Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

BÀI 1:
a) \(ĐKXĐ:\) \(x-3\)\(\ne\)\(0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x\)\(\ne\)\(3\)
b) \(A=\frac{x^3-3x^2+4x-1}{x-3}\)
\(=\frac{\left(x^3-3x^2\right)+\left(4x-12\right)+11}{x-3}\)
\(=\frac{x^2\left(x-3\right)+4\left(x-3\right)+11}{x-3}\)
\(=x^2+4+\frac{11}{x-3}\)
Để \(A\)có giá trị nguyên thì \(\frac{11}{x-3}\)có giá trị nguyên
hay \(x-3\)\(\notinƯ\left(11\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm11\right\}\)
Ta lập bảng sau
\(x-3\) \(-11\) \(-1\) \(1\) \(11\)
\(x\) \(-8\) \(2\) \(4\) \(14\)
Vậy....

a: \(B=\dfrac{x^2-1-2x+3x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+x}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\)
a) B = \(\dfrac{x+1}{x}-\dfrac{2}{x-1}+\dfrac{3x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\) (ĐK: \(x\ne0;1\))
= \(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}{x\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{2x}{x\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{3x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)
= \(\dfrac{x^2-1-2x+3x+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+x}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\)
b) \(\left|x\right|=1< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(L\right)\\x=-1\left(C\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay x = -1 vào B, ta có:
\(\dfrac{-1+1}{-1-1}=0\)
c) B nguyên <=> \(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\) nguyên <=> \(1+\dfrac{2}{x-1}\) nguyên
<=> 2\(⋮x-1\)
<=> x-1 \(\in\left\{-2;-1;1;2\right\}\)
| x-1 | -2 | -1 | 1 | 2 |
| x | -1 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| C | L | C | C |
KL: x \(\in\left\{-1;2;3\right\}\)

a: \(A=\left(\dfrac{x}{x^2-4}+\dfrac{4}{x-2}+\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right):\dfrac{3x+3}{x^2+2x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+4x+8+x-2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{3\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{6\left(x+1\right)\cdot x\left(x+2\right)}{3\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x}{x-2}\)

a) A = \(\frac{3x^2+3x-3}{x^2+x-2}-\frac{x+1}{x+2}+\frac{x-2}{x}\cdot\left(\frac{1}{1-x}-1\right)\)
A = \(\frac{3x^2+3x-3}{x^2+2x-x-2}-\frac{x+1}{x+2}+\frac{x-2}{x}\cdot\left(\frac{1-1+x}{1-x}\right)\)
A = \(\frac{3x^2+3x-3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\frac{x+1}{x+2}+\frac{x-2}{x}\cdot\frac{x}{1-x}\)
A = \(\frac{3x^2+3x-3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\frac{x+1}{x+2}-\frac{x-2}{x-1}\)
A = \(\frac{3x^2+3x-3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\frac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\frac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
A = \(\frac{3x^2+3x-3-x^2+1-x^2+4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
A = \(\frac{x^2+3x+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
A = \(\frac{x^2+2x+x+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
A = \(\frac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
A = \(\frac{x+1}{x-1}\) (Đk: \(x-1\ge0\) => x \(\ge\)1)
b) Ta có: A = \(\frac{x+1}{x-1}=\frac{\left(x-1\right)+2}{x-1}=1+\frac{2}{x-1}\)
Để A \(\in\)Z <=> 2 \(⋮\)x - 1
<=> x - 1 \(\in\)Ư(2) = {1; -1; 2; -2}
<=> x \(\in\){2; 0; 3; -1}
c) Ta có: A < 0
=> \(\frac{x+1}{x-1}< 0\)
=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x+1< 0\\x-1>0\end{cases}}\) hoặc \(\hept{\begin{cases}x+1>0\\x-1< 0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\hept{\begin{cases}x< -1\\x>1\end{cases}}\)(loại) hoặc \(\hept{\begin{cases}x>-1\\x< 1\end{cases}}\)
=> -1 < x < 1
Edogawa Conan
Thiếu dòng đầu \(ĐKXĐ:\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne1\\x\ne-2\\x\ne0\end{cases}}\)

Ta có : \(ĐKXĐ:x\ne-\frac{1}{2}\)
\(A=\left(x+1\right)+\frac{2}{2x+1}\) vì \(x\in Z\) nên A nguyên thì \(\frac{2}{2x+1}\) nguyên
Hay \(2x+1\) là ước của 2 . Nên :
\(2x+1=2\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{2}\) ( loại )
\(2x+1=1\Rightarrow x=0\) ( t/m)
\(2x+1=-1\Rightarrow x=-1\) ( t/m)
\(2x+1=-2\Rightarrow x=-\frac{3}{2}\) ( loại )
Với \(x=0;x=-1\) thì A nhận giá trị nguyên
Chúc bạn học tốt !!!

\(a,P=\frac{x+2}{x-2}+\frac{x}{x+2}-\frac{4}{x^2-4}\)
\(P=\frac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\frac{x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\frac{4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^2+4x+4+x^2-2x-4}{x^2-4}\)
\(P=\frac{2x^2+2x}{x^2-4}\)
\(P=\frac{2x^2+2x}{x^2-4}\) (1)
\(b,x^2-3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\left(ktm\right)\\x=3\left(tm\right)\end{cases}}\)
thay vào (1) ta có :
\(P=\frac{2\cdot3^2+2\cdot3}{3^2-4}=\frac{24}{5}\)

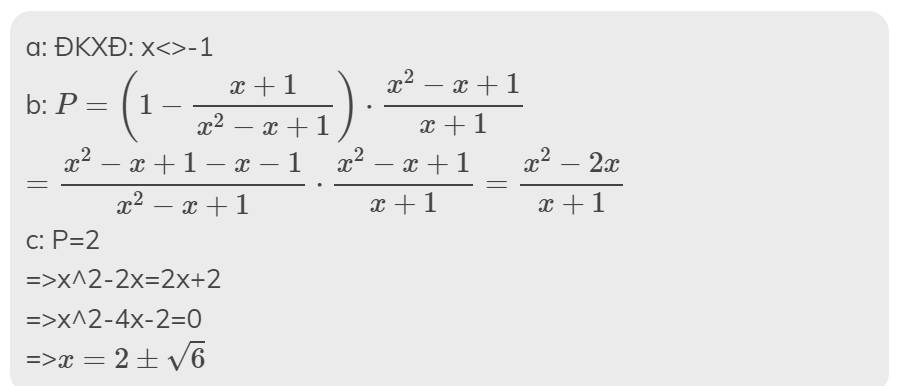
a: ĐKXĐ: x<>-1
b: \(P=\left(1-\dfrac{x+1}{x^2-x+1}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-x+1-x-1}{x^2-x+1}\cdot\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x+1}=\dfrac{x^2-2x}{x+1}\)
c: P=2
=>x^2-2x=2x+2
=>x^2-4x-2=0
=>\(x=2\pm\sqrt{6}\)
`A=[3x+1]/[x+2]=[3x+6-5]/[x+2]=3-5/[x+2]`
Để `A` nhận giá trị nguyên thì `3-5/[x+2] in ZZ`
`=>x+2 in Ư_5`
Mà `Ư_5 ={+-1;+-5}`
`@x+2=1=>x=-1`
`@x+2=-1=>x=-3`
`@x+2=5=>x=3`
`@x+2=-5=>x=-7`
Cảm ơn ạ 👉💖👈