
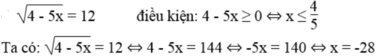
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

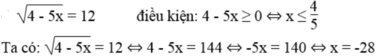


Nếu chưa quen giải toán căn thức, em tìm ĐKXĐ cho x, rồi đặt \(\sqrt{x}=t\ge0\Rightarrow x=t^2\) rồi thế vào giải là nó ra 1 pt bình thường theo biến t thôi



\(\sqrt{4\left(1-x\right)^2}-6=0\)
<=> \(\left|2\left(1-x\right)\right|=6\)
TH1: x \(\ge\)1 Khi đó pt trở thành:
\(2\left(x-1\right)=6\)
<=> x - 1 = 3
<=> x = 4 (tm)
TH2: x < 1, khi đó pt trở thành:
2(1 - x) = 6
<=> 1 - x = 3
<=> x = -2(tm)
vậy S= {4; -2}
Trả lời:
\(\sqrt{4\left(1-x\right)^2}-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2.\left|1-x\right|=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|1-x\right|=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}1-x=3\\1-x=-3\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=4\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(x=\left\{-2,4\right\}\)
\(\sqrt{4x^2+4x+1}=x+2\)\(\left(x\ge-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+4x+1=\left(x+2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+4x+1=x^2+4x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\left(TM\right)\\x=-1\left(TM\right)\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(x=\left\{1,-1\right\}\)
\(\sqrt{\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{29-12\sqrt{5}}}}\)
\(=\sqrt{\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{20-12\sqrt{5}+9}}}\)
\(=\sqrt{\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{\left(2\sqrt{5}-3\right)^2}}}\)
\(=\sqrt{\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{\sqrt{3}-2\sqrt{5}+3}}\)

a) \(\sqrt{4-5x}=12\)
ĐK : x ≤ 4/5
Bình phương hai vế
⇔ \(4-5x=144\)
⇔ \(-5x=140\)
⇔ \(x=-28\)( tm )
b) \(\sqrt{1-4x+4x^2}=5\)
⇔ \(\sqrt{\left(1-2x\right)^2}=5\)
⇔ \(\left|1-2x\right|=5\)
⇔ \(\orbr{\begin{cases}1-2x=5\\1-2x=-5\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
c) \(\sqrt{4x+20}-3\sqrt{5+x}+\frac{3}{4}\sqrt{9x+45}=6\)
ĐK : x ≥ -5
⇔ \(\sqrt{2^2\left(x+5\right)}-3\sqrt{x+5}+\frac{3}{4}\sqrt{3^2\left(x+5\right)}=6\)
⇔ \(\left|2\right|\sqrt{x+5}-3\sqrt{x+5}+\frac{3}{4}\cdot\left|3\right|\sqrt{x+5}=6\)
⇔ \(2\sqrt{x+5}-3\sqrt{x+5}+\frac{9}{4}\sqrt{x+5}=6\)
⇔ \(\frac{5}{4}\sqrt{x+5}=6\)
⇔ \(\sqrt{x+5}=\frac{24}{5}\)
⇔ \(x+5=\frac{576}{25}\)
⇔ \(x=\frac{451}{25}\)( tm )
d)\(\sqrt{x-2}\le3\)
ĐK : x ≥ 2
⇔ \(x-2\le9\)
⇔ \(x\le11\)
Kết hợp với điều kiện => Nghiệm của bpt là 2 ≤ x ≤ 11

1)
Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=ax^4+bx^3+cx^2+dx+e.\)( a khác 0 )
Ta có:
\(f\left(1\right)=a+b+c+d+e=0\) (1)
\(f\left(2\right)=16a+8b+4c+2d+e=0\) (2)
\(f\left(3\right)=81a+27b+9c+3d+e=0\) (3)
\(f\left(4\right)=256a+64b+16c+4d+e=6\) (4)
\(f\left(5\right)=625a+125b+25c+5d+e=72\) (5)
\(A=f\left(2\right)-f\left(1\right)=15a+7b+3c+d=0\)
\(B=f\left(3\right)-f\left(2\right)=65a+19b+5c+d=0\)
\(C=f\left(4\right)-f\left(3\right)=175a+37b+7c+d=6\)
\(D=f\left(5\right)-f\left(4\right)=369a+61b+9c+d=72-6=66\)
\(E=B-A=50a+12b+2c=0\)
\(F=C-B=110a+18b+2c=6\)
\(G=D-C=194a+24b+2c=66-6=60\)
Tiếp tục lấy H=F-E; K=G-F; M=H-K
Ta tìm được a
Thay vào tìm được b,c,d,e
1. gọi đa thức cần tìm là f(x) =a.x^4+b.x^3+c.x^2+dx+e
có f(1)=f(2)=f(3) = 0 nên x=1,2,3 la nghiệm của f(x) = 0 vậy f(x) có thể viết dưới dạng f(x) = (x-1)(x-2)(x-3)(mx+n)
thay f(4)=6 và f(5)=72 tìm được m =2 và n= -7
Vậy đa thức f(x) =(x-1)(x-2)(x-3)(2x-7) => e = (-1).(-2).(-3).(-7) = 42
Với x=2010 thì (a 2010^4+b.2010^3+c.2010^2+d.2010 ) luôn chia hết 10 vậy số dư f(2010) chia 10 = số dư d/10 = 2 (42 chia 10 dư 2).
2. Thiếu dữ liệu
3. đa thức f(x) chia đa thức (x-3) có số dư là 2 =>bậc f(x) = bậc (x-3)=1 và f(x) = m.(x-3) +2=mx+2-3m (1)
...........................................(x+4)...................9..........................................f(x) = n(x+4) + 9=nx+4n+9 (2)
để (1)(2) cùng xảy ra thì m=n và (2-3m)=(4n+9) => m = n = -1 khi đó đa thức f(x) = -x +5
Không hiếu dữ liệu cuối f(x) chia 1 đa thức bậc 2 lại có thương là 1 đa thức bậc 2? => vô lý

Điều kiện: x \(\ge\)0; y \(\ge\) 1
PT <=> \(x-4\sqrt{x}+y-6\sqrt{y-1}+12=0\)
<=> \(\left(x-4\sqrt{x}+4\right)+\left(\left(y-1\right)-6\sqrt{y-1}+9\right)=0\)
<=> \(\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{y-1}-3\right)^2=0\)
<=> \(\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)^2=\left(\sqrt{y-1}-3\right)^2=0\) (Vì \(\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)^2;\left(\sqrt{y-1}-3\right)^2\ge0\) với mọi x >=0 và y>= 1 )
<=> \(\sqrt{x}-2=0;\sqrt{y-1}-3=0\) <=> x= 4; y - 1 =9 <=> x =4 và y = 10 (TMĐK)
Vậy...

cậu cho mk xin link facebook của jonathan galindo đi rồi mk sẽ trả lời câu hỏi của cậu