
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Để 3 số hạng đó lập thành cấp số cộng, ta có :
\(\left(5^{1+x}+5^{1-x}\right)+\left(25^x+25^{-x}\right)=2\left(\frac{a}{2}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a=5\left(5^x+\frac{1}{5^x}\right)+\left(5^{2x}+\frac{1}{5^{2x}}\right)\)
Theo bất đẳng thức côsi, ta có : \(5^x+\frac{1}{5^x}\ge2\sqrt{1}=2,5^{2x}+\frac{1}{5^{2x}}\ge2\)
\(\Rightarrow a\ge5.2+2=12\)
Vậy với : \(a\ge12\), thì 3 số đó lập thành cấp số cộng.

Theo giả thiết ta có : \(\begin{cases}\left(5x-y\right)+\left(x+2y\right)=2\left(2x+3y\right)\\\left(y+1\right)^2\left(x-1\right)^2=\left(xy+1\right)^2\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}2x=5y\\x+y=2\end{cases}\) hoặc \(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}2x=5y\\xy+x+y=0\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}2x=5y\\x+y=2\end{cases}\) hoặc \(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}2x=5y\\y\left(5y\right)+5y+2y=0\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}x=\frac{10}{3}\\y=\frac{4}{3}\end{cases}\) hoặc \(\begin{cases}x=0,y=0\\x=-\frac{3}{4},y=-\frac{3}{10}\end{cases}\)

a/ \(y'=3x^2-4x\Rightarrow y''=6x-4\)
b/ \(y'=x^3-2x+1\Rightarrow y''=3x^2-2\)
c/ \(y'=-x^4+12x^3-6x^2+8x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow y''=-4x^3+36x^2-12x+8\)

16.
\(y'=\frac{\left(cos2x\right)'}{2\sqrt{cos2x}}=\frac{-2sin2x}{2\sqrt{cos2x}}=-\frac{sin2x}{\sqrt{cos2x}}\)
17.
\(y'=4x^3-\frac{1}{x^2}-\frac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}\)
18.
\(y'=3x^2-2x\)
\(y'\left(-2\right)=16;y\left(-2\right)=-12\)
Pttt: \(y=16\left(x+2\right)-12\Leftrightarrow y=16x+20\)
19.
\(y'=-\frac{1}{x^2}=-x^{-2}\)
\(y''=2x^{-3}=\frac{2}{x^3}\)
20.
\(\left(cotx\right)'=-\frac{1}{sin^2x}\)
21.
\(y'=1+\frac{4}{x^2}=\frac{x^2+4}{x^2}\)
22.
\(lim\left(3^n\right)=+\infty\)
11.
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^+}\frac{-2x+1}{x-1}=\frac{-1}{0}=-\infty\)
12.
\(y=cotx\Rightarrow y'=-\frac{1}{sin^2x}\)
13.
\(y'=2020\left(x^3-2x^2\right)^{2019}.\left(x^3-2x^2\right)'=2020\left(x^3-2x^2\right)^{2019}\left(3x^2-4x\right)\)
14.
\(y'=\frac{\left(4x^2+3x+1\right)'}{2\sqrt{4x^2+3x+1}}=\frac{8x+3}{2\sqrt{4x^2+3x+1}}\)
15.
\(y'=4\left(x-5\right)^3\)

Giả sử 4 nghiệm phân biệt của phương trình là : \(x_1;x_2;x_3;x_4\)
Đặt \(x^2=y\ge0\), ta có phương trình :
\(\Leftrightarrow y^2-\left(3m+5\right)y+\left(m+1\right)^2=0\left(1\right)\)
Ta phải tìm m sao cho (1) có hai nghiệm phân biệt \(0 < y1 < y2\)
Khi đó (1) có 4 nghiệm là : \(x_1=-\sqrt{y_2};x_2=-\sqrt{y_1};x_3=-\sqrt{y_1};x_4=-\sqrt{y_2}\)
Rõ ràng \(x2 < x2 < x3 < x4\)
Theo đầu bài thì bốn nghiệm lập thành cấp số cộng, nên :
\(\Rightarrow x_3+x_1=2x_2\) V \(x_4+x_1=2x_3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{y_1}-\sqrt{y_2}=2\sqrt{y_1}\)
\(\Rightarrow3\sqrt{y_1}=\sqrt{y_2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9y_1=y_2\) (*)
Áp dụng Viet cho phương trình (1) ta có hệ :
\(\begin{cases}\Delta=\left(3m+5\right)^2-4\left(m+1\right)^2>0\\S=y_1+y_2=10y_1=3m+5\\P=y_1y_2=9y_1^2=\left(m+1\right)^2\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}m=5\\m=-\frac{25}{19}\end{cases}\)

\(a=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x-1\right)}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}{x^2+x-1}=\frac{4}{1}=4\)
\(b=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1}\frac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^4-x^3+x^2-x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1}\frac{x^4-x^3+x^2-x+1}{x^2-x+1}=\frac{5}{3}\)
\(c=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3}\frac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x^2-9\right)}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3}\frac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\frac{0}{60}=0\)
\(d=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{4x^6-5x^5+x}{x^2-2x+1}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{24x^5-25x^4+1}{2x-2}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{120x^4-100x^3}{2}=10\)
\(e=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\frac{mx^{m-1}}{nx^{n-1}}=\frac{m}{n}\)
\(f=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-2}\frac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)}{\left(x+2\right)x^2}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-2}\frac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)}{x^2}=-8\)
Hai câu d, e khai triển thì dài quá nên làm biếng sử dụng L'Hopital
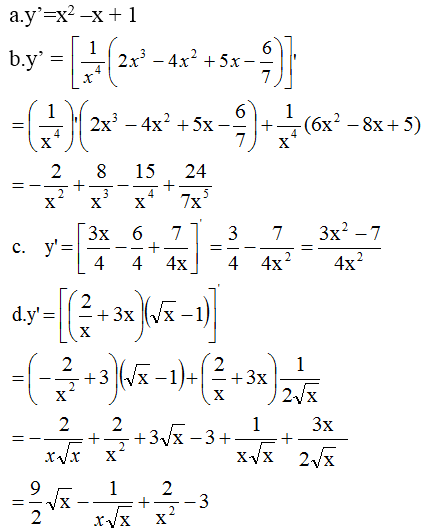
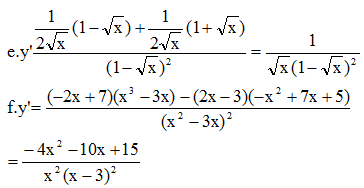
Chọn B
Ta có: x 2 + 1, x − 2,1 − 3 x lập thành cấp số cộng
⇔ x 2 + 1 + 1 − 3 x = 2 ( x − 2 ) ⇒ x 2 + 2 − 3 x = 2 x − 4 ⇔ x 2 − 5 x + 6 = 0 ⇔ x = 2 ; x = 3
Vậy x = 2; x = 3 là những giá trị cần tìm.