Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: \(\Leftrightarrow x^4+x^3-x^3-x^2+\left(a+1\right)x^2+\left(a+1\right)x-\left(a+1\right)x-a-1+b⋮x+1\)
=>b=0 và a+1=0
=>a=-1 và b=0
b: \(\dfrac{2x^3+ax+b}{x+1}=\dfrac{2x^3+2x^2-2x^2-2x+\left(a+2\right)x+a+2+b-a-2}{x+1}\)
=>b-a-2=6
\(\dfrac{2x^3+ax+b}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^3-2x^2+2x^2-2x+\left(a+2\right)x-a-2+a+2+b}{x-1}\)
=>a+b+2=21
=>a=11/2; b=27/2

Đặt f(x) =x10+ax+b
x2-1=(x-1)(x+1)
-> f(1)=2x+1-> 110+a.13+b=2x+1->a+b=2
f(-1)=2x+1-> -a+b=-2
-> 2a=4->a=2,b=0

2x^3+3x^2-x+a x^2+x-1 2x+1 2x^3+x^2 - - 2x^2-x+a 2x^2+x -2x+a -2x-1 - a+1
Để \(A\left(x\right)⋮B\left(x\right)\Leftrightarrow a+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a=-1\)
Vậy ...
2x^3+3x^2-x+a x^2+x-1 2x+1 2x^3+x^2 - - 2x^2-x+a 2x^2+x -2x+a -2x-1 - a+12x^3+3x^2-x+a x^2+x-1 2x+1 2x^3+x^2 - - 2x^2-x+a 2x^2+x -2x+a -2x-1 - a+1
Để \(A \left(\right. x \left.\right) B \left(\right. x \left.\right) \Leftrightarrow a + 1 = 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a = - 1\)

Lời giải:
Đặt \(f(x)=x^{10}+ax^3+b=(x^2-1)Q(x)+2x+1\) trong đó $Q(x)$ là đa thức thương.
Khi đó:
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} f(1)=1+a+b=0.Q(1)+2.1+1\\ f(-1)=1-a+b=0.Q(-1)+2(-1)+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} 1+a+b=3\\ 1-a+b=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} a=2\\ b=0\end{matrix}\right.\)


a) Ta có: \(g\left(x\right)=x^2-3x+2\)
\(=x^2-x-2x+2\)
\(=x\left(x-1\right)-2\left(x-1\right)\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\)
Vì \(f\left(x\right)⋮g\left(x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)q\left(x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}f\left(1\right)=\left(1-1\right)\left(1-2\right)q\left(1\right)=0\left(1\right)\\f\left(2\right)=\left(1-2\right)\left(2-2\right)q\left(2\right)=0\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
Từ \(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow1^4-3.1^3+1^2+a+b=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-1+a+b=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a+b=1\left(3\right)\)
Từ \(\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow2^4-3.2^3+2^2+2a+b=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4+2a+b=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a+b=4\left(4\right)\)
Từ \(\left(3\right);\left(4\right)\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}a+b=1\\2a+b=4\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}a=3\\b=-2\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy a=3 và b=-2 để \(f\left(x\right)⋮g\left(x\right)\)
Các phần sau tương tự
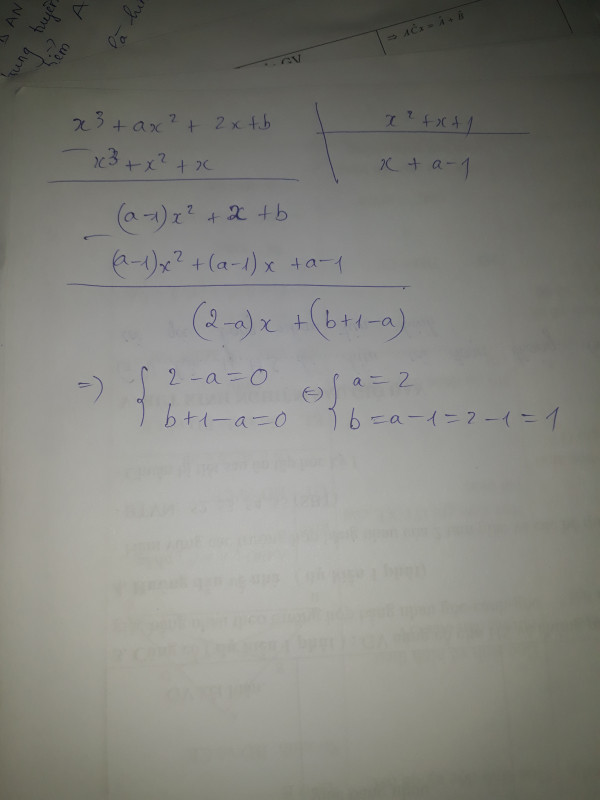
Lời giải:
Theo định lý Bezout về phép chia đa thức thì số dư của \(f(x)=2x^3+ax+b\) cho \(x+1\) và \(x-2\) lần lượt là \(f(-1)\) và \(f(2)\)
Do đó:
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} f(-1)=-2-a+b=-6\\ f(2)=16+2a+b=21\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} -a+b=-4\\ 2a+b=5\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} a=3\\ b=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)