Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) Lấy (1)+(2)+(3) là tìm được z rồi thế z vào tìm x, y
b) Lấy (1) + (2) - (3) là tìm được y
\(a)\hept{\begin{cases}x-2y+z=12\\2x-y+3z=18\\-3x+3y+2z=-9\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x-2y+z=12\\3y+z=-6\\6z=21\end{cases}}}\)
\(\text{Đáp số: }(x;y;z)=(\frac{16}{3};-\frac{19}{6};\frac{7}{2})\)
\(b)\hept{\begin{cases}x+y+z=7\\3x-2y+2z=5\\4x-y+3z=10\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\hept{\begin{cases}x+y+z=7\\-5y-z=16\\0y+0z=-2\end{cases}}\)
\(\text{ Hệ phương trình vô nghiệm.}\)

- Áp dụng BĐT Bunhia- Cốp xki ta có:
\(\left(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{5-x}\right)^2\le\left(1^2+1^2\right)\left(x-1+5-x\right)\)\(=2.4=8\).
Suy ra: \(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{5-x}\le2\sqrt{2}\).
Vậy max \(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{5-x}=2\sqrt{2}\) khi:
\(\sqrt{x-1}=\sqrt{5-x}\)\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=5-x\)\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\).
- Ta có: \(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{5-x}\ge\sqrt{x-1+5-x}=\sqrt{4}=2\).
Vậy GTNN của \(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{5-x}=2\) khi:
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\5-x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\).

a ) \mathbb{R} \backslash (-3; \, 1]R\(−3;1]=(-∞;-3]∪(1;+∞)
b) (-\infty; \, 1) \backslash [-2; \, 0](−∞;1)\[−2;0]=(- (-\infty; \, 1) \backslash [-2; \, 0]∞;-2)∪(0;1)
a ) R\(−3;1]=(-∞;-3]∪(1;+∞)
b) [-2; \, 0](−∞;1)\[−2;0]= [-2; \, 0]∞;-2)∪(0;1)

1: ĐKXĐ: \(x^3-6x^2+11x-6< >0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-x^2-5x^2+5x+6x-6\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-5x+6\right)\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)\ne0\)
hay \(x\notin\left\{1;2;3\right\}\)
2; ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3-2x>=0\\x+1< >-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =\dfrac{3}{2}\\x< >-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
3: ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2< >0\\x-1< >0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< >-2\\x< >1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in R\)

có nghĩa với x ∈ R sao cho 2x + 1 ≥ 0
có nghĩa với x ∈ R sao cho 3 – x ≥ 0
Vậy tập xác định của hàm số là:
D = D1 ∩ D2, trong đó:
D1 = {x ∈ R/2x + 1 ≥ 0} =
D2 = {x ∈ R/3 – x ≥ 0} =

a) (-\infty ; \, 2) \cap (-1; \, +\infty)(−∞;2)∩(−1;+∞)=(-1;2)
b) (−1;6) ∪ [4;8)=(-1;8]
c) (−∞;−5] ∩(−5;1)={-5}a) (-\infty ; \, 2) \cap (-1; \, +\infty)(−∞;2)∩(−1;+∞)=(-1;2)
b) (−1;6) ∪ [4;8)=(-1;8]
c) (−∞;−5] ∩(−5;1)={-5}

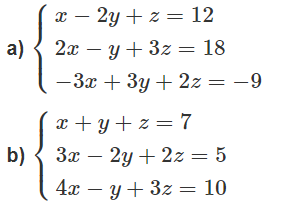 Giúp nhanh vs ạ, đng cần gấp
Giúp nhanh vs ạ, đng cần gấp
Do 0 < x < 1 nên 1/x > 1, 1/(1-x) > 1 suy ra y > 2, ∀x ∈ D, do chọn B và C sai. Mặt khác, dễ thấy khi x = 1/2 thì y = 4 suy ra D sai
Đáp án: A