Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Ta có:
Khi \(x\in\left[-3;0\right]\) thì \(f\left(x\right)\in\left[-4;5\right]\) (dùng BBT)
Lại có:
\(y=f\left(f\left(x\right)\right)=f^2\left(x\right)+6f\left(x\right)+5\)
Khi \(f\left(x\right)\in\left[-4;5\right]\) thì \(f\left(f\left(x\right)\right)\in\left[-4;60\right]\) (dùng BBT)
Do đó, \(m=-4\Leftrightarrow f\left(x\right)=-3\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
và \(M=60\Leftrightarrow f\left(x\right)=5\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow S=m+M=-4+60=56\)

\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge2\\3\left(x^2-4x\right)-\left(x-2\right)>12\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 2\\3\left(x^2-4x\right)-\left(2-x\right)>12\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge2\\3x^2-13x-10>0\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 2\\3x^2-11x-14>0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>5\\x< -1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-1\\b=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
3x2 - 12x - |x - 2| > 12
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge2\\3x^2-12x-\left(x-2\right)>12\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 2\\3x^2-12x-\left(2-x\right)>12\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge2\\3x^2-12x-x+2>12\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 2\\3x^2-12x+x-2>12\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
⇔ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>5\\x< -1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy tập nghiệm là \(S=\left(-\infty;-1\right)\cup\left(5;+\infty\right)\)

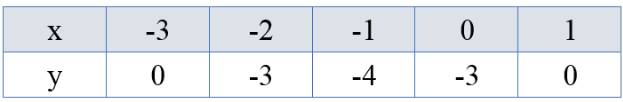
a) Thay \(x = - 3\) vào hàm số ta được:
\(y = {\left( { - 3} \right)^2} + 2.\left( { - 3} \right) - 3 = 0\). Điền 0 vào ô tương ứng.
Thay \(x = - 2\) vào hàm số ta được:
\(y = {\left( { - 2} \right)^2} + 2.\left( { - 2} \right) - 3 = - 3\). Điền \( - 3\) vào ô tương ứng.
Thay \(x = - 1\) vào hàm số ta được:
\(y = {\left( { - 1} \right)^2} + 2.\left( { - 1} \right) - 3 = - 4\). Điền \( - 4\) vào ô tương ứng.
Thay \(x = 0\) vào hàm số ta được:
\(y = - 3\). Điền \( - 3\) vào ô tương ứng.
Thay \(x = 1\) vào hàm số ta được:
\(y = {\left( 1 \right)^2} + 2.\left( 1 \right) - 3 = 0\). Điền 0 vào ô tương ứng.
Vậy ta có:
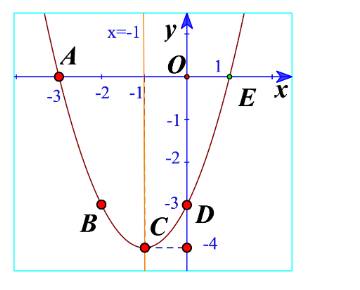
b) Các điểm có trong hình 11.
c) Đường cong đi qua 5 điểm là parabol trong hình 11.
d) Từ đồ thị ta thấy điểm thấp nhất là điểm C(-4;-1)
Phương trình trục đối xứng là x=-1
Đồ thị có bề lõm lên trên.

Lời giải:
Đặt $\sqrt{x+2}=t(t\geq 0)$ thì pt trở thành:
$t^2-2-2t-m-3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow t^2-2t-(m+5)=0(*)$
Để PT ban đầu có 2 nghiệm pb thì PT $(*)$ có 2 nghiệm không âm phân biệt.
Điều này xảy ra khi \(\left\{\begin{matrix} \Delta'=1+m+5>0\\ S=2>0\\ P=-(m+5)\geq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} m>-6\\ m\leq -5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đáp án B.
a) Thay t=1 ta được:
\(S = \frac{1}{2}.9,{8.1^2} = 4,8\left( m \right)\)
Thay t=2 vào ta được: \(S = \frac{1}{2}.9,{8.2^2} = 19,6\left( m \right)\)
b) Với mỗi giá trị của t có 1 giá trị tương ứng của S.