
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


x : \(\dfrac{2}{7}\)= 0,8
= > x = 0,8 x\(\dfrac{2}{7}\)
=> x = \(\dfrac{8}{35}\)
Vậy x = \(\dfrac{8}{35}\)
x : \(\dfrac{2}{7}\) = 0,8
x : \(\dfrac{2}{7}\) = \(\dfrac{8}{10}\)
x = \(\dfrac{4}{5}.\dfrac{2}{7}\)
x = \(\dfrac{8}{35}\)
Tìm \(x\), biết :
a) \(x=\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{2}{13}\)
b) \(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{-1}{7}\)

a) \(x=\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{2}{13}\)
=> \(x=\dfrac{13}{52}+\dfrac{8}{52}\)
=> \(x=\dfrac{21}{52}\)
b) \(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{-1}{7}\)
=> \(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{14}{21}+\dfrac{-3}{21}\)
=> \(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{11}{21}\)
=> \(x=\dfrac{11}{21}\)x \(3\)
=> \(x=\dfrac{11}{7}\)

\(a.\dfrac{5}{4}.x=\dfrac{4}{7}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{7}:\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{7}.\dfrac{4}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{16}{35}\)
\(b.\dfrac{3}{4}:x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{4}:\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{4}.2\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{6}{4}\)

a)\(x-\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(x=\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(x=-\dfrac{1}{4}\)

a) Thực hiện phép nhân ở vế phải rồi áp dụng quy tắc chuyển vế.
b) Thực hiện phép nhân ở về phải rồi quy đồng mẫu hai vế.
ĐS. a) ; b) x = -40.

a) \(x\)=1 \(y\)= 12
b)\(x\)=4 \(y\)= 14
hoặc \(x\)= 6 \(y \)=21
...

9) \(\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{9}{x}\)
Theo định nghĩa về hai phân số bằng nhau, ta có:
\(4\cdot9=x^2\\ 36=x^2\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
8)
\(x:\dfrac{5}{3}+\dfrac{1}{3}=-\dfrac{2}{5}\\ x:\dfrac{5}{3}=-\dfrac{2}{5}+\dfrac{1}{3}\\ x:\dfrac{5}{3}=-\dfrac{1}{15}\\ x=\dfrac{1}{15}\cdot\dfrac{5}{3}\\ x=\dfrac{1}{9}\)
7)
\(2x-16=40+x\\ 2x-x=40+16\\ x\left(2-1\right)=56\\ x=56\)
6)
\(1\dfrac{1}{2}+x=\dfrac{3}{2}-7\\ \dfrac{3}{2}+x=\dfrac{3}{2}-7\\ \dfrac{3}{2}-\dfrac{3}{2}=-7-x\\ -7-x=0\\ x=-7-0\\ x=-7\)
5)
\(3\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\ \dfrac{7}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\ \dfrac{1}{2}x=\dfrac{7}{2}-\dfrac{2}{3}\\ \dfrac{1}{2}x=\dfrac{17}{6}\\ x=\dfrac{17}{6}:\dfrac{1}{2}\\ x=\dfrac{17}{3}\)
4)
\(x\cdot\left(x+1\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
3)
\(\left(\dfrac{2x}{5}+2\right):\left(-4\right)=-1\dfrac{1}{2}\\ \left(\dfrac{2x}{5}+2\right):\left(-4\right)=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\ \dfrac{2x}{5}+2=-\dfrac{3}{2}\cdot\left(-4\right)\\ \dfrac{2x}{5}+2=6\\ \dfrac{2x}{5}=6-2\\ \dfrac{2x}{5}=4\\ 2x=4\cdot5\\ 2x=20\\ x=20:2\\ x=10\)
2)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{2}:x=-0,25\\ \dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{2}:x=-\dfrac{1}{4}\\ \dfrac{1}{2}:x=-\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{3}\\ \dfrac{1}{2}:x=-\dfrac{7}{12}\\ x=\dfrac{1}{2}:-\dfrac{7}{12}\\ x=-\dfrac{6}{7}\)
1)
\(\dfrac{4}{3}+x=\dfrac{2}{15}\\ x=\dfrac{2}{15}-\dfrac{4}{3}x=-\dfrac{6}{5}\)
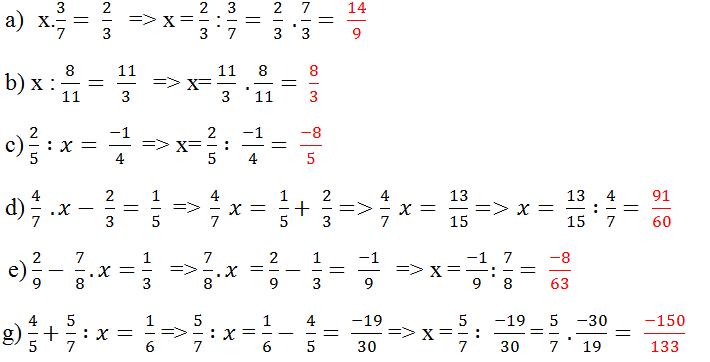
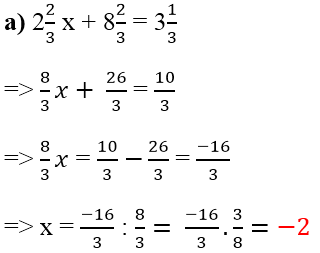
=> x= 0,8 x \(\dfrac{2}{7}\)
=> x=2,8
Tìm x biết:
\(x:\dfrac{2}{7}=0,8\)
\(\Rightarrow x=0,8.\dfrac{2}{7}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1,6}{7}\)