Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Đặt x2−2x+m=tx2−2x+m=t, phương trình trở thành t2−2t+m=xt2−2t+m=x
Ta có hệ {x2−2x+m=tt2−2t+m=x{x2−2x+m=tt2−2t+m=x
⇒(x−t)(x+t−1)=0⇒(x−t)(x+t−1)=0
⇔[x=tx=1−t⇔[x=tx=1−t
⇔[x=x2−2x+mx=1−x2+2x−m⇔[x=x2−2x+mx=1−x2+2x−m
⇔[m=−x2+3xm=−x2+x+1⇔[m=−x2+3xm=−x2+x+1
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của y=−x2+x+1y=−x2+x+1 và y=−x2+3xy=−x2+3x:
−x2+x+1=−x2+3x−x2+x+1=−x2+3x
⇔x=12⇒y=54⇔x=12⇒y=54
Đồ thị hàm số y=−x2+3xy=−x2+3x và y=−x2+x+1y=−x2+x+1:

Câu 1:
ĐKXĐ: x>=3
\(PT\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-3}=2x-m\)
=>x-3=(2x-m)^2
=>4x^2-4xm+m^2=x-3
=>4x^2-x(4m-1)+m^2+3=0
Δ=(4m-1)^2-4*4*(m^2+3)
=16m^2-8m+1-16m^2-48
=-8m-47
Để phương trình có nghiệm thì -8m-47>=0
=>m<=-47/8

Bài đã đăng bạn hạn chế không đăng lại gây spam box toán nhé.

Lời giải:
Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì:
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} m+1\neq 0\\ \Delta=(m-3)^2-4(m+1)^2=-(m+5)(3m-1)\geq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m\neq -1; -5\leq m\leq \frac{1}{3}\)
Pt có 2 nghiệm $x_1,x_2\geq -1$
\(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x_1+x_2\geq -2\\ (x_1+1)(x_2+1)\geq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x_1+x_2\geq -2\\ x_1x_2+(x_1+x_2)+1\geq 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} \frac{m-3}{m+1}\geq -2\\ \frac{m+1+m-3}{m+1}+1\geq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \frac{3m-1}{m+1}\geq 0\)
Vì $m\leq \frac{1}{3}$ nên $3m-1\leq 0$
$\Rightarrow m+1<0\Leftrightarrow m< -1$
Vậy $-5\leq m< -1$

a: TH1: m=2
Pt sẽ là 3x-4=0
=>x=4/3(loại)
TH2: m<>2
\(\text{Δ}=\left(5-m\right)^2-4\left(m-2\right)\left(m-6\right)\)
\(=m^2-10m+25-4\left(m^2-8m+12\right)\)
\(=m^2-10m+25-4m^2+32m-48\)
\(=-3m^2+22m-23\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì -3m^2+22m-23>0
=>\(\dfrac{11-2\sqrt{13}}{3}< x< \dfrac{11+2\sqrt{13}}{3}\)
a: |x1-x2|=2
=>\(\sqrt{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{m-5}{m-2}\right)^2-4\cdot\dfrac{m-6}{m-2}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(m-5\right)^2-4\left(m^2-8m+12\right)}{\left(m-2\right)^2}=4\)
=>\(m^2-10m+25-4m^2+32m-48=4m^2-16m+16\)
=>-7m^2+38m-39=0
hay \(m=\dfrac{19\pm2\sqrt{22}}{7}\)
c: TH1: x1<x2<0<1
=>x1+x2<0 và x1x2>0
=>(m-5)/(m-2)<0 và (m-6)/(m-2)>0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2< m< 5\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}m>6\\m< 2\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m\in\varnothing\)
TH2: 0<x1<x2<1
=>x1x2<1 và 0<x1+x2<2
=>0<m-5/m-2<2 và m-6/m-2<1
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{m-5-2m+4}{m-2}< 0\\\dfrac{m-6-m+2}{m-2}< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{m+1}{m-2}>0\\\dfrac{-4}{m-2}< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>m>2

1) \(x^2-2mx+m-2=0\) (1)
pt (1) có \(\Delta'=\left(-m\right)^2-\left(m-2\right)=m^2-m+2=\left(m-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{7}{4}>0\left(\forall m\right)\)
=> pt luôn có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1, x2
Vi-et: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=2m\\x_1x_2=m-2\end{cases}}\)\(\Rightarrow\)\(M=\frac{2x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)}{x_1^2+x_2^2-6x_1x_2}=\frac{2x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)}{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-8x_1x_2}=\frac{2m-4-2m}{\left(2m\right)^2-8m-16}\)
\(=\frac{-4}{4m^2-8m-16}=\frac{-4}{4\left(m-1\right)^2-20}\ge\frac{-4}{-20}=\frac{1}{5}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\)\(m=1\)
xin 1slot sáng giải

Lời giải:
Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì:
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} m\neq 0\\ \Delta'=(m+1)^2-m(m+5)=1-3m\geq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} m\neq 0\\ m\leq\frac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.(1)\)
Áp dụng định lý Viet:
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} x_1+x_2=\frac{2(m+1)}{m}\\ x_1x_2=\frac{m+5}{m}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để $x_1< 0< x_2$
$\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2< 0$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{m+5}{m}< 0$
$\Leftrightarrow -5< m< 0(2)$
$x_1< x_2< 2$
\(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} (x_1-2)(x_2-2)>0\\ x_1+x_2<4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x_1x_2-2(x_1+x_2)+4>0\\ x_1+x_2<4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} \frac{m+1}{m}>0\\ \frac{1-m}{m}< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} m>1\\ m< -1\end{matrix}\right.(3)\)
Từ $(1);(2);(3)$ suy ra $-5< m< -1$

a) Với m = 1 phương trình trở thành:
x 2 + 4x + 4 = 0 ⇔ (x + 2 ) 2 = 0 ⇔ x = -2
Vậy x = -2
b) Ta có: Δ' = m 2 - 5m + 4
Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt
⇔ Δ' > 0 ⇔
m
2
- 5m + 4 > 0 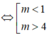
Do x1 < x2 < 1
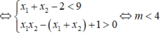

\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+1\ne0\\\Delta'=m^2-\left(m+1\right)\left(m+6\right)>0\\x_1+x_2=\dfrac{2m}{m+1}>0\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{m+6}{m+1}>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne1\\-7m-6>0\\\dfrac{2m}{m+1}>0\\\dfrac{m+6}{m+1}>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< -\dfrac{6}{7}\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}m>0\\m< -1\end{matrix}\right.\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}m>-1\\m< -6\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow m< -6\)