Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

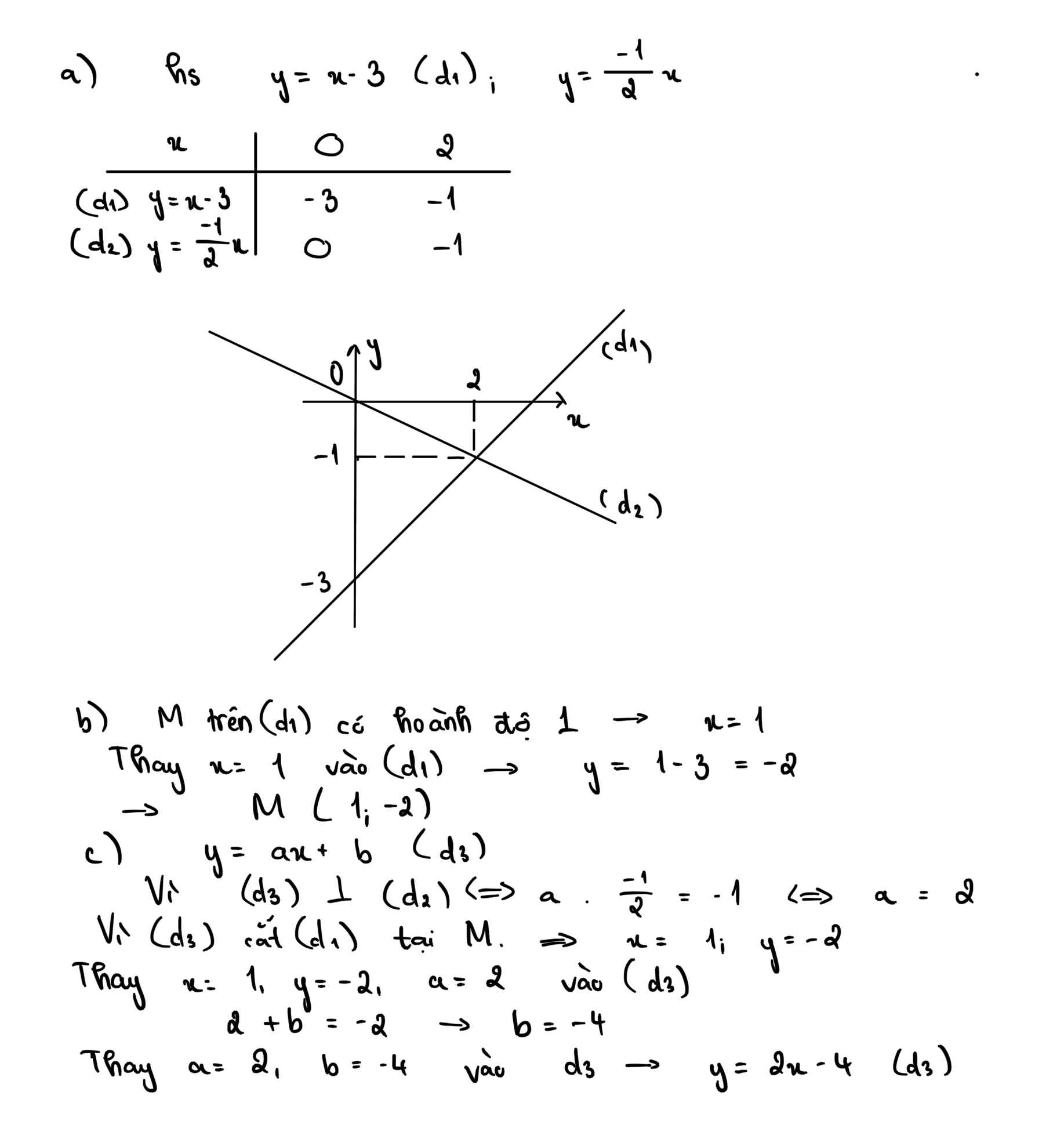
a: Tọa độ A là nghiệm của hệ phương trình:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x-1=x-5\\y=x-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2x=-4\\y=x-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=2-5=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>A(2;-3)
b: Vì \(a_1\cdot a_2=1\cdot\left(-1\right)=-1\)
nên (d1) vuông góc với (d2)
Gọi B,C lần lượt là giao điểm của (d1) với trục Oy, (d2) với trục Oy
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=-x-1=-0-1=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>B(0;-1)
Tọa độ C là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=x-5=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>C(0;-5)
B(0;-1); C(0;-5); A(2;-3)
\(BC=\sqrt{\left(-5+1\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=4\)
\(BA=\sqrt{\left(2-0\right)^2+\left(-3+1\right)^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(2-0\right)^2+\left(-3+5\right)^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
Chu vi tam giác ABC là:
\(4+2\sqrt{2}+2\sqrt{2}=4\sqrt{2}+4\)

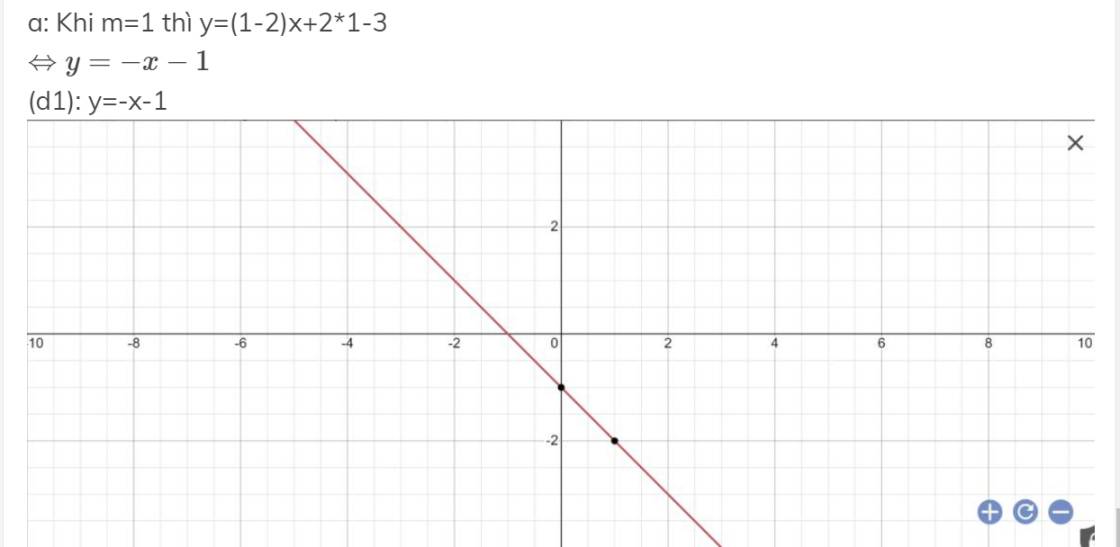
a: Khi m=1 thì y=(1-2)x+2*1-3
\(\Leftrightarrow y=-x-1\)
(d1): y=-x-1
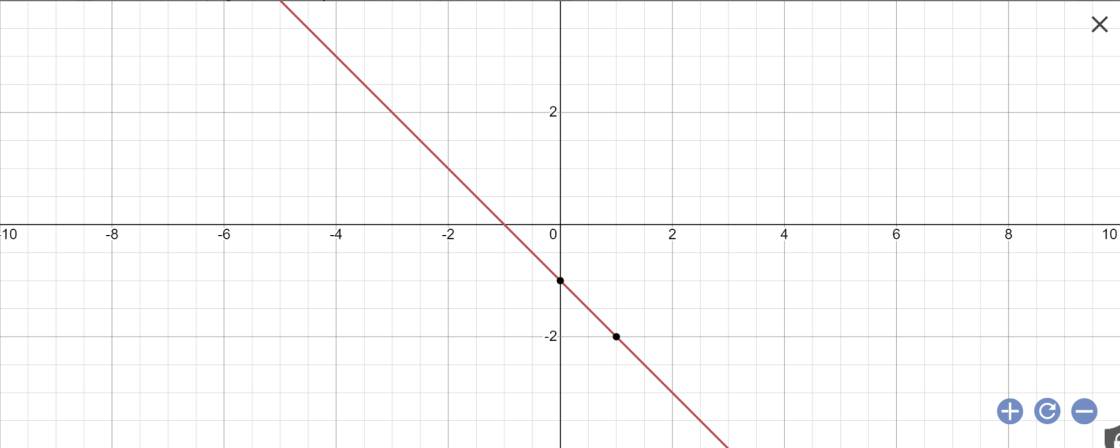
b: Tọa độ A là nghiệm của hệ phương trình sau:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x-1=x-5\\y=x-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2x=-4\\y=x-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=2-5=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: \(a_1\cdot a_2=1\cdot\left(-1\right)=-1\)
=>\(\left(d1\right)\perp\left(d2\right)\)

a) \(\left(d_1\right):y=mx+2m\)
\((d_1)\parallel (d_2)\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=2m-3\\2m\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=3\\m\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow m=3\)
b) \(\left(d_1\right)\equiv\left(d_2\right)\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=2m-3\\2m=2\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=3\\m=1\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\) không có m thỏa
c) \(\left(d_1\right)\bot\left(d_2\right)\Rightarrow m.\left(2m-3\right)=-1\Rightarrow2m^2-3m+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(m-1\right)\left(2m-1\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=1\\m=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: (d1): y=m(x+2)
nên y=mx+2m
a) Để (d1)//(d2) thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=2m-3\\2m\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-2m=-3\\m\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=3\\m\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m=3\)

BÀI 1
để d1 và d2 // thì: m-3=-1(1) ; m khác 3 (2)
ta có: (1) <=> m=2 (3)
từ (2) và (3) => để d1//d2 thì m = 2

Lời giải:
Vì $(d_1)\parallel (d_2)$ nên $a=1$
$A\in (d_1)$ nên $y_A=ax_A+b\Leftrightarrow 2=a(-1)+b$
$\Leftrightarrow b=2+a=2+1=3$
Vậy $a=1; b=3$

a, cắt : a khác a'
b, b= b'; a khác a'
c, a=a' ; b khác b'
d, a*a'= -1
e, a= a' ;b= b'

a) Để d1 trùng d2 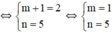
Vậy m = 1, n = 5
b) Để d1 cắt d2 thì: m + 1 ≠ 2 ⇒ m ≠ 1
c) Để d1 song song d2 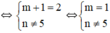
Vậy m = 1, n ≠ 5.