Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a)
y(1) =a-4+c=\(-2\)\(\Rightarrow\) a+c=2
y(2)=4a-8+c=3 \(\Rightarrow\)4a+c=3
Trừ cho nhau\(\Rightarrow\)3a=1 \(\Rightarrow\)a=\(\dfrac{1}{3}\)\(\Rightarrow\) \(c=2-\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{5}{3}\).
Vậy: \(y=\dfrac{1}{3}x^2-4x+\dfrac{5}{3}\).
b)
I(-2;1)\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{4}{2a}=-2\)\(\Leftrightarrow a=-1\).
y(-2) \(=-4+8+c=1\)\(\Rightarrow\) \(c=-3\)
Vậy: \(y=-x^2-4x-3\).
c)\(\dfrac{4}{2a}=-3\)\(\Leftrightarrow a=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(y\left(-2\right)=-\dfrac{2}{3}.4+8+c=1\)\(\Leftrightarrow c=-\dfrac{13}{3}\)
Vậy: \(y=-\dfrac{2}{3}x^3-4x-\dfrac{13}{3}\).

Hàm số đi qua \(A\left(8;0\right)\) nên: \(a.8^2+8b+c=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow64a+8b+c=0\).
Hàm số có đỉnh là: \(I\left(6;-12\right)\) nên: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{-b}{2a}=6\\6^2.a+6b+c=-12\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}12a+b=0\\36a+6b+c=-12\end{matrix}\right.\).
Vậy ta có hệ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}64a+8b+c=0\\-b=12a\\36a+6b+c=-12\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-3\\b=-36\\c=96\end{matrix}\right.\).
Vậy : \(y=-3x^2-36x+96\).

Lời giải:
Để ĐTHS có đỉnh $I$ thì $a< 0$
Tọa độ đỉnh $I$:
\(x_I=\frac{-b}{2a}=-1\Rightarrow b=2a(1)\)
Điểm $I$ thuộc ĐTHS $y$ nên:
\(y_I=y(x_I)\Leftrightarrow 5=a(-1)^2+b(-1)+c\Leftrightarrow 5=a-b+c(2)\)
ĐTHS đi qua điểm $A(1;1)$
$\Leftrightarrow y_A=y(x_A)$
$\Leftrightarrow 1=a.1^2+b.1+c=a+b+c(3)$
Từ $(1);(2); (3)\Rightarrow a=-1; b=-2; c=4$
Lời giải:
Để ĐTHS có đỉnh $I$ thì $a< 0$
Tọa độ đỉnh $I$:
\(x_I=\frac{-b}{2a}=-1\Rightarrow b=2a(1)\)
Điểm $I$ thuộc ĐTHS $y$ nên:
\(y_I=y(x_I)\Leftrightarrow 5=a(-1)^2+b(-1)+c\Leftrightarrow 5=a-b+c(2)\)
ĐTHS đi qua điểm $A(1;1)$
$\Leftrightarrow y_A=y(x_A)$
$\Leftrightarrow 1=a.1^2+b.1+c=a+b+c(3)$
Từ $(1);(2); (3)\Rightarrow a=-1; b=-2; c=4$

Để xác định các hệ số a và b ta dựa vào tọa độ các điểm mà đồ thị đi qua, lập hệ phương trình có hai ẩn a và b
a) Vì đồ thị đi qua \(A\left(\dfrac{2}{3};-2\right)\) nên ta có phương trình \(a.\dfrac{2}{3}+b=-2\)
Tương tự, dựa vào tọa độ của \(B\left(0;1\right)\) ta có \(0+b=1\)
Vậy, ta có hệ phương trình :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2a}{b}+b=-2\\b=1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-\dfrac{9}{2}\\b=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(a=0;b=-2\)
c) \(a=\dfrac{1}{3};b=\dfrac{2}{3}\)

a) (P) cắt trục Ox tại điểm M(2;0) nên :
0=a.2^2+3.2-2=>a=-1
vậy (P): y=-x^2+3x-2
b) trục đối xứng x=-3 hay
\(-\dfrac{b}{2a}=-3\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-3}{2a}=-3\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{1}{2}\\ \Rightarrow\left(P\right):y=\dfrac{1}{2}x^2+3x-2\)
c) có đỉnh I(-1/2;-11/4)=>
\(a.\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+3.\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)-2=-\dfrac{11}{4}\Rightarrow a=3\Rightarrow\left(P\right):y=3x^2+3x-2\)

a) Thay x, y trong phương trình y = ax + b bằng tọa độ của A và của B ta được hệ phương trình:
Vậy phương trình của đường thẳng đi qua A(0; 3) và là: y = - 5x + 3.
b) Thay \(x,y\) trong phương trình \(y=ax+b\) bằng tọa độ A và B ta được hệ phương trình: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}1.a+b=2\\2.a+b=1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-1\\b=3\end{matrix}\right.\).
Vậy phương trình đường thẳng cần tìm là: \(y=-x+3\).
c) Thay \(x,y\) trong phương trình \(y=ax+b\) bằng tọa độ A và B ta được hệ phương trình: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}15a+b=-3\\21a+b=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=0\\b=-3\end{matrix}\right.\).
Vậy phương trình đường thẳng cần tìm là: \(y=-3\).

a,\(\Delta_a\) : 3 (x-1) - 2 (y-1) =3x-2y-1=0
b, \(\Delta_b\) : y=-\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)(x-2) =-\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)x =>\(\Delta_b\) : x+2y=0
c,\(\overrightarrow{AB}\)=(-2;-3) =>vtpt \(\overrightarrow{n}\)=(3;-2)
=>\(\Delta_c\): 3 (x-2) - 2(y-0) =0
=>\(\Delta_c\): 3x-2y-6=0
Lời giải
a) \(\Delta_a=3\left(x-1\right)-2\left(y-1\right)=3x-2y+5=0\)
b)\(\Delta_b:y=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(x-2\right)-1=-\dfrac{1}{2}x\Rightarrow\Delta_b:x+2y=0\)
c) \(\Delta_c:\left(3+0\right)\left(x-2\right)+\left(0-2\right)\left(y-0\right)=3x-2y-6\)
a) Vì parabol đi qua M(1; 5) nên tọa độ của M nghiệm đúng phương trình của parabol: 5 = a.12 + b.1 + 2.
Tương tự, với N(- 2; 8) ta có: 8 = a.(- 2)2 + b.(- 2) + 2
Giải hệ phương trình: ta được a = 2, b = 1.
ta được a = 2, b = 1.
Parabol có phương trình là: y = 2x2 + x + 2.
b) Giải hệ phương trình:
Parabol: y =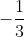 x2 - x + 2.
x2 - x + 2.
c) Giải hệ phương trình: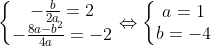
Parabol: y = x2 - 4x + 2.
d) Ta có:
Parabol: y = 16x2 + 12x + 2 hoặc y = x2 - 3x + 2.