_1 = \frac{4 - 2}{2} = 1, \quad x_2 = \frac{4 + 2}{2} = 3.x1=24−2=1,x2=24+2=3.
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là x=1x = 1x=1 hoặc x=3x = 3x=3.
Câu 2
Phương trình:
x2−2(m−1)x+m2−m−4=0x^2 - 2(m-1)x + m^2 - m - 4 = 0x2−2(m−1)x+m2−m−4=0
Có hai nghiệm phân biệt khi:
Δ′=(m−1)2−(m2−m−4)>0.\Delta' = (m-1)^2 - (m^2 - m - 4) > 0.Δ′=(m−1)2−(m2−m−4)>0.
Tính toán:
m2−2m+1−m2+m+4>0.m^2 - 2m + 1 - m^2 + m + 4 > 0.m2−2m+1−m2+m+4>0. −m+5>0.- m + 5 > 0.−m+5>0. m<5.m < 5.m<5.
Ta có điều kiện:
x12−2x2(x2−2)+m2−5m=0.x_1^2 - 2x_2(x_2 - 2) + m^2 - 5m = 0.x12−2x2(x2−2)+m2−5m=0.
Sử dụng định lý Vi-ét
x1+x2=2(m−1),x_1 + x_2 = 2(m-1),x1+x2=2(m−1), x1x2=m2−m−4.x_1 x_2 = m^2 - m - 4.x1x2=m2−m−4.
Dùng đẳng thức:
x12=(x1+x2)2−2x1x2.x_1^2 = (x_1 + x_2)^2 - 2x_1 x_2.x12=(x1+x2)2−2x1x2.
Thay vào:
(2(m−1))2−2(m2−m−4)−2x2(x2−2)+m2−5m=0.(2(m-1))^2 - 2(m^2 - m - 4) - 2x_2(x_2 - 2) + m^2 - 5m = 0.(2(m−1))2−2(m2−m−4)−2x2(x2−2)+m2−5m=0.
Biến đổi:
4(m−1)2−2(m2−m−4)−2x22+4x2+m2−5m=0.4(m-1)^2 - 2(m^2 - m - 4) - 2x_2^2 + 4x_2 + m^2 - 5m = 0.4(m−1)2−2(m2−m−4)−2x22+4x2+m2−5m=0.
Dùng x22=(x1+x2)2−2x1x2x_2^2 = (x_1 + x_2)^2 - 2x_1x_2x22=(x1+x2)2−2x1x2, thay vào:
4(m−1)2−2(m2−m−4)−2[(2(m−1))2−2(m2−m−4)]+4x2+m2−5m=0.4(m-1)^2 - 2(m^2 - m - 4) - 2[(2(m-1))^2 - 2(m^2 - m - 4)] + 4x_2 + m^2 - 5m = 0.4(m−1)2−2(m2−m−4)−2[(2(m−1))2−2(m2−m−4)]+4x2+m2−5m=0.
Rút gọn:
4(m2−2m+1)−2m2+2m+8−2[4(m2−2m+1)−2m2+2m+8]+4x2+m2−5m=0.4(m^2 - 2m + 1) - 2m^2 + 2m + 8 - 2[4(m^2 - 2m + 1) - 2m^2 + 2m + 8] + 4x_2 + m^2 - 5m = 0.4(m2−2m+1)−2m2+2m+8−2[4(m2−2m+1)−2m2+2m+8]+4x2+m2−5m=0.
Sau khi tiếp tục biến đổi và rút gọn, ta giải phương trình để tìm các giá trị mmm thỏa mãn.
Kết quả cuối cùng là m=3m = 3m=3 (thỏa mãn cả hai điều kiện trên).