



Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.





Đáp án A.
+ Điều kiện: x > 0
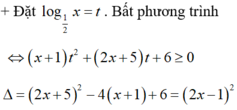
Bất phương trình
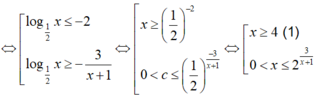
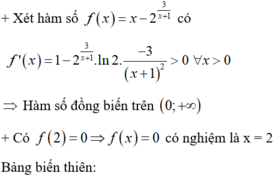
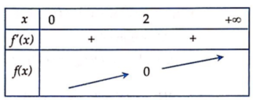
=> Bất phương trình x ≤ 2 3 x + 1 ⇔ f ( x ) ≤ 0 ⇔ 0 < x ≤ 2 ( 2 ) .
Từ (1) và (2) => Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là
S = ( 0 ; 2 ] ∪ [ 4 ; + ∞ ) .
Vậy có 2016 nghiệm nguyên thỏa mãn.


\(log\left(5\left(x^2+1\right)\right)\ge log\left(mx^2+4x+m\right)\)
- BPT đúng \(\forall x\Rightarrow log\left(mx^2+4x+m\right)\) xác định \(\forall x\in R\)
\(\Rightarrow mx^2+4x+m>0\) \(\forall x\in R\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=m>0\\\Delta'=4-m^2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow m>2\) (1)
- Lại có \(x^2+1\ge1\) \(\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow5\left(x^2+1\right)\ge mx^2+4x+m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\left(x^2+1\right)-4x\ge m\left(x^2+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5-\dfrac{4x}{x^2+1}\ge m\)
Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=5-\dfrac{4x}{x^2+1}\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\ge m\) \(\forall x\Leftrightarrow m\le min\left(f\left(x\right)\right)\)
Ta có \(f\left(x\right)=3+2-\dfrac{4x}{x^2+1}=3+\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2+1}\ge3\)
\(\Rightarrow min\left(f\left(x\right)\right)=3\Rightarrow m\le3\) (2)
Kết hợp (1), (2) \(\Rightarrow2< m\le3\Rightarrow m=3\)
Vậy có 1 giá trị nguyên duy nhất của m để BPT đúng với mọi x
Đáp án B

Câu 1:
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+5+\sqrt{x^2-4x+5}-5=m\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x^2-4x+5}=\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2+1}=a\ge1\)
\(\Rightarrow a^2+a-5=m\) (1)
Xét phương trình: \(x^2-4x+5=a^2\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+5-a^2=0\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=4\\x_1x_2=5-a^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Nếu \(5-a^2>0\Rightarrow1\le a< \sqrt{5}\) thì pt có 2 nghiệm dương
Nếu \(5-a^2\le0\) \(\Leftrightarrow a\ge\sqrt{5}\) thì pt có 1 nghiệm dương
Vậy để pt đã cho có đúng 2 nghiệm dương thì: (1) có đúng 1 nghiệm thỏa mãn \(1\le a< \sqrt{5}\) hoặc có 2 nghiệm pb \(a_1>a_2\ge\sqrt{5}\)
Xét \(f\left(a\right)=a^2+a-5\) với \(a\ge1\)
\(f'\left(a\right)=0\Rightarrow a=-\frac{1}{2}< 1\Rightarrow f\left(a\right)\) đồng biến \(\forall a\ge1\) \(\Rightarrow y=m\) chỉ có thể cắt \(y=f\left(a\right)\) tại nhiều nhất 1 điểm có hoành độ \(a\ge1\)
\(f\left(1\right)=-3\) ; \(f\left(\sqrt{5}\right)=\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Để pt có 2 nghiệm pb đều dương thì \(-3\le m< \sqrt{5}\)
Câu 2:
\(x^2-3x+2\le0\Leftrightarrow1\le x\le2\) (1)
Ta có: \(mx^2+\left(m+1\right)x+m+1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(x^2+x+1\right)\ge-x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ge\frac{-x-1}{x^2+x+1}=f\left(x\right)\) (2)
Để mọi nghiệm của (1) là nghiệm của (2) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(2\right)\) đúng với mọi \(x\in\left[1;2\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow m\ge\max\limits_{\left[1;2\right]}f\left(x\right)\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=\frac{-\left(x^2+x+1\right)+\left(2x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)^2}=\frac{x^2+2x}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)^2}>0\) \(\forall x\in\left[1;2\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) đồng biến \(\Rightarrow\max\limits_{\left[1;2\right]}f\left(x\right)=f\left(2\right)=-\frac{3}{7}\)
\(\Rightarrow m\ge-\frac{3}{7}\)