
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) Ta lần lượt có :
f ( - 2 ) = | 2-(-2)-3 | = | -4 - 3 | = | -7 | = 7
f( 8 ) = | 2x - 3 | = | 2 . 8 - 3 | = | 16 - 3 | = | 13 | = 13
b) Ta lần lượt có :
- Với y = -1 thì | 2x - 3 | = -1 , vô nghiệm bởi | 2x - 3 | > 0
- Với y = 3 thì | 2x - 3 | = 3
↔ 2x - 3 = 3 hoặc 2x - 3 = -3
↔ 2x = 6 hoặc 2x = 0
↔ x = 3 hoặc x = 0

Câu 5:
a: Khi m=3 thì \(f\left(x\right)=\left(2\cdot3+1\right)x-3=7x-3\)
\(f\left(-3\right)=7\cdot\left(-3\right)-3=-21-3=-24\)
\(f\left(0\right)=7\cdot0-3=-3\)
b: Thay x=2 và y=3 vào f(x)=(2m+1)x-3, ta được:
\(2\left(2m+1\right)-3=3\)
=>2(2m+1)=6
=>2m+1=3
=>2m=2
=>m=1
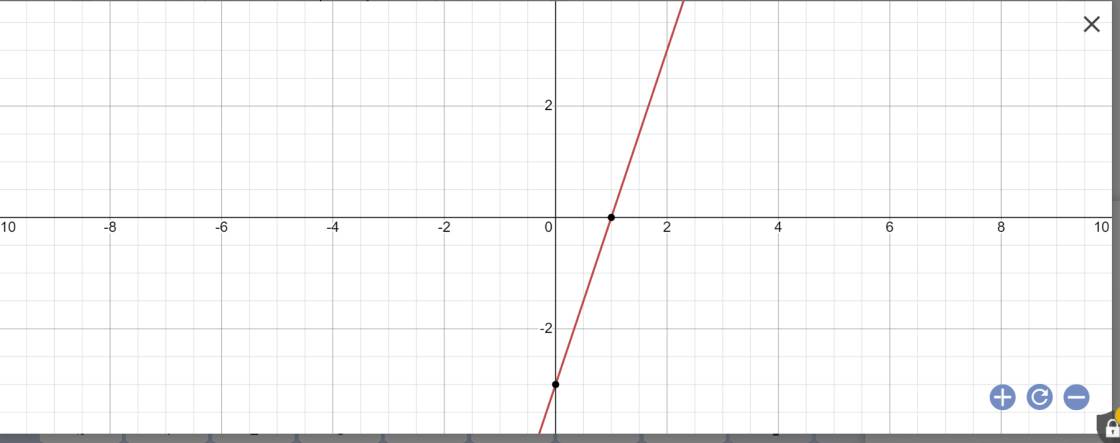
c: Thay m=1 vào hàm số, ta được:
\(y=\left(2\cdot1+1\right)x-3=3x-3\)
*Vẽ đồ thị
d: Để hàm số y=(2m+1)x-3 là hàm số bậc nhất thì \(2m+1\ne0\)
=>\(2m\ne-1\)
=>\(m\ne-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
e: Để đồ thị hàm số y=(2m+1)x-3 song song với đường thẳng y=5x+1 thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m+1=5\\-3\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>2m+1=5
=>2m=4
=>m=2

a) Ta có:
\(f\left( {\dfrac{1}{5}} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\dfrac{1}{5}}} = \dfrac{5}{{\dfrac{4}{5}}} = 5:\dfrac{4}{5} = 5.\dfrac{5}{4} = \dfrac{{25}}{4};\)
\(f\left( { - 5} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - 5} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 20}} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{4};\)
\(f\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\dfrac{4}{5}}} = \dfrac{5}{{\dfrac{{16}}{5}}} = 5:\dfrac{{16}}{5} = 5.\dfrac{5}{{16}} = \dfrac{{25}}{{16}}\)
b) Ta có:
\(f\left( { - 3} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - 3} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 12}} = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{{12}};\)
\(f\left( { - 2} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - 2} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 8}} = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{8};\)
\(f\left( { - 1} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - 1} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 4}} = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{4};\)
\(f\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{\dfrac{{ - 4}}{2}}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 2}} = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}\);
\(f\left( {\dfrac{1}{4}} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\dfrac{1}{4}}} = \dfrac{5}{{\dfrac{4}{4}}} = \dfrac{5}{1} = 5\);
\(f\left( 1 \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.1}} = \dfrac{5}{4}\);
\(f\left( 2 \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.2}} = \dfrac{5}{8}\)
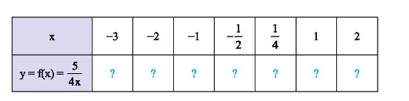
Ta có bảng sau:
\(x\) | –3 | –2 | –1 | \( - \dfrac{1}{2}\) | \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) | 1 | 2 |
\(y = f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4x}}\) | \(\dfrac{{ - 5}}{{12}}\) | \(\dfrac{{ - 5}}{8}\) | \(\dfrac{{ - 5}}{4}\) | \(\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}\) | 5 | \(\dfrac{5}{4}\) | \(\dfrac{5}{8}\) |

Ta có : f(0)=2014=>ax2+bx+c=2014
=>0+0+c=2014
=>c=2014 (1)
f(1)=2015=>ax2+bx+c=2015
=>a+b=2015-c
=>a+b=2015-2014=1 (2)
f(-1)=2017=>ax2+bx+c=2017
=>a+(-b)+2014=2017
=>a-b=2017-2014=3 (3)
Từ 2 và 3:+) (a+b)+(a-c)=1+3
=>a+b+a-b=4
=>2a=4
=>a=2 (4)
+) (a+b)-(a-b)=1-3
=>a+b-a+b=-2
=>2b=-2
=>b=-1 (5)
Từ 1 ; 4 và 5 => f(-2)=ax2+bx+c
=2.(-2)2+(-1).(-2)+2014
=2.4+2+2014
=2024
Vậy f(-2)=2024

a: \(F\left(3\right)=3\left(3-2\right)=3\cdot1=3\)
\(\left[F\left(\dfrac{2}{3}\right)\right]^2=\left[\dfrac{2}{3}\cdot\left(\dfrac{2}{3}-2\right)\right]^2\)
\(=\left[\dfrac{2}{3}\cdot\dfrac{-4}{3}\right]^2=\left(-\dfrac{8}{9}\right)^2=\dfrac{64}{81}\)
\(G\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=-\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)+6=6+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{13}{2}\)
b: F(x)=0
=>x(x-2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: F(a)=G(a)
=>\(a\left(a-2\right)=-a+6\)
=>\(a^2-2a+a-6=0\)
=>\(a^2-a-6=0\)
=>(a-3)(a+2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}a-3=0\\a+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=3\\a=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(a,\)Có :\(f\left(0\right)=3.0+1=1\)
\(f\left(-1\right)=-1.3-1=-3-1=-4\)
\(f\left(-\frac{1}{3}\right)=3.\left(-\frac{1}{3}\right)-1=-1-1=-2\)
\(b,\)Có \(3x-1=-16\)
\(\Rightarrow3x=-15\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-5\)
Vậy x = - 5 để y = -16
GIẢI:
a) f(0)=-1
f(-1)=-4
f(-1/3)=-2
b) 3x-1=-16
3x=-16+1
3x=-15
x=-15:3
x=-5.
vậy x=-5

a) Ta có:
\(f\left(-2\right)=\left|3\cdot-2-1\right|=\left|-6-1\right|=\left|-7\right|=7\)
\(f\left(2\right)=\left|3\cdot2-1\right|=\left|6-1\right|=5\)
\(f\left(-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)=\left|3\cdot-\dfrac{1}{4}-1\right|=\left|-\dfrac{3}{4}-1\right|=\left|-\dfrac{7}{4}\right|=\dfrac{7}{4}\)
b) Ta có:
\(f\left(x\right)=10\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|3x-1\right|=10\)
Với \(x\ge\dfrac{1}{3}\Rightarrow3x-1=10\)
\(\Rightarrow3x=11\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{11}{3}\left(tm\right)\)
Với \(x< \dfrac{1}{3}\Rightarrow3x-1=-10\)
\(\Rightarrow3x=-9\Rightarrow x=-3\left(tm\right)\)
_______
\(f\left(x\right)=-3\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|3x-1\right|=-3\)
Mà: \(\left|3x-1\right|\ge0\forall x\) và \(-3< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|3x-1\right|=-3\) (vô lý)
\(\Rightarrow\) không có x thỏa mãn
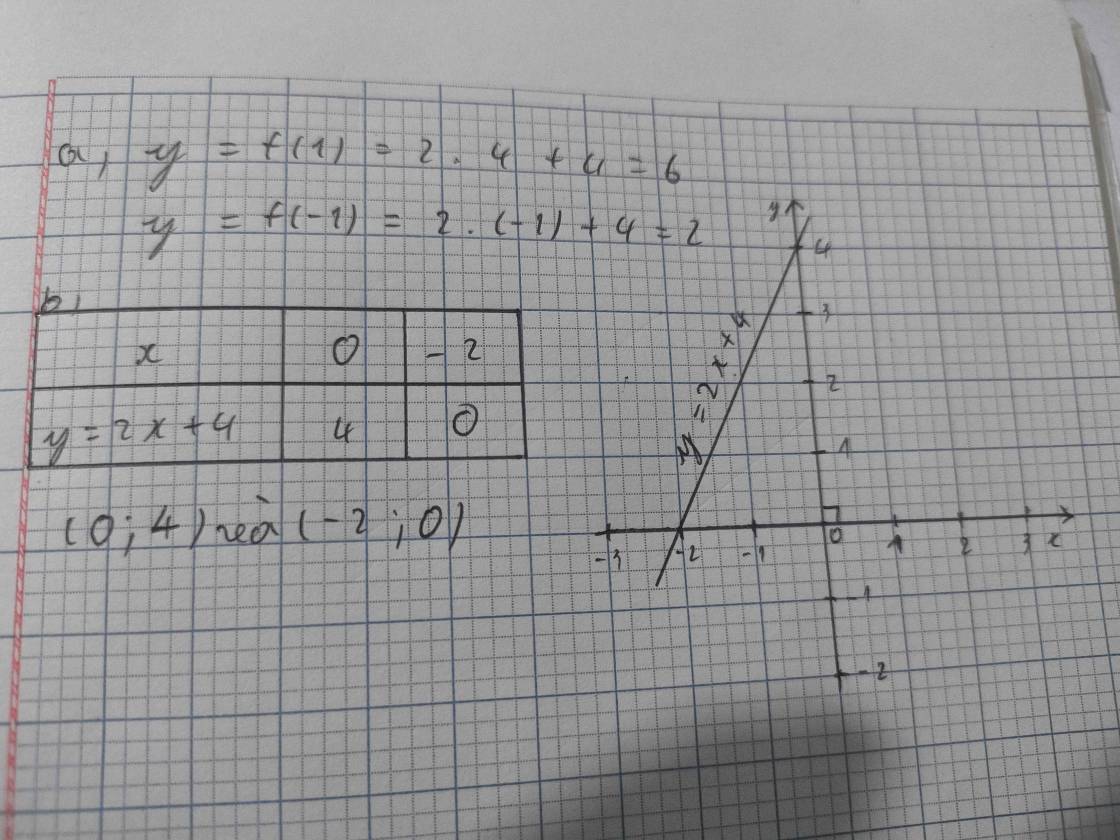
`y = f(x) = 2x - 5`
`f(0) = 2 . 0 - 5 = -5`
`f(-1) = 2 . (-1) - 5 = -2 - 5 = -7`
Vậy ...