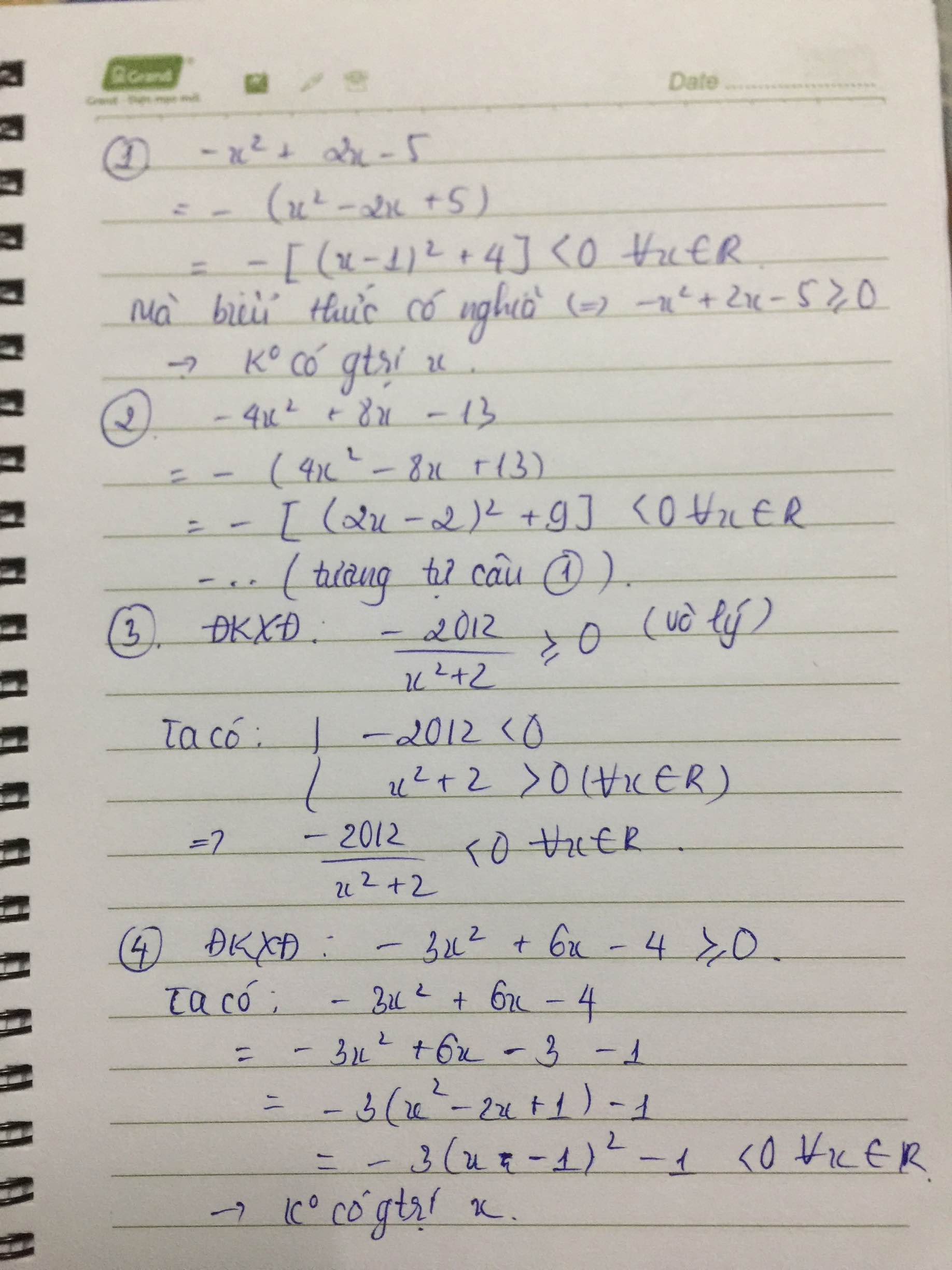Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) ĐKXĐ : \(\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{1}{1-x^2}>0\\1-x^2\ne0\end{cases}}\)
Mà 1 > 0 nên \(\Leftrightarrow1-x^2>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2< 1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-1< x< 1\)
Vậy ...
b) Có \(\frac{1}{1+x^2}>0\) với mọi x nên biểu thức XĐ với mọi x.

Để biểu thức tồn tại được thì :
a) 4 - x2 \(\ge\)0
=> (2 - x)(2 + x) \(\ge\)0
=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge-2\\x\le2\end{cases}}\Rightarrow-2\le x\le2\)
dễ tek,,,,bạn cứ cho những cái trong căn lớn hơn bằng 0 là xong mà

Bài 12:
Để N là số nguyên thì \(\sqrt{x}+3⋮\sqrt{x}+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2⋮\sqrt{x}+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+5\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)(vô lý
Bài 11:
Để M là số nguyên thì \(3\sqrt{x}+1⋮\sqrt{x}+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+3\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4;8;-8\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+3\in\left\{4;8\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{1;25\right\}\)

Câu hỏi của Nguyễn Thanh Thảo - Toán lớp 8 - Học toán với OnlineMath
Bạn xem tham khảo nha

Để biểu thức \(\sqrt{\frac{-1}{1-3x}}\) tồn tại thì:
\(\frac{-1}{1-3x}>=0\)
<=>1-3x<0
<=> 1<3x
<=> \(\frac{1}{3}\)<x
Câu kia tương tự nha

a, \(-x^2+2x-5=-\left(x^2-2x+5\right)=-\left(x^2-2x+1+4\right)\)
\(=-\left[\left(x-1\right)^2+4\right]\)
do \(\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0=>\left(x-1\right)^2+4\ge4=>-\left[\left(x-1\right)^2+4\right]\le-4< 0\)
Vậy ko tồn tại..........
b, \(-4x^2+8x-13=-4\left(x^2-2x+\dfrac{13}{4}\right)\)
\(=-4\left[x^2-2x+1+\dfrac{9}{4}\right]=-4\left[\left(x-1\right)^2+\dfrac{9}{4}\right]\le-9< 0\)
vậy....
c, \(\dfrac{-2021}{x^2+2}\) do \(x^2+2>2=>\dfrac{-2012}{x^2+2}< -1006< 0\)
vậy,,,,,,,,,,
d, \(-3x^2+6x-4=-3\left(x^2-2x+\dfrac{4}{3}\right)=-3\left(x^2-2x+1+\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\)
\(=-3\left[\left(x-1\right)^2+\dfrac{1}{3}\right]\le-1< 0\)
vậy...