
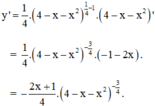
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

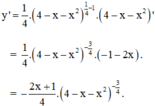

\(y=\left(\frac{2}{3}\right)^x-\left(\frac{1}{6}\right)^x\Rightarrow y'=\frac{1}{x\ln\frac{2}{3}}+\frac{1}{x\ln6}\)
\(=\frac{2\ln2}{x\ln6\left(\ln2-\ln3\right)}\)

Ta có \(y'=e^{\sqrt[3]{x^2+1}-x}\left(\sqrt[3]{x^2+1}-x\right)+3^{3x-1}\left(3x-1\right)'\ln3\)
\(=e^{\sqrt[3]{x^2+1}-x}\left(\frac{2x}{3\sqrt[3]{\left(x^2+1\right)^2}}-1\right)+3^{3x}\ln3\)

a) Hàm số \(y=\left(x^3-8\right)^{\frac{\pi}{3}}\) xác định khi và chỉ khi \(x^8-8>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+4\right)>0\Leftrightarrow x-2>0\Leftrightarrow x>2\)
Vậy tập xác định của hàm số là \(\left(2;+\infty\right)\)
Đạo hàm của hàm số là :
\(y'=\frac{\pi}{3}\left(x^3-8\right)'.\left(x^3-8\right)^{\frac{\pi}{3}-1}=\frac{\pi}{3}.3x^2\left(x^3-8\right)^{\frac{\pi}{3}-1}=x^2\left(x^3-8\right)^{\frac{\pi}{3}-1}\)
b) Hàm số xác định khi và chỉ khi \(x^2+x-6>0\Leftrightarrow x<-3\) hoặc \(x\ge2\)
Vậy tập xác định của hàm số là : \(\left(-\infty;-3\right)\cup\left(2;+\infty\right)\)
Đạo hàm của hàm số là :
\(y'=\frac{-1}{3}\left(x^2+x-6\right)'.\left(x^2+x-6\right)^{\frac{-1}{3}-1}=\frac{-\left(2x+1\right)\left(x^2+x-6\right)^{\frac{-4}{3}}}{3}\)

\(y'=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(x^2-4x+10\right)^{-\dfrac{3}{4}}\left(x^2-4x+10\right)'\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2}{2\sqrt[4]{\left(x^2-4x+10\right)^3}}\)

`a)TXĐ:R\\{1;1/3}`
`y'=[-4(6x-4)]/[(3x^2-4x+1)^5]`
`b)TXĐ:R`
`y'=2x. 3^[x^2-1] ln 3-e^[-x+1]`
`c)TXĐ: (4;+oo)`
`y'=[2x-4]/[x^2-4x]+2/[(2x-1).ln 3]`
`d)TXĐ:(0;+oo)`
`y'=ln x+2/[(x+1)^2].2^[[x-1]/[x+1]].ln 2`
`e)TXĐ:(-oo;-1)uu(1;+oo)`
`y'=-7x^[-8]-[2x]/[x^2-1]`
Lời giải:
a.
$y'=-4(3x^2-4x+1)^{-5}(3x^2-4x+1)'$
$=-4(3x^2-4x+1)^{-5}(6x-4)$
$=-8(3x-2)(3x^2-4x+1)^{-5}$
b.
$y'=(3^{x^2-1})'+(e^{-x+1})'$
$=(x^2-1)'3^{x^2-1}\ln 3 + (-x+1)'e^{-x+1}$
$=2x.3^{x^2-1}.\ln 3 -e^{-x+1}$
c.
$y'=\frac{(x^2-4x)'}{x^2-4x}+\frac{(2x-1)'}{(2x-1)\ln 3}$
$=\frac{2x-4}{x^2-4x}+\frac{2}{(2x-1)\ln 3}$
d.
\(y'=(x\ln x)'+(2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}})'=x(\ln x)'+x'\ln x+(\frac{x-1}{x+1})'.2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}}\ln 2\)
\(=x.\frac{1}{x}+\ln x+\frac{2}{(x+1)^2}.2^{\frac{x-1}{x+1}}\ln 2\\ =1+\ln x+\frac{2^{\frac{2x}{x+1}}\ln 2}{(x+1)^2}\)
e.
\(y'=-7x^{-8}-\frac{(x^2-1)'}{x^2-1}=-7x^{-8}-\frac{2x}{x^2-1}\)